FGF9
-
Official Full Name
Fibroblast growth factor 9 (glia-activating factor) -
Overview
FGF9 (Fibroblast growth factor 9) is a member of the fibroblast growth factor (FGF) family of proteins. Human FGF9 is a protein of 208 amino acids with sequence similarity of approximately 30 percent to other members of the family of FGF. FGF9 is found in the conditioned medium of a Human glioma cell line and acts on cells of the central nervous system. It is a potent mitogen for glial cells. -
Synonyms
FGF9;fibroblast growth factor 9 (glia-activating factor);GAF;SYNS3;HBFG-9;Glia-activating factor;Fibroblast growth factor 9;FGF-9;Heparin-binding growth factor 9;OTTHUMP00000018804;heparin-binding growth factor
Recombinant Proteins
- Human
- Rat
- Canine
- Mouse
- Chicken
- HEK293
- E.coli
- CHO
- Mammalian Cells
- Sf21 Cells
- Human Cells
- Wheat Germ
- Fc
- Non
- mFc
- His
- S
- Avi
- GST
Background
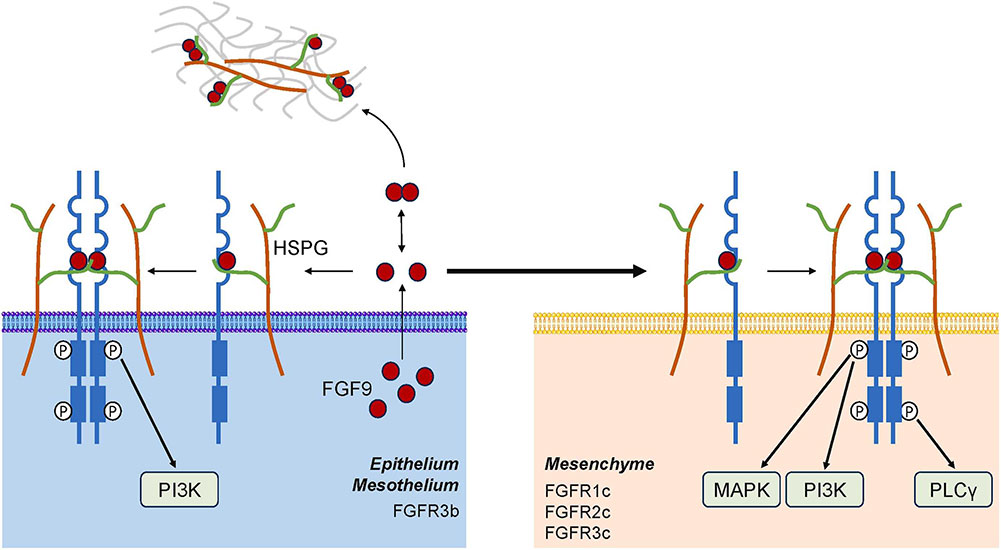
Fig1. FGF9 expression, binding, and signaling. (Hao Yin, 2024)
What is FGF9 protein?
FGF9 gene (fibroblast growth factor 9) is a protein coding gene which situated on the long arm of chromosome 13 at locus 13q12. The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the fibroblast growth factor (FGF) family. FGF family members possess broad mitogenic and cell survival activities, and are involved in a variety of biological processes, including embryonic development, cell growth, morphogenesis, tissue repair, tumor growth and invasion. This protein was isolated as a secreted factor that exhibits a growth-stimulating effect on cultured glial cells. The FGF9 protein is consisted of 276 amino acids and FGF9 molecular weight is approximately 30.7 kDa.
What is the function of FGF9 protein?
FGF9 protein is a protein that plays an important role in embryonic development, cell proliferation, cell differentiation and cell migration. FGF9 is particularly important in the development of the nervous system, where it is primarily produced by neurons and may be critical for glial cell development. FGF9 may also play a role in the growth and differentiation of glial cells, repair and regeneration of brain tissue after injury, differentiation and survival of neuronal cells, and growth stimulation of gliomas. In addition, FGF9 expression is regulated by Sonic hedgehog (Shh) signaling, and in some cases, such as in mice where the FGF9 gene is missing, may result in male-to-female sex reversal, suggesting that FGF9 also plays a role in testicular embryogenesis. In adults, FGF9 expression is more limited, but it can still be detected in the central nervous system and kidneys.
FGF9 related signaling pathway
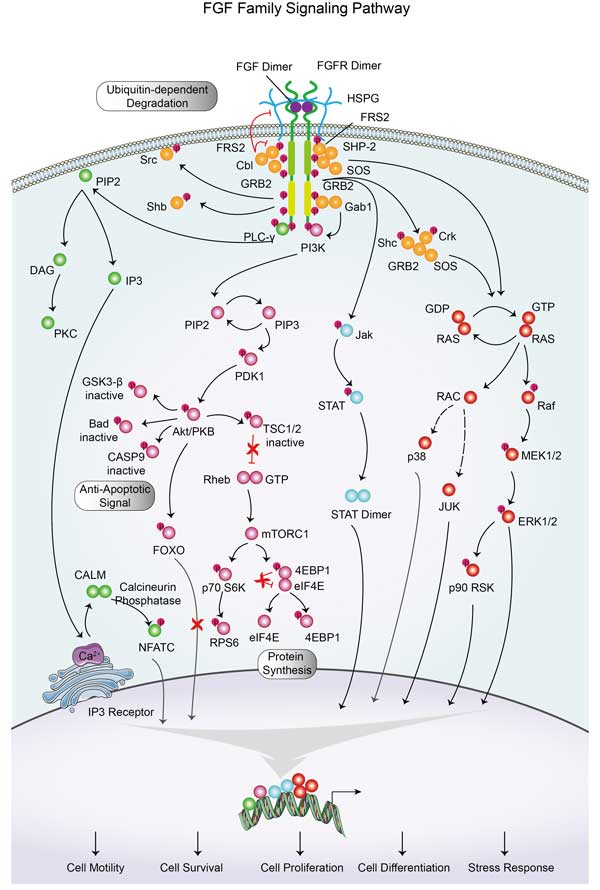
Fibroblast Growth Factor 9 (FGF9) binds to its specific receptors, predominantly FGFR2 and FGFR3, initiating intracellular signaling cascades primarily via the MAPK/ERK and PI3K/AKT pathways. This interaction promotes cell proliferation, migration, and survival, playing essential roles in organogenesis, particularly in the development of the lungs, limbs, and nervous system. Additionally, FGF9 modulates angiogenesis and wound healing by stimulating endothelial cell proliferation and migration. Dysregulation of this pathway can lead to developmental disorders, cancerous growth due to uncontrolled cell division, and tissue fibrosis.
FGF9 related diseases
FGF9-related diseases encompass a range of conditions primarily associated with aberrant cell proliferation, differentiation, and development. This includes cancers, such as lung, breast, and colorectal cancers, where overexpression or mutations in FGF9 can lead to uncontrolled cell growth and tumorigenesis. Additionally, dysregulation of the FGF9 signaling pathway is implicated in skeletal disorders, including craniosynostosis and achondroplasia, due to its role in bone development. Furthermore, FGF9 has been linked to neurodevelopmental disorders, such as intellectual disability and autism spectrum disorder, by influencing neural progenitor cell proliferation and differentiation.
Bioapplications of FGF9
The bioapplications of recombinant human FGF9 (rhFGF9) are centered around promoting tissue repair, enhancing developmental processes, and modulating cellular responses in various therapeutic contexts. By activating its receptors, FGFR2 and FGFR3, rhFGF9 can stimulate the proliferation and differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells, thereby facilitating bone and cartilage regeneration, making it a promising candidate for treating fractures and osteoarthritis. Additionally, its role in lung development suggests potential applications in respiratory diseases characterized by impaired alveolar growth. Moreover, rhFGF9 holds promise in regenerative medicine for neurological disorders by promoting neural precursor cell proliferation and differentiation, as well as in wound healing by enhancing angiogenesis and epithelialization processes. Thus, rhFGF9 offers a versatile tool for advancing treatments across multiple medical fields, leveraging its ability to regulate fundamental aspects of tissue growth and repair.
Case Study
Case Study 1: Tatjana Seitz, 2020
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is linked to liver fibrosis, with hepatic stellate cells (HSC) and cancer-associated myofibroblasts playing central roles. Overexpressed fibroblast growth factor (FGF) receptors are implicated in HCC's development. This study focused on FGFs' role in HSC-HCC interactions. FGF9, expressed by HSC but not HCC cells, correlated with poor survival rates. Recombinant FGF9 stimulated HCC cell proliferation, clonogenicity, migration, and reduced sorafenib sensitivity. FGF9's effects were largely blocked by the FGFR1/2/3 inhibitor BGJ398, not by the FGFR4 inhibitor BLU9931.
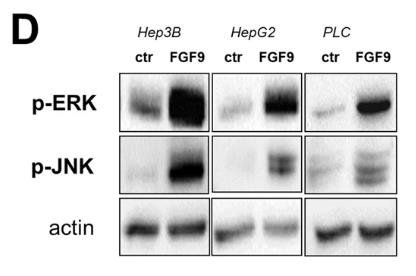
Fig1. Western Blot analysis of phosphorylated ERK and JNK1/2 in rFGF9 (20 ng/ml) treated and control cells.
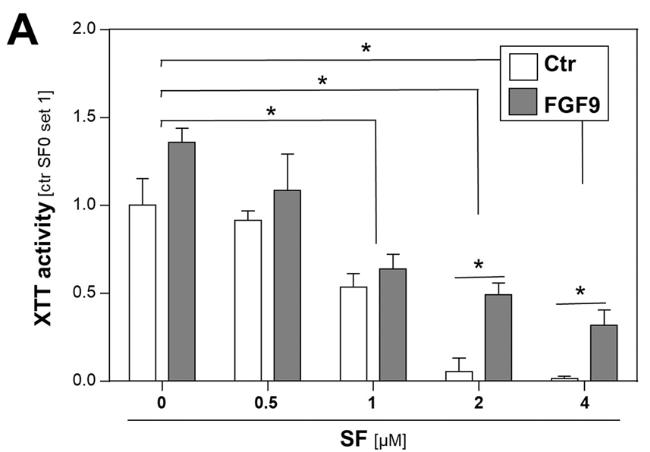
Fig2. Proliferation of HCC cells treated with depicted doses of sorafenib (SF) and rFGF9 (20 ng/ml).
Case Study 2: Chih-Chieh Chang, 2024
FGF9, a potent growth factor, is typically found at low levels in adult tissues and its abnormal expression is often linked to cancer. While its mechanism of action is not fully understood, it's known that FGF1 and FGF2 bind integrin αvβ3, which is crucial for their signaling. Researchers hypothesized that FGF9 also requires integrin binding for signaling. The docking simulations predicted that FGF9 binds to αvβ3 at a classical site. This binding and created an FGF9 mutant (R108E) that cannot bind integrin. This mutant failed to activate FRS2α and ERK1/2, induce DNA synthesis, or promote cancer cell migration and invasion, and it also inhibited these activities when induced by wild-type FGF9, suggesting a dominant-negative effect.
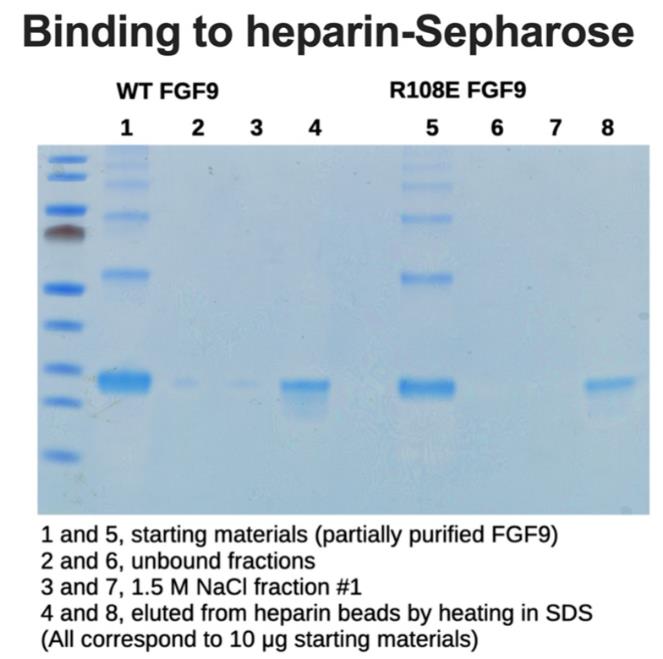
Fig3. Binding of R108E to heparin; partially purified WT and mutant FGF9 incubated with heparin–Sepharose.
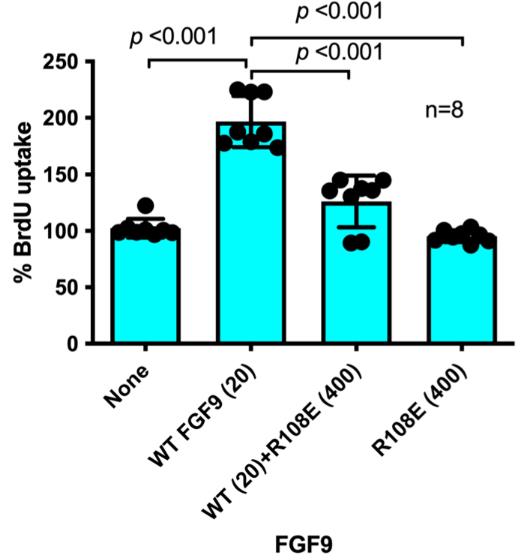
Fig4. NIH3T3 cells were starved for 24 h and stimulated with WT FGF9 and/or R108E.
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
.jpg)
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (FGF9-107H)
.
.jpg)
Fig2. SDS-PAGE (FGF9-647H)
Involved Pathway
FGF9 involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways FGF9 participated on our site, such as MAPK signaling pathway,Ras signaling pathway,Rap signaling pathway, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with FGF9 were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| Rap signaling pathway | LCP2,Adcy4,ANGPT2,RAC1,FGF17,FGF8,TLN1,GNAI2,F2RL3,FGF20 |
| Regulation of Actin Cytoskeleton | ACTB1,PFN2L,FGD3,ITGB1B.2,ITGB1A,PAK2B,PIP5K1BA,PDGFAA,ACTN2B,FGF20B |
| MAPK signaling pathway | CACNA2D1A,MAP3K7,MECOM,SRFA,NFKB2,MAP3K13,HRASB,FGF18,FGF3,TGFBR1A |
| PIK-Akt signaling pathway | PPP2R2B,AKT2,PTEN,PGF,ITGA7,FGFR3,TCL1B4,VWF,PKN2,STK11 |
| Ras signaling pathway | NRAS,GNGT1,GNGT2,PIK3CA,TBK1,FGFR1,PIK3CD,Fgf15,CALM1,SOS1 |
| Pathways in cancer | WNT9A,LAMB3,ITGB1,RAF1,BCL2,WNT9B,FGF21,PLCB4,RB1,ROCK2 |
| Melanoma | FGF14,TRP53,ARAF,Fgf15,FGF7,PDGFRB,FGFR1,FGF22,FGF12,FGF16 |
Protein Function
FGF9 has several biochemical functions, for example, fibroblast growth factor receptor binding,growth factor activity,heparin binding. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by FGF9 itself. We selected most functions FGF9 had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with FGF9. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| heparin binding | WISP2,FGF14,TENM1,FMODA,ECM2,SELL,Itgam&Itgb2,LTF,ANG,MMP7 |
| fibroblast growth factor receptor binding | FGF20A,FGF10B,FGF6,FGF1A,FGF3,FGF20B,FRS2,FGF8,FGF20,FRS3 |
| growth factor activity | IL11,FGF10A,IL3,SPAW,CSF1A,KLK1B3,GDF9,IL5,PPBP,FGF2 |
Interacting Protein
FGF9 has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with FGF9 here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of FGF9.
FGF9 Related Signal Pathway
Resources
Gene Families
Research Area
Related Services
Related Products
References
- Correa, D; Somoza, RA; et al. Sequential exposure to fibroblast growth factors (FGF) 2, 9 and 18 enhances hMSC chondrogenic differentiation. OSTEOARTHRITIS AND CARTILAGE 23:443-453(2015).
- Zheng, ZL; Kim, J; et al. Histometric changes and epidermal FGF9 expression in carbon photoenhancer-assisted Nd:YAG laser treatment. JOURNAL OF DERMATOLOGICAL TREATMENT 25:278-282(2014).