What is NRAS Protein
The NRAS protein, fully known as Neuroblastoma RAS viral oncogene homolog, is part of a larger family of proteins recognized as RAS proteins. It is an essential component in cellular signaling, particularly transducing signals inside the cells, thus enabling communication between cells and orchestrating various cell functions, including cell division, survival, and differentiation.
Function of NRAS protein
The RAS proteins are activators of downstream effectors, initiating a cascade of signal transduction, and NRAS is closely intertwined with this critical process. The NRAS protein functions as a signaling molecule by cycling between an inactive state, where it is bound to GDP (Guanosine diphosphate), and an active state, where it is bound to GTP (Guanosine triphosphate). This delicate balance supports cell growth and cell division but, if disrupted, can lead to aberrant cellular activities.
NRAS protein related signal pathway
NRAS resides at the heart of an important signal transduction pathway known as the Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase (MAPK) Pathway. This pathway balances cell growth and cellular apoptosis, a naturally occurring process where cells commit to programmed death. The NRAS protein binds with GTP and turns on, interacting with a cascade of proteins to activate the MAPK pathway. The activated NRAS interacts with its effector protein, RAF, which, in turn, stimulates MEK, and finally, ERK, leading to gene transcription and, ultimately, necessary cell functions such as proliferation, differentiation, and maintenance of cell survival. Keeping this pathway in check is crucial to maintaining equilibrium within the cell.
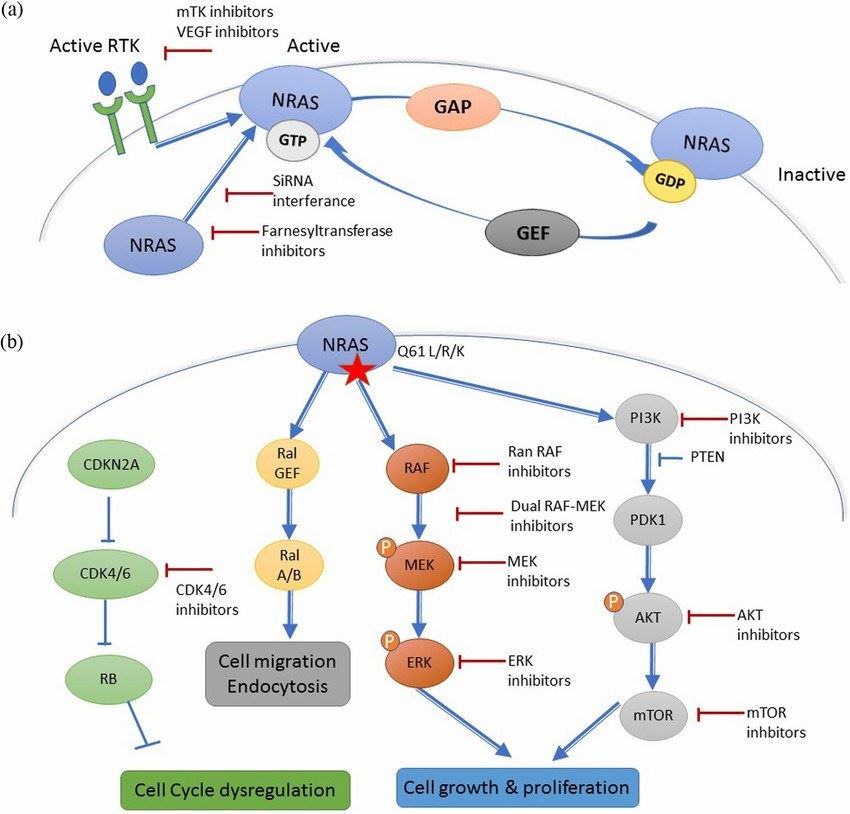
Fig1. Mechanism of NRAS activation (Boespflug, et al. 2017)
NRAS protein related diseases
Importantly, changes in the function of the NRAS protein can give rise to a range of diseases. Mutations in the NRAS gene, which instructs the making of this protein, can lead to the production of an active NRAS protein that can't switch off. The continuous signaling via the MAPK pathway could drive cells into uncontrolled growth, giving rise to numerous types of cancer, like melanoma, acute myeloid leukemia, and others. Congenitally, NRAS gene mutations can also cause a disorder known as Noonan Syndrome, characterized by unique facial features, heart defects and short stature. Other related conditions include cardiofaciocutaneous syndrome and Costello syndrome, both of which include developmental and cardiovascular abnormalities.
NRAS protein's applications in biomedical
Significant progress has been made in exploiting our understanding of NRAS for therapeutic utilities in biomedicine. The primary avenue of intervention concerns the blocking of NRAS protein signaling, thus curbing its oncogenic capacity. However, direct targeting of NRAS has proved to be challenging due to the protein's structure. Therefore, shuttling the focus to components downstream in the signaling pathway, such as MEK and ERK, has gained momentum, and inhibitors of these proteins are currently in clinical trials illustrating effectiveness against NRAS-mutated cancers.
In conclusion, the NRAS protein towers as a paramount molecule within the vast network of proteins that make life possible. Its oscillation between an active and inactive state plays a role in maintaining cellular balance – a disruption of which could lead to various diseases. This protein's crucial part in certain diseases has provided the impetus for unravelling its complexities and exploiting this knowledge towards therapeutic advancements in biomedicine. Despite the challenges, the unrelenting advances in understanding the NRAS protein and its related signaling pathways continue to inspire hope for a future of precision oncology and transformative therapeutics.
Our Featured Products
| Cat.No. | Product Name | Species | Source (Host) | Tag |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NRAS-01H | Active Recombinant Human NRAS Protein, His-tagged | Human | Bacterial expression system | His |
| NRAS-1544H | Recombinant Human NRAS Protein, His (Fc)-Avi-tagged | Human | HEK293 | His (Fc)-Avi |
| NRAS-6106H | Recombinant Human NRAS Protein, GST-tagged | Human | Wheat Germ | GST |
| NRAS-172HFL | Recombinant Full Length Human NRAS Protein, C-Flag-tagged | Human | Mammalian cells | Flag |
| NRAS-0940H | Recombinant Human NRAS Protein (M1-K169), Biotinylated tagged | Human | E.coli | biotinylated |
| NRAS-0941H | Recombinant Human NRAS Protein (M1-K169, G13D), Biotinylated tagged | Human | E.coli | biotinylated |
| Nras-4494M | Recombinant Mouse Nras Protein, Myc/DDK-tagged | Mouse | HEK293T | Myc/DDK |
| NRAS-3735R | Recombinant Rat NRAS Protein, His (Fc)-Avi-tagged | Rat | HEK293 | His (Fc)-Avi |
Reference
- Boespflug, Amélie & Caramel, Julie & Dalle, Stéphane & Thomas, Luc. (2017). Treatment of NRAS -mutated advanced or metastatic melanoma: Rationale, current trials and evidence to date. Therapeutic Advances in Medical Oncology. 9. 175883401770816. 10.1177/1758834017708160.

