BGLAP
-
Official Full Name
bone gamma-carboxyglutamate (gla) protein -
Overview
Osteocalcin, also known as bone gamma-carboxyglutamic acid-containing protein (BGLAP), is a noncollagenous protein found in bone and dentin. In humans, the osteocalcin is encoded by the BGLAP gene. -
Synonyms
BGLAP;bone gamma-carboxyglutamate (gla) protein;OC;BGP;osteocalcin;bone Gla protein;OTTHUMP00000016586;gamma-carboxyglutamic acid-containing protein;bone gamma-carboxyglutamate (gla) protein (osteocalcin)
Recombinant Proteins
- Human
- Rat
- Mouse
- Rhesus macaque
- Zebrafish
- Chicken
- Rabbit
- Pig
- Dog
- Bovine
- E.coli
- Mouse Plasma
- Wheat Germ
- HEK293
- Mammalian Cells
- Plasma
- In Vitro Cell Free System
- Bovine
- GST
- His
- Non
- DDK
- Myc
- Flag
- Avi
- Fc
- KSI
- SUMO
Background
What is BGLAP protein?
BGLAP (bone gamma-carboxyglutamate protein) gene is a protein coding gene which situated on the long arm of chromosome 1 at locus 1q22. This gene encodes a highly abundant bone protein secreted by osteoblasts that regulates bone remodeling and energy metabolism. The encoded protein contains a Gla (gamma carboxyglutamate) domain, which functions in binding to calcium and hydroxyapatite, the mineral component of bone. Serum osteocalcin levels may be negatively correlated with metabolic syndrome. Read-through transcription exists between this gene and the neighboring upstream gene, PMF1 (polyamine-modulated factor 1), but the encoded protein only shows sequence identity with the upstream gene product. BGLAP protein is consisted of 100 amino acids and its molecular mass is approximately 11.0 kDa.
What is the function of BGLAP protein?
BGLAP is secreted by osteoblasts and is involved in the regulation of bone remodeling, which is the process of bone resorption and formation. The protein contains a Gla (gamma carboxyglutamate) domain that is essential for binding to calcium and hydroxyapatite, the mineral component of bone. The uncarboxylated form of osteocalcin acts as a hormone secreted by osteoblasts. It is involved in regulating various cellular processes such as energy metabolism, male fertility, and brain development. BGLAP promotes pancreatic beta-cell proliferation, insulin secretion, and sensitivity, as well as energy expenditure. BGLAP hormone crosses the blood-brain barrier and acts as a ligand for GPR158 on neurons, playing a role in preventing neuronal apoptosis in the hippocampus and regulating neurotransmitter synthesis.
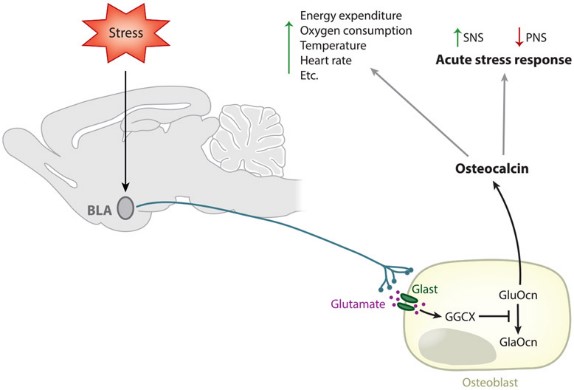
Fig1. Osteocalcin regulates the acute stress response. (Gerard Karsenty, 2023)
BGLAP Related Signaling Pathway
BGLAP may affect the balance between bone resorption and bone formation through the RANKL/OPG signaling pathway. This pathway involves interactions between osteoblasts, osteoclasts, and osteoblasts. BGLAP is also associated with the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway, which is critical for osteoblast proliferation and differentiation. BGLAP expression can be positively regulated by Wnt signal. The osteogenic pathway is also involved in the Hedgehog signaling pathway, and BGLAP is involved in this pathway to further promote bone formation and accelerate bone healing. In pancreatic cancer cells, the expression of BGLAP is regulated by tumor necrosis factor α (TNF-α), which can reduce the expression level of BGLAP, indicating that BGLAP may be a target of TNF-α, and suggesting that BGLAP may have a tumor-promoting role in pancreatic cancer.
BGLAP Related Diseases
BGLAP, also known as Bone Gla Protein (BGP) and Osteocalcin (OCN), is a protein closely associated with bone health that plays a role in a variety of physiological and pathological processes. BGLAP has been linked to conditions such as osteoporosis, fracture healing, diabetes (especially type 2 diabetes), rheumatoid arthritis, cirrhosis of the liver, prostate cancer, chronic hepatitis B, osteoarthritis, high blood pressure, and vitamin K deficiency. In addition, BGLAP may have tumor-promoting functions in certain types of cancer, such as pancreatic cancer.
Bioapplications of BGLAP
Because BGLAP is a negative regulator of bone formation, monitoring its levels can be helpful in evaluating the efficacy of osteoporosis treatment and disease progression. Recombinant BGLAP protein can be used to study its role in disease models, such as the effect of osteocalcin deficiency on bone mass, bone density, bone formation, or bone resorption by knocking out or replacing mouse models produced by the Bglap gene. To evaluate the biological activity of recombinant BGLAP protein, such as its promotion of insulin secretion and its potential effect on skeletal muscle insulin sensitivity. In drug development, recombinant BGLAP protein can be used to screen and evaluate the effects of potential drugs on bone formation and bone resorption, as well as in studies of their efficacy in the treatment of diseases such as osteoporosis.
Case Study
Case Study 1: Hany Kayed, 2007
Bone gamma-carboxyglutamate protein (BGLAP; osteocalcin) is a small, highly conserved molecule first identified in the mineralized matrix of bone. It has been implicated in the pathophysiology of various malignancies. In this study, the researchers analyzed the expression and role of BGLAP in the normal human pancreas, chronic pancreatitis (CP), and pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) using quantitative RT-PCR, immunohistochemistry, immunocytochemistry and enzyme immunoassays, as well as cell proliferation and invasion assays. Gene silencing was carried out using specific siRNA molecules. Compared to the normal pancreas, BGLAP mRNA and protein levels were not significantly different in CP and PDAC tissues. BGLAP was faintly present in the cytoplasm of normal acinar cells but was strongly expressed in the cytoplasm and nuclei of tubular complexes and PanIN lesions of CP and PDAC tissues. Furthermore, BGLAP expression was found in the cancer cells in PDAC tissues as well as in 4 cultured pancreatic cancer cell lines. TNFalpha reduced BGLAP mRNA and protein expression levels in pancreatic cancer cell lines. In addition, BGLAP silencing led to reduction of both cell growth and invasion in those cells.
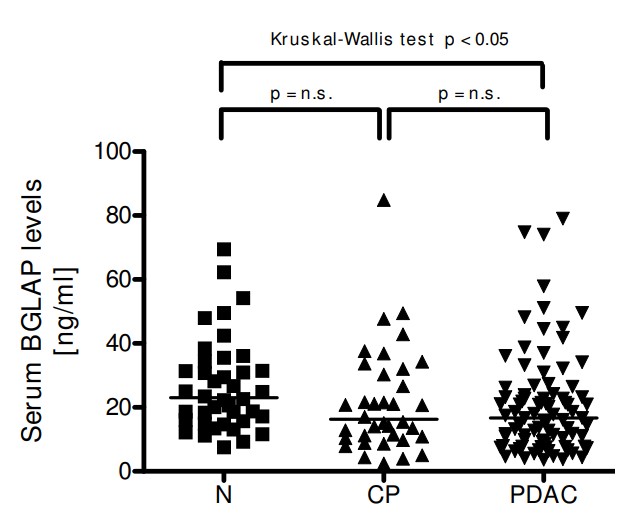
Fig1. Enzyme immunoassay of BGLAP levels in normal pancreatic, CP and PDAC tissue samples.
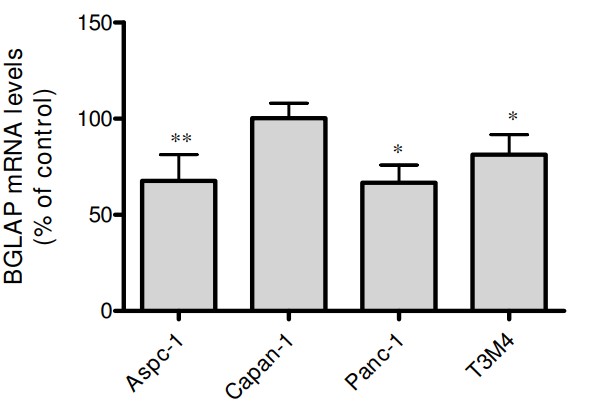
Fig2. Effects of TNF-α on BGLAP expression in pancreatic cancer cells.
Case Study 2: Fujian Zhao, 2022
Bone augmentation materials usually cannot provide enough new bone for dental implants due to the material degradation and mucosal pressure. The use of hydrogels with self-swelling properties may provide a higher bone augmentation, although swelling is generally considered to be a disadvantage in tissue engineering. Herein, a double-crosslinked gelatin-hyaluronic acid hydrogels (GH) with self-swelling properties were utilized. Meanwhile, niobium doped bioactive glasses (NbBG) was dispersed in the hydrogel network to prepare the GH-NbBG hydrogel. The composite hydrogel exhibited excellent biocompatibility and the addition of NbBG significantly improved the mechanical properties of the hydrogel. In vivo results found that GH-NbBG synergistically promoted angiogenesis and increased bone augmentation by self-swelling at the early stage of implantation. In addition, at the late stage after implantation, GH-NbBG significantly promoted new bone formation by activating RUNX2/Bglap signaling pathway.
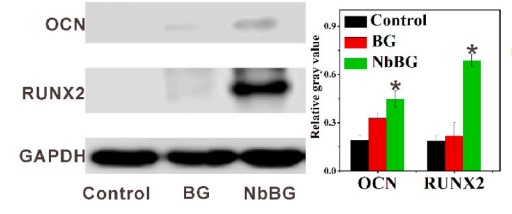
Fig3. Western bloting analysis of RUNX2 and OCN expression.
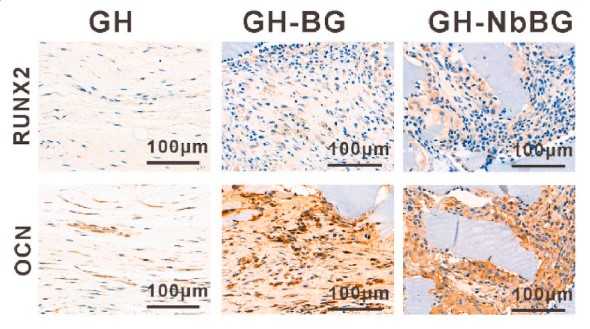
Fig4. Immunohistochemical staining of RUNX2 and OCN at the bone augmentation vertices.
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
.jpg)
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (BGLAP-204H)
.
.jpg)
Fig2. SDS-PAGE (BGLAP-205H)
Involved Pathway
BGLAP involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways BGLAP participated on our site, such as FGF signaling pathway,Glucocorticoid receptor regulatory network,Interleukin-11 Signaling Pathway, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with BGLAP were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| Notch-mediated HES/HEY network | MYOD1,CTBP1,GATA6,TLE1,YY1,HEY1,RCAN1,GATA1,ASCL1,MYB |
| Interleukin-11 Signaling Pathway | IL11 |
| FGF signaling pathway | PAK4,SP8B,FGF24,FGFRL1A,SOX32,JUNBA,FGFRL1B,SP8A,EGR2A,EGR2B |
| Regulation of retinoblastoma protein | SMARCB1,AATF,CKM,MYOD1,ATF7,BRD2,ELF1,CBX4,GSC |
| Glucocorticoid receptor regulatory network | KRT17,POU2F1,KRT14,SMARCC2,KRT5,CSN2,SMARCA4,NR1I3,SMARCD1,EGR1 |
| Validated transcriptional targets of AP1 family members Fra1 and Fra2 | USF2,MGP,CXorf15,IVL |
Protein Function
BGLAP has several biochemical functions, for example, calcium ion binding,hydroxyapatite binding,structural constituent of bone. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by BGLAP itself. We selected most functions BGLAP had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with BGLAP. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| calcium ion binding | PVALB1,PCDH2G5,S100A13,EFHA1,CIB2,PCDH1G31,SYT1A,GCH1,ANXA2,ANXA11 |
| hydroxyapatite binding | STATH,PTPLA,AMELX,BGLAP2,HTN1 |
| structural constituent of bone | BGLAP-RS1,MGP,BGLAP2 |
| structural molecule activity | TUBB,LMNL3,TUBB5,BVES,COPE,CLDN8,CLDN18,FLG2,MTAP7D2,CLDNA |
Interacting Protein
BGLAP has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with BGLAP here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of BGLAP.
Resources
Research Area
Related Services
Related Products
References



