What is MYC Protein
What is MYC Protein?
The MYC protein family, comprising c-MYC, N-MYC, and L-MYC, represents a pivotal group of transcription factors crucial for cellular regulation. Discovered in the 1980s, MYC proteins have since been the focus of intense scrutiny in the realm of molecular biology.
MYC proteins share a conserved basic helix-loop-helix (bHLH) motif and leucine zipper domain, enabling dimerization and DNA binding. This structural framework facilitates their role as transcription factors, modulating gene expression across a diverse array of cellular processes.
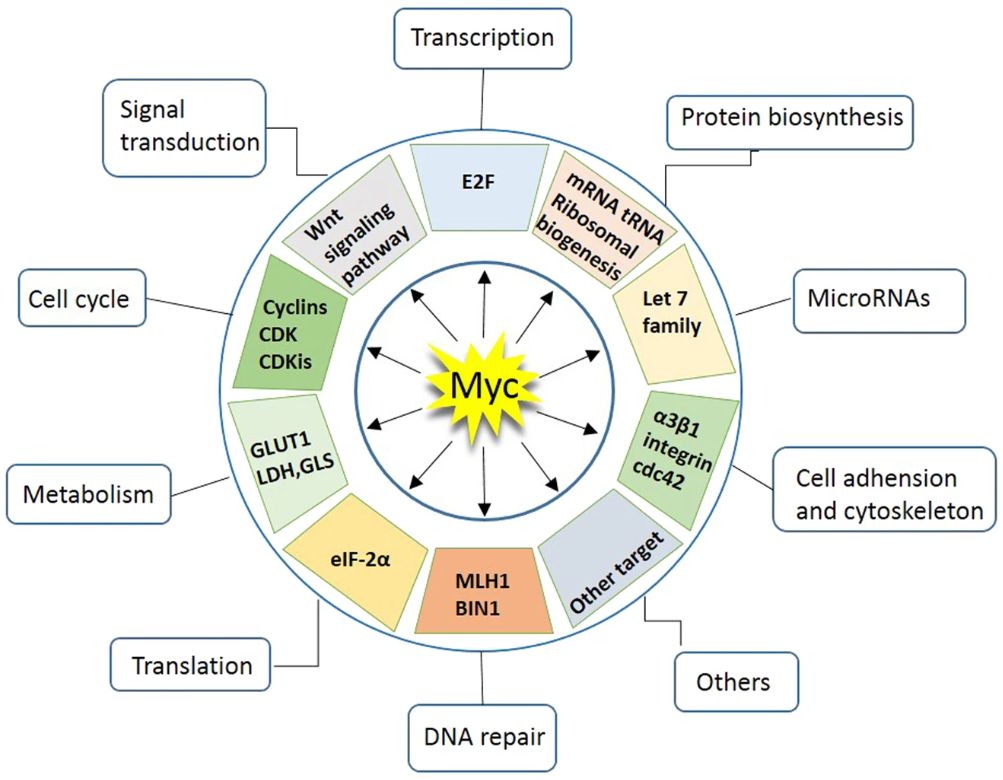
Figure 1. Myc regulates a spectrum of cellular functions. (Chen, H., et al. 2018)
The Function of MYC Protein
- Cell Cycle Regulation
Central to MYC's function is its role in cell cycle regulation. By orchestrating the expression of genes involved in cell division, MYC ensures a controlled progression through the cell cycle. However, dysregulation leads to unbridled proliferation, a hallmark of cancer.
- Apoptosis Regulation
MYC's influence extends to apoptosis, where it orchestrates the delicate balance between cell survival and programmed cell death. While promoting apoptosis under certain conditions, abnormal activation can confer resistance to programmed cell death, contributing to tumorigenesis.
- Metabolic Control
Beyond cell cycle and apoptosis, MYC plays a pivotal role in metabolic control. Its activation induces a metabolic shift, enhancing glucose uptake and glycolysis, a phenomenon known as the Warburg effect. This metabolic reprogramming fuels the energy demands of rapidly dividing cancer cells.
MYC-Related Diseases
Aberrant MYC expression is a common denominator in various cancers. Mechanisms such as gene amplification, translocation, and increased protein stability contribute to MYC overexpression, driving uncontrolled cell proliferation, survival, and angiogenesis.
Efforts to target MYC directly face challenges due to its complex structure. Researchers are exploring alternative strategies, such as disrupting MYC interactions or targeting downstream effectors, offering potential avenues for novel cancer therapies with reduced side effects.
MYC Related Signaling Pathways
- Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling
The intricate crosstalk between MYC and the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway plays a pivotal role in cell fate decisions and tissue homeostasis. Disruptions in this interplay contribute to pathological conditions, including cancer.
- Notch Signaling Pathway
The Notch signaling pathway intersects with MYC, influencing cell fate determination and differentiation. Dysregulation of Notch-MYC crosstalk is implicated in various diseases, providing potential targets for therapeutic interventions.
Applications of MYC in Biomedical Research
- Modeling Disease
Transgenic animal models expressing deregulated MYC provide invaluable insights into the consequences of MYC dysregulation in vivo. These models mimic human diseases, aiding researchers in understanding complex interactions and facilitating the development of targeted therapies.
- Biomarker Discovery
MYC's aberrant expression makes it a potential biomarker for diagnostic and prognostic purposes in various cancers. Detection of MYC levels in tissues or circulating biomarkers holds promise for improving cancer diagnosis and treatment stratification.
- Therapeutic Development
Despite challenges, progress in developing drugs targeting MYC or its downstream signaling pathways offers hope for more effective and targeted cancer therapies. Small molecules and peptides designed to interfere with MYC function represent a burgeoning field with potential clinical implications.
The MYC protein, with its intricate functions and diverse implications in health and disease, continues to be a focal point of intensive research. As our understanding of MYC deepens, so does the potential for groundbreaking advancements in personalized medicine and cancer therapeutics.
Recommended Products for MYC Protein
| Cat.# | Species | Product name | Source (Host) | Tag |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MYC-79H | Human | Active Recombinant Human MYC protein, arginine-tagged | E.coli | Arg |
| MYC-254H | Human | Recombinant Human MYC protein, T7/His-tagged | E.coli | T7/His |
| MYC-1029H | Human | Recombinant Human MYC, His-tagged | E.coli | His |
| MYC-574H | Human | Recombinant Human MYC protein, His & GST-tagged | E.coli | His/GST |
| MYC-060H | Human | Recombinant Human MYC Protein, MYC/DDK-tagged, C13 and N15-labeled | HEK293 | C-Myc/DDK |
| MYC-1461H | Human | Recombinant Human MYC Protein, His (Fc)-Avi-tagged | HEK293 | His (Fc)-Avi |
| Myc-6774M | Mouse | Recombinant Mouse Myc protein, His & GST-tagged | E.coli | His/GST |
| MYC-3498R | Rat | Recombinant Rat MYC Protein, His (Fc)-Avi-tagged | HEK293 | His (Fc)-Avi |
| MYC-2916R | Rhesus Macaque | Recombinant Rhesus monkey MYC Protein, His-tagged | Mammalian Cell | His |
| MYC-2641C | Chicken | Recombinant Chicken MYC | Mammalian Cell | His |
Reference
- Chen, H., et al. Targeting oncogenic Myc as a strategy for cancer treatment. Sig Transduct Target Ther. 2018, 3: 5.

