What is FGF21 Protein
FGF21, or Fibroblast Growth Factor 21, is a member of the endocrine FGF superfamily, playing a significant role in regulating metabolism. As a multifunctional protein, FGF21 directly participates in various metabolic processes, including glucose metabolism, lipid metabolism, insulin sensitivity, and energy expenditure.
Function of FGF21 Protein
FGF21 protein mainly acts as a hormone and mediates several metabolic processes. It interacts with cellular receptors, enabling glucose uptake, lipid metabolism, and modulation of energy utilization in different tissues, such as liver, fat tissues, and the brain. Thus, it significantly influences insulin sensitivity, curtailing the chances of insulin resistance - often linked with obesity and type 2 diabetes.
FGF21 also regulates adaptive responses to starvation. When nutrient intake is limited, FGF21 levels increase, triggering fatty acid oxidation, ketogenesis, and autophagy - all vital for survival during times of prolonged fasting or starvation.
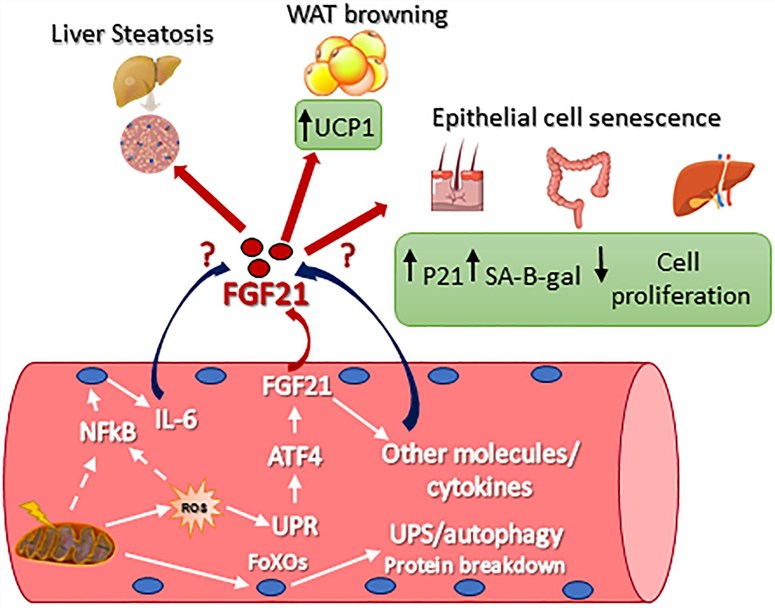
Fig1. FGF21 as Modulator of Metabolism in Health and Disease. (Caterina Tezze, et al. 2019)
FGF21 Protein Related Signal Pathway
The metabolic effects of FGF21 are orchestrated via its binding to a cell surface co-receptor complex, consisting primarily of beta-Klotho and FGF receptors. This binding facilitates the activation of the FGF21 signaling pathway. The downstream activation pathway, named RAS/RAF/MEK/ERK pathway, modulates gene expressions involved in glucose and lipid metabolism, promoting beneficial metabolic changes.
FGF21 Protein Related Diseases
Given its metabolic modulating effect, any alteration in the levels or function of FGF21 may lead to metabolic disorders. Recent studies point towards the role of FGF21 in the pathogenesis of conditions like obesity, type 2 diabetes, and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD).
Elevated levels of FGF21 in the plasma of obese individuals and those with type 2 diabetes suggest that these conditions may be associated with FGF21 resistance, much like insulin resistance. It means that cells might begin to lose their ability to respond effectively to the presence of FGF21, contributing to metabolic dysfunction.
Similarly, studies found more significant FGF21 levels in patients with NAFLD than in healthy individuals, implying that FGF21 might regulate lipid metabolism in the liver and that alterations in FGF21 activity could contribute to NAFLD development.
FGF21 protein's Applications in Biomedical field
The unique role of FGF21 in energy metabolism, insulin sensitivity, and weight control makes it a prime candidate for therapeutic uses. Upon its discovery as a potent metabolic regulator, the interest in FGF21 as a potential therapeutic agent for metabolic disease amelioration has grown significantly.
Pharmaceuticals are currently developing FGF21 analogs for the treatment of metabolic diseases such as obesity and type 2 diabetes. Initial trials show promising results, demonstrating the potential benefits of FGF21-based treatments in improving lipid profiles, reducing body weight, and enhancing insulin sensitivity.
Moreover, the potential protective role of FGF21 against conditions like cardiovascular disease has prompted investigations into FGF21's effectiveness as a therapeutic agent in this field.
FGF21 also has implications in aging. Experiments with mice showed that an overexpression of the FGF21 gene extended their lifespan, suggesting the potential of FGF21 in age-related disease modulation.
In conclusion, the FGF21 protein appears to be a significant modulator in various metabolic events. While its clinical usage is still in investigational stages, FGF21's therapeutic role in the management of metabolic diseases, cardiovascular conditions, and age-related alterations indeed holds great promise for the future of biomedicine. Investigations on FGF21 are paving the way for novel therapeutic approaches and developing a better understanding of metabolic diseases, enhancing our arsenal in the fight against these conditions. Despite the promise, it's important to note that much remains to be understood about this protein and its role in human physiology and disease before it can transition fully into clinical use.
Our Featured Products
| Cat.No. | Product Name | Species | Source (Host) | Tag |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| FGF21-564H | Active Recombinant Human FGF21 protein, His-tagged | Human | E.coli | His |
| Fgf21-563M | Recombinant Mouse Fgf21 protein | Mouse | E.coli | N/A |
| Fgf21-574M | Recombinant Mouse Fgf21, His tagged | Mouse | Human Cell | His |
| FGF21-879H | Recombinant Human FGF21 Protein, mFc-Avi-tagged | Human | HEK293 | mFc-Avi |
| FGF21-4822HF | Recombinant Full Length Human FGF21 Protein, GST-tagged | Human | In Vitro Cell Free System | GST |
| FGF21-4111H | Recombinant Human FGF21 Protein, GST-tagged | Human | Wheat Germ | GST |
| Fgf21-256M | Recombinant Mouse Fgf21, FLAG-tagged | Mouse | HEK293 | Flag |
| Fgf21-1491R | Recombinant Rat Fgf21 Protein, His-tagged | Rat | E.coli | N-His |
| FGF21-626B | Recombinant Bovine Fibroblast Growth Factor 21 | Bovine | Bovine | N/A |
| FGF21-1236C | Recombinant Cynomolgus FGF21 Protein, His-tagged | Cynomolgus Monkey | HEK293 | His |
| FGF21-4310Z | Recombinant Zebrafish FGF21 | Zebrafish | Mammalian Cell | His |
| FGF21-932P | Recombinant Pig FGF21 Protein, His&GST-tagged | Pig | E.coli | N-His&GST |
Reference
- Caterina Tezze, Vanina Romanello, Marco Sandri. FGF21 as Modulator of Metabolism in Health and Disease. Front. Physiol., 17 April 2019. Sec. Striated Muscle Physiology. Volume 10 - 2019 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fphys.2019.00419

