What is IRAK4 Protein?
The Interleukin-1 receptor-associated kinases or IRAK protein is an integral part of the immune response in many life forms. Among these proteins lies IRAK4, which plays a crucial role in the immune response system. Understanding IRAK4 isn't just about understanding the immunity framework; it can also help discern multiple diseases and potential therapeutic interventions.
Discovery and Background
IRAK4, previously known as IRAK-4/ NY-RAK, was discovered in the early 2000s. Scientists identified it as a crucial member of the IRAK protein family, vital for immune response signaling in many life forms. Although scientists had already identified other IRAK proteins involved in immune functions, IRAK4's discovery was a pivotal step due to its unique structure and function.
Gene Locus and Protein Structure
The gene IRAK4 is located on the short (p) arm of chromosome 12 at position 12. The protein encoded is a kinase, a member of the serine/threonine protein kinase family. It was quickly revealed that IRAK4 is distinctly different in terms of structure and function among its IRAK counterparts.
The IRAK4 protein is structurally composed of an N-terminal death domain and a C-terminal kinase domain. The death domain allows it to interact with other proteins, resulting in signal amplification. The kinase domain, on the other hand, is responsible for catalyzing the phosphorylation of target proteins.
Function of IRAK4 Protein
IRAK4 is primarily involved in the signal transduction from various immune response receptors like toll-like receptors (TLRs) and interleukin-1 receptors (IL-1Rs). These receptors recognize external pathogens and trigger a series of signaling cascades that result in the activation of the immune response.
IRAK4 acts as the first kinase in this cascading pathway, phosphorylating and activating other IRAK family members. It's acting as a gateway to the downstream signal transduction pathway is thereby crucial in defenses against bacterial and viral infections.
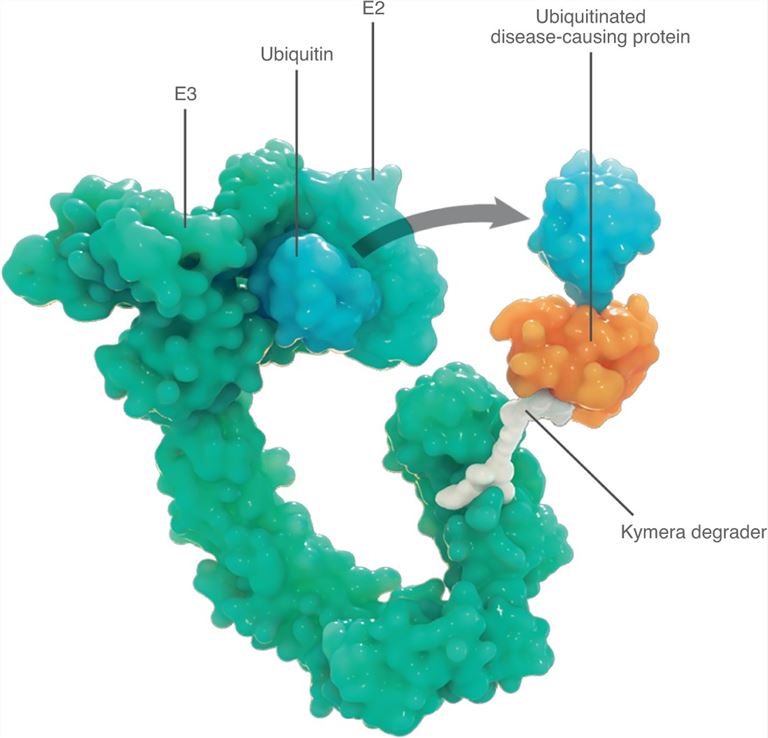
Fig1. IRAK4 degrader to take on innate immunity
IRAK4 Protein-Related Signal Pathway
IRAK4 is an active player in the toll-like receptor (TLR) mediated signaling pathway. It's the master kinase activating IRAK1 and IRAK2 following TLR activation, initiating a subsequent signaling cascade that leads to the activation of transcription factors like nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB) and activator protein 1 (AP1). These transcription factors then mediate the production of inflammatory cytokines to eliminate the invading pathogens.
IRAK4 Protein-Related Diseases
Defects in the IRAK4 protein can lead to several diseases due to its importance in the immune response. Mutations in the IRAK4 gene can precipitate IRAK4 deficiency, severely impairing the immune system's ability to fight off infections. Disruptions in the signaling cascade where IRAK4 plays a key role can also lead to autoimmune diseases like lupus and rheumatoid arthritis. Moreover, overexpression of IRAK4 has been found in several types of cancer, including breast and pancreatic, suggesting its possible role in carcinogenesis.
IRAK4 Protein's Applications in Biomedicine
Given IRAK4's central role in the immune response and its association with various diseases, it has attracted enormous interest in biomedical research. Several IRAK4 inhibitors are under development or in clinical trials as potential treatments for autoimmune diseases and cancer. These inhibitors aim to interrupt the signaling pathway IRAK4 is a part of and subsequently disrupt the pathological inflammatory responses commonly seen in such diseases.
Furthermore, IRAK4 protein's genetic diagnostics are employed to detect IRAK4 mutations to predict susceptibility to several diseases, emphasizing its role in personalized medicine.
In the grand scheme, understanding IRAK4 remains critical in deciphering how our immune system tackles external pathogens and how malfunctions in this system can lead to disease. Consequently, IRAK4 protein potentially holds the key to unlocking more effective treatments and preventive strategies against various autoimmune diseases and cancer.
Our Featured Products
| Cat.No. | Product Name | Species | Source (Host) | Tag |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| IRAK4-46H | Active Recombinant Human IRAK4 protein, His-tagged | Human | Insect Cell | His |
| RAK4-1418H | Active Recombinant Human IRAK4 (Active), GST-tagged | Human | Sf9 Insect Cell | GST |
| IRAK4-2438H | Recombinant Full Length Human IRAK4 Protein, MYC/DDK-tagged | Human | HEK293 | Myc/DDK |
| IRAK4-5733HF | Recombinant Full Length Human IRAK4 Protein, GST-tagged | Human | In Vitro Cell Free System | GST |
| IRAK4-1193H | Recombinant Human IRAK4 Protein, His (Fc)-Avi-tagged | Human | HEK293 | His (Fc)-Avi |
| IRAK4-1168H | Recombinant Human IRAK4 Protein (E154-S460), Tag Free | Human | Insect Cell | No tag |
| Irak4-3570M | Recombinant Mouse Irak4 Protein, Myc/DDK-tagged | Mouse | HEK293T | Myc/DDK |
| IRAK4-4597M | Recombinant Mouse IRAK4 Protein, His (Fc)-Avi-tagged | Mouse | HEK293 | His (Fc)-Avi |
Reference
- Mullard, A. (2020). IRAK4 degrader to take on innate immunity. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41587-020-0724-8

