What is PROM1 Protein
PROM1, or Prominin-1, is a protein encoded by the PROM1 gene. It is also known by several synonyms, including CD133, AC133 antigen, and MACS1. This glycoprotein belongs to the prominin family and plays a pivotal role in various biological processes. The PROM1 gene is located on chromosome 4, and its official full name is "prominin 1."
PROM1 Protein Structural Characteristics and Classification
PROM1 protein is characterized by its unique structure, consisting of five transmembrane domains and two large glycosylated extracellular loops. This distinct configuration contributes to its role as a cell surface marker. The protein is predominantly found on the surface of various cell types, serving as a marker for stem and progenitor cells.
Belonging to the prominin family, PROM1 is involved in cellular differentiation, proliferation, and survival. Recent advances in research have shed light on the intricate details of its structure and function, unlocking new possibilities for understanding its role in health and disease.
PROM1 Biological Functions and Molecular Mechanisms
The biological functions of PROM1 are diverse and crucial for the maintenance of cellular homeostasis. One of its primary roles is in stem cell biology, where PROM1 serves as a marker for identifying and isolating stem and progenitor cells. By interacting with cholesterol and other membrane components, PROM1 contributes to the organization and dynamics of lipid rafts on the cell surface.
Moreover, PROM1 is implicated in the regulation of cellular processes such as cell adhesion, migration, and intracellular signaling. The molecular mechanisms underlying PROM1's functions involve its interaction with various signaling pathways, influencing gene expression, and modulating cellular responses.
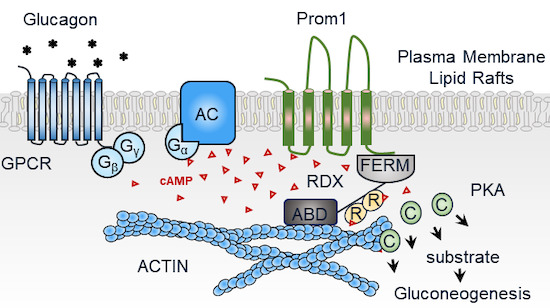
Figure 1. Prominin‐1‐Radixin axis controls hepatic gluconeogenesis by regulating PKA activity. (Lee H, et al., 2020)
PROM1 Related Signaling Pathway
The signaling pathways associated with PROM1 are intricate and multifaceted. Notably, PROM1 has been implicated in the regulation of Wnt/β-catenin signaling, a pathway crucial for embryonic development and tissue homeostasis. The interaction between PROM1 and Wnt signaling influences cell fate decisions, including the maintenance of stem cell characteristics and the promotion of cell differentiation.
Additionally, PROM1 is involved in the Notch signaling pathway, contributing to the regulation of cell fate determination and tissue development. The intricate crosstalk between PROM1 and various signaling cascades highlights its role as a key player in orchestrating cellular responses.
PROM1 Related Diseases
Dysregulation of PROM1 has been linked to several diseases, emphasizing its significance in maintaining normal cellular function. Aberrant expression of PROM1 is associated with the development and progression of certain cancers, including glioblastoma, colorectal cancer, and ovarian cancer. The overexpression of PROM1 in cancer cells is often linked to increased tumorigenicity and resistance to chemotherapy.
In addition to cancer, PROM1 has been implicated in retinal degenerative disorders, where mutations in the PROM1 gene can lead to impaired vision and retinal degeneration. Understanding the role of PROM1 in these diseases provides valuable insights for developing targeted therapeutic interventions.
PROM1's Applications in Biomedicine
The unique properties of PROM1, particularly its cell surface localization and association with stem cells, make it a valuable tool in biomedical research and applications. PROM1 is widely used as a marker for isolating and characterizing stem and progenitor cells from various tissues. This has significant implications for regenerative medicine and the development of novel cell-based therapies.
Moreover, PROM1 has emerged as a promising target for diagnostic and therapeutic purposes in cancer. The specific expression of PROM1 in cancer stem cells makes it a potential marker for early detection and prognosis assessment. Targeting PROM1 in cancer therapy holds promise for developing more effective and personalized treatment strategies.
In vaccine development, PROM1's involvement in immune responses and cellular interactions positions it as a potential candidate for vaccine design. Understanding its role in modulating immune cell function could contribute to the development of vaccines with enhanced efficacy.
Recommended Products
| Cat.# | Product name | Species | Source (Host) | Tag |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Prom1-120RAF555 | Recombinant Rat Prom1 Protein, Fc-tagged, Alexa Fluor 555 conjugated | Rat | HEK293 | Fc |
| Prom1-120RAF488 | Recombinant Rat Prom1 Protein, Fc-tagged, Alexa Fluor 488 conjugated | Rat | HEK293 | Fc |
| Prom1-120RAF647 | Recombinant Rat Prom1 Protein, Fc-tagged, Alexa Fluor 647 conjugated | Rat | HEK293 | Fc |
| Prom1-120RF | Recombinant Rat Prom1 Protein, Fc-tagged, FITC conjugated | Rat | HEK293 | Fc |
| PROM1-46H | Recombinant Human PROM1, MYC/DDK-tagged | Human | HEK293 | Myc/DDK |
| PROM1-399HF | Recombinant Full Length Human PROM1 Protein | Human | In Vitro Cell Free System | |
| PROM1-73H | Recombinant Human Prominin 1, GST-tagged | Human | Wheat Germ | GST |
| PROM1-1493H | Recombinant Human PROM1 Protein (508-792 aa), His-tagged | Human | Yeast | His |
| PROM1-45H | Recombinant Human PROM1, MYC/DDK-tagged | Human | HEK293 | Myc/DDK |
| PROM1-161H | Recombinant Human PROM1 Protein, C-His-tagged | Human | E.coli | C-His |
Reference
- Lee H, et al. Prominin‐1‐Radixin axis controls hepatic gluconeogenesis by regulating PKA activity. EMBO Reports. 2020, 21(11): e49416.

