What is S100A9 Protein?
The S100A9 protein, also commonly called myeloid-related protein 14 (MRP14), is a part of the S100 family of proteins, characterized by their relatively small size (approximately 100 amino acids) and the presence of two calcium-binding EF-hand motives. This unique protein is of great scientific interest due to its role in various disease processes and potential applications in biomedical science.
Background and Discovery of S100A9 Protein
The discovery of the S100A9 protein can be traced back to the late 20th century. Initially, it was identified among the proteins necessary for the calcium-dependent regulation of cellular processes. The protein was subsequently classified as part of the S100 family, known for their involvement in a wide array of intracellular and extracellular functions.
The gene coding for the S100A9 protein is located on chromosome locus 1q21, also known as the epithelial differentiation complex (EDC), which is a gene region accounting for various skin diseases. The S100A9 protein is predominantly expressed in myeloid cells, whose gene structure encompasses three exons spanning 2kb.
What Is The Structure of S100A9 Protein?
The protein structure of S100A9 exhibits an intricate design. It comprises two EF-hand calcium-binding motifs, one located in the N-terminal region and the other in the C-terminal region. These regions are conjoined by a central hinge region that facilitates the protein's various functional activities.
What Is The Function of S100A9 Protein?
The function of the S100A9 protein is multifaceted. In its unbound state, it has both intracellular and extracellular functions. Intracellularly, it is involved in the regulation of various cellular processes like cell cycle progression and differentiation. Extracellularly, it plays a crucial role in the modulation of inflammatory responses as a part of the innate immune system.
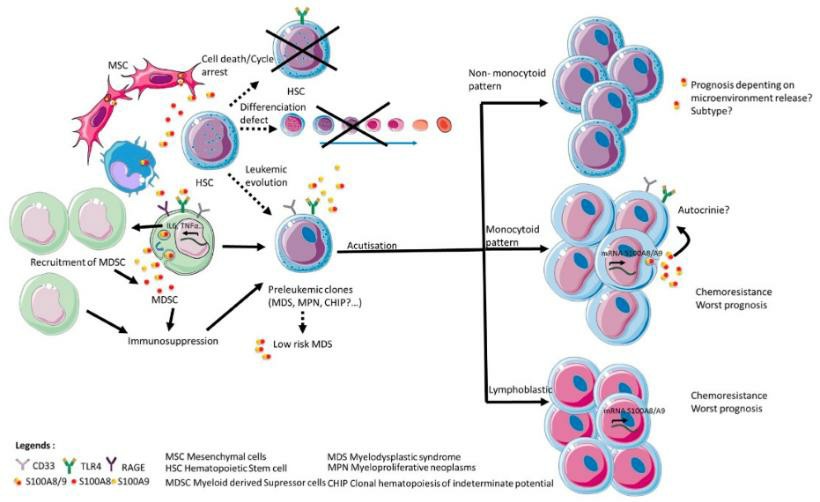
Fig1. Impact of S100A8 and S100A9 in disruption of hematopoiesis and leukemic progression
S100A9 protein related signal pathway
A crucial area of focus in studying S100A9 protein is its related signaling pathway. S100A9 interacts with several receptors, including the transmembrane receptor for advanced glycation end products (RAGE) and Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4). Through interaction with these receptors, S100A9 regulates various cellular processes and responses to stress.
S100A9 protein related diseases
Accumulating research has implicated S100A9 in several diseases. Its upregulation is usually associated with inflammation, autoimmune diseases, cancer, and other conditions marked by chronic inflammation, such as cardiovascular and neurodegenerative diseases.
In cancer, S100A9 is reported to promote tumor development and metastasis by modulating tumor microenvironment and enhancing the survival and proliferation of cancer cells. Additionally, it is implicated in Alzheimer's disease, as its interaction with amyloid-beta leads to the creation of complexes that accelerate plaque accumulation.
S100A9 protein's applications in biomedical
The discovery and subsequent research into S100A9 protein have guided advances in biomedicine. Because of its involvement in disease processes, it can be a target for therapeutic developments. For example, the utilization of S100A9 inhibitors can reduce inflammation and slow the progression of diseases like cancer and Alzheimer's.
Additionally, the S100A9 protein could potentially serve as a biomarker in clinical diagnosis. Its increased expression levels in blood and tissue samples have been associated with several diseases, including various cancer types and chronic inflammatory conditions.
In conclusion, the S100A9 protein presents a compelling focal point in biomedical research due to its multifunctional role as a central player in various disease processes. As we deepen our understanding of this fascinating protein, its applications in disease diagnosis, prognosis, and treatment could become even more prolific, underlining its immense potential in advancing human health.
Our Featured Products
| Cat.No. | Product Name | Species | Source (Host) | Tag |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| S100A9-255H | Active Recombinant Human S100A9 protein | Human | E.coli | N/A |
| S100A9-300H | Active Recombinant Human S100A9, His-tagged | Human | Insect Cell | His |
| S100A8 & S100A9-2217H | Recombinant Human S100A8 & S100A9 Heterodimer Protein, His & Flag tagged | Human | Insect Cells | His & Flag |
| S100A9-3879H | Recombinant Human S100A9, None tagged | Human | E.coli | N/A |
| S100A9-2215H | Active Recombinant Human S100A9, His tagged | Human | Insect Cells | His |
| S100A9-1944H | Recombinant Human S100A9 Protein, His (Fc)-Avi-tagged | Human | HEK293 | His (Fc)-Avi |
Reference
- Mondet, J., Chevalier, S., & Mossuz, P. (2020). Pathogenic Roles of S100A8 and S100A9 Proteins in Acute Myeloid and Lymphoid Leukemia: Clinical and Therapeutic Impacts. Molecules, 26(5), 1323. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26051323

