What is FGF9 Protein
The Fibroblast Growth Factor 9, commonly known as the FGF9 protein, is a growth factor member of the Fibroblast Growth Factor (FGF) family, involved in various biological processes including embryonic development and tissue repair. Its discovery in the mid-1990s expanded our understanding of cellular communication, development, and disease progression.
FGF9 was initially identified in the culture medium of GL261Glioma cells. This discovery was not only a significant scientific breakthrough, but it also set the stage for immense medical advancements. FGF9 is encoded by the FGF9 gene positioned in the human chromosome region 13q11-q12, and encompasses four exons and three introns. The protein structure of FGF9 is similar to the other members of the FGF family, showcasing a beta-trefoil structure - a triple-beta fold consisting of 12 antiparallel beta strands.
Function of FGF9 protein
This protein plays a determinant role in many cellular processes including proliferation, survival, migration and differentiation. It exerts its function by binding to the receptors namely FGF receptor 2 (FGFR2) and FGF receptor 3 (FGFR3), triggering a series of signaling cascades. FGF9 can activate mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) and phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K) via phosphorylation, influencing multiple downstream processes. Functioning at the intersection of these pathways, FGF9 plays a vital role in organ development, wound healing, and tumor growth.
In the context of organ development, FGF9 is vital for the development of the lungs, testes, and CNS. During lung development, FGF9 stimulates the proliferation of mesenchymal cells and also influences the differentiation of endodermal cells, contributing to the intricate architecture of the lung. Similarly, in testes development, FGF9 promotes the survival of Sertoli cells and regulates vascular development.
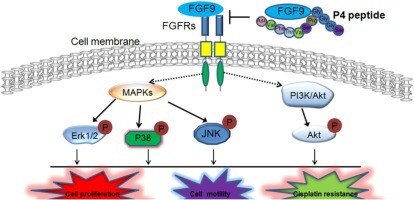
Fig1. FGF9 inhibition (Wang, J., et al. 2020)
FGF9 protein related signal pathway
The perturbation in the FGF9 signaling can lead to a myriad of diseases. Increased FGF9 expression has been linked to numerous types of cancers including prostate, lung, and testicular germ cell tumors. The increased level of FGF9 triggers uncontrolled cellular proliferation leading to tumor growth. Moreover, FGF9 mutations have been implicated in skeletal disorders like multiple synostoses syndrome, a condition characterized by fused bones in the fingertips, elbows, and ankles.
FGF9 protein related diseases
In addition to FGF9's vital role in normal physiology and disease progression, the protein has begun to make its mark in the biomedical field. FGF9's ability to stimulate cellular proliferation and tissue repair has made it a compelling candidate for promoting wound healing. Current studies are focusing on developing FGF9-loaded biomaterials for wound healing applications. Also, the role of FGF9 in organ development has potential applications in organo-genesis and regenerative medicine.
FGF9 protein's applications in biomedical
Nevertheless, the role of FGF9 in cancer poses a significant challenge to its therapeutic application. Therefore, understanding the FGF9 protein's role in different contexts is crucial to harness its therapeutic abilities effectively. In cancer therapy, FGF9 might serve as a potential target for pharmacological intervention. Small molecules that can inhibit the function of FFG9 or block its interaction with its receptors can be potential anti-cancer drugs.
Ultimately, the FGF9 protein plays a substantial role in diverse biological processes, from development to pathology. Its pivotal role in disease progression and development has made it an intriguing candidate for therapeutic studies. Despite some hurdles, the harnessing of FGF9's potential could usher a new era in the field of biomedical science. The road towards this era requires a deeper understanding of FGF9, further highlighting the need for continued research into this protein.
In conclusion, the FGF9 protein's discovery has brought enlightenment to our understanding of cellular functions. With its crucial role in organ development, wound healing, tumor growth and a host of diseases, FGF9 is not only valuable in biological studies but also in developing groundbreaking therapeutic approaches. As we continue exploring FGF9, it unveils exciting avenues for both basic biology and therapeutic innovations.
Our Featured Products
| Cat.No. | Product Name | Species | Source (Host) | Tag |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| FGF9-202H | Active Recombinant Human FGF9 protein, hFc-tagged | Human | HEK293 | hFc |
| FGF9-790H | Recombinant Human FGF9 Protein, His-tagged | Human | E.coli | His |
| FGF9-4117H | Recombinant Human FGF9 Protein, GST-tagged | Human | Wheat Germ | GST |
| FGF9-94H | Active Recombinant Human FGF9 Protein | Human | E.coli | |
| FGF9-95M | Active Recombinant Mouse FGF9 Protein | Mouse | E.coli | |
| FGF9-3239M | Recombinant Mouse FGF9 Protein, His (Fc)-Avi-tagged | Mouse | HEK293 | His (Fc)-Avi |
| FGF9-1993R | Recombinant Rat FGF9 Protein, His (Fc)-Avi-tagged | Rat | HEK293 | His (Fc)-Avi |
Reference
- Wang, J., Tan, X., Guo, Q., Lin, X., Huang, Y., Chen, L., Zeng, X., Li, R., Wang, H., & Wu, X. (2020). FGF9 inhibition by a novel binding peptide has efficacy in gastric and bladder cancer per se and reverses resistance to cisplatin. Pharmacological Research, 152, 104575. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phrs.2019.104575

