What is NTN1 Protein
In the human biology, proteins play a pivotal role, orchestrating a myriad of functions necessary for life. One such protein that has captivated the attention of researchers and clinicians alike is Netrin-1 (NTN1), a molecule whose significance extends from embryonic development to its implications in various diseases.
NTN1, a member of the laminin-related secreted protein family, stands as a linchpin in the intricate choreography of human biological processes. Unveiling its nature provides a foundational understanding of its multifaceted roles. NTN1, discovered in the early 1990s, is pivotal for axon guidance and neuronal development during embryogenesis.
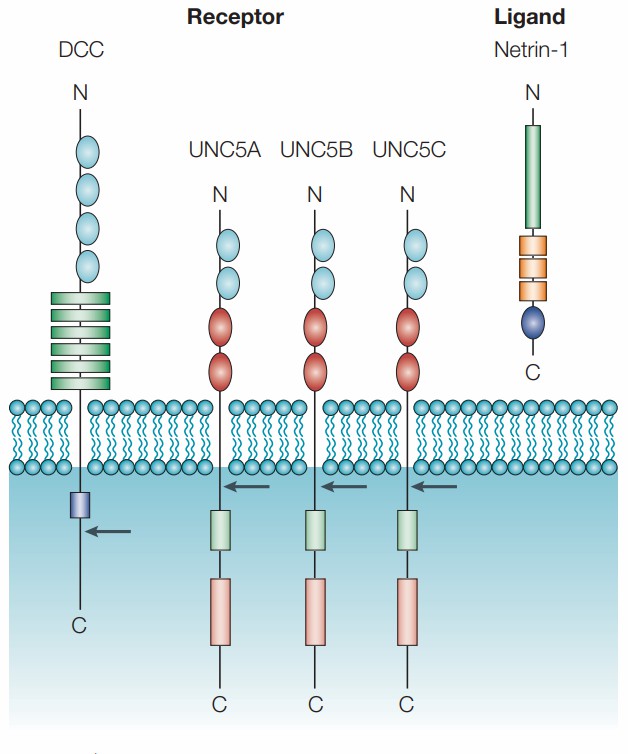 Figure 1. Structure of human netrin-1 and its receptors. (Arakawa, H. 2004)
Figure 1. Structure of human netrin-1 and its receptors. (Arakawa, H. 2004)The Function of NTN1 Protein
- Axon Guidance and Neuronal Development
NTN1 is recognized for its pivotal role in guiding axons during the formation of the nervous system. It acts as a chemoattractant for developing axons, guiding them to their appropriate destinations. This function is vital for the establishment of neural circuits and the proper functioning of the nervous system.
- Angiogenesis
Beyond its neurocentric functions, NTN1 plays a dual role by influencing angiogenesis – the formation of new blood vessels. It exerts its influence on endothelial cells, promoting migration and subsequent blood vessel growth. This dual functionality underscores NTN1's pleiotropic nature, contributing to both neural and vascular development.
NTN1-Related Diseases
The exquisite balance maintained by NTN1 is disrupted in various pathological conditions, leading to its association with several diseases.
- Cancer
In the realm of oncology, NTN1 emerges as a key player in tumor progression. Its influence on cell migration and angiogenesis promotes tumor growth, particularly notable in colorectal cancer. NTN1's modulation holds promise for targeted therapies aimed at impeding cancer progression.
- Neurological Disorders
NTN1 has been associated with neurological disorders, including neurodegenerative diseases and psychiatric disorders. Its involvement in axon guidance suggests a potential link to conditions characterized by disrupted neural connectivity, such as Alzheimer's disease and schizophrenia.
- Cardiovascular Diseases
The involvement of NTN1 in angiogenesis extends its relevance to cardiovascular diseases. Aberrant NTN1 expression is observed in atherosclerosis, linking it to conditions where the formation of new blood vessels plays a crucial role in disease progression.
NTN1 Related Signaling Pathways
Understanding NTN1's involvement in various physiological and pathological processes necessitates unraveling the intricate signaling pathways it engages.
- UNC-5 Receptor-Mediated Signaling Pathway
A pivotal player in NTN1 signaling is the UNC-5 receptor-mediated pathway. This pathway dictates the repulsion of axons, preventing them from venturing into inappropriate regions during development. The delicately balanced interplay between repulsive and attractive signals ensures the precision of axonal navigation.
- DCC Receptor-Mediated Signaling Pathway
NTN1's interaction with Deleted in Colorectal Cancer (DCC) receptors results in attractive guidance of axons. This pathway further contributes to the intricacies of axon guidance, highlighting NTN1's role in ensuring the accurate wiring of the nervous system.
Applications of NTN1 in Biomedical Research
- Neuroregeneration
Exploiting NTN1's regenerative potential emerges as a beacon of hope in developing therapies for neural regeneration after injury or in neurodegenerative conditions. Strategies involving the enhancement of NTN1 expression or exogenous administration hold potential for promoting axon regeneration.
- Cancer Therapy
The intricate involvement of NTN1 in tumor growth and angiogenesis positions it as an attractive target for cancer therapy. Inhibition of NTN1 signaling pathways presents a potential avenue for impeding cancer progression, paving the way for innovative and targeted cancer treatments.
- Cardiovascular Interventions
The angiogenic role of NTN1 propels it into the spotlight for cardiovascular interventions. Stimulating NTN1-mediated angiogenesis holds promise in conditions where promoting blood vessel growth is therapeutically relevant, such as in ischemic heart disease.
- Neurological Disorders Treatment
Unraveling the role of NTN1 in neurological disorders opens avenues for therapeutic interventions. Modulating NTN1 expression or its interaction with receptors emerges as a strategy for conditions characterized by disrupted neural connectivity, offering potential treatments for neurodevelopmental disorders or psychiatric illnesses.
The NTN1 protein, with its intricate functions and diverse implications in health and disease, represents a captivating subject in the ever-evolving landscape of biological research. From axon guidance to angiogenesis and its involvement in diseases ranging from cancer to cardiovascular conditions, NTN1's versatility positions it as a focal point for future biomedical advancements and therapeutic innovations.
Recommended Products for NTN1 Protein
| Cat.# | Species | Product name | Source (Host) | Tag |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NTN1-428H | Human | Active Recombinant Human NTN1, Fc-tagged | HEK293 | Fc |
| NTN1-1088H | Human | Active Recombinant Human NTN1 | Mammalian cells | His |
| NTN1-2173H | Human | Recombinant Human Netrin 1, FLAG-tagged | HEK293 | Flag |
| NTN1-22H | Human | Active Recombinant Human NTN1 Protein, FLAG-tagged | HEK 293 | FLAG |
| NTN1-10937M | Mouse | Recombinant Mouse NTN1 Protein | Mammalian Cell | His |
| Ntn1-1854M | Mouse | Recombinant Mouse Ntn1 protein, His & GST-tagged | E.coli | His/GST |
| Ntn1-257R | Rat | Recombinant Rat Ntn1 protein, His/GST-tagged | E.coli | His/GST |
| Ntn1-4442R | Rat | Recombinant Rat Ntn1 protein, His-tagged | E.coli | His |
| NTN1-6970C | Chicken | Recombinant Chicken NTN1 | Mammalian Cell | His |
| NTN1-2172C | Chicken | Recombinant Chicken NTN1 Protein, FLAG-tagged | HEK 293 | FLAG |
Reference
- Arakawa, H. Netrin-1 and its receptors in tumorigenesis. Nat Rev Cancer. 2004, 4: 978–987.

