DNM1
-
Official Full Name
dynamin 1 -
Overview
This gene encodes a member of the dynamin subfamily of GTP-binding proteins. The encoded protein possesses unique mechanochemical properties used to tubulate and sever membranes, and is involved in clathrin-mediated endocytosis and other vesicular trafficking processes. Actin and other cytoskeletal proteins act as binding partners for the encoded protein, which can also self-assemble leading to stimulation of GTPase activity. More than sixty highly conserved copies of the 3 region of this gene are found elsewhere in the genome, particularly on chromosomes Y and 15. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been described. -
Synonyms
DNM1;dynamin 1;DNM;dynamin-1
Recombinant Proteins
- Human
- Rat
- Mouse
- E.coli
- HEK293
- Mammalian Cells
- Yeast
- HeLa
- GST
- DDK
- Myc
- His
- T7
- Non
- Avi
- Fc
- SUMO
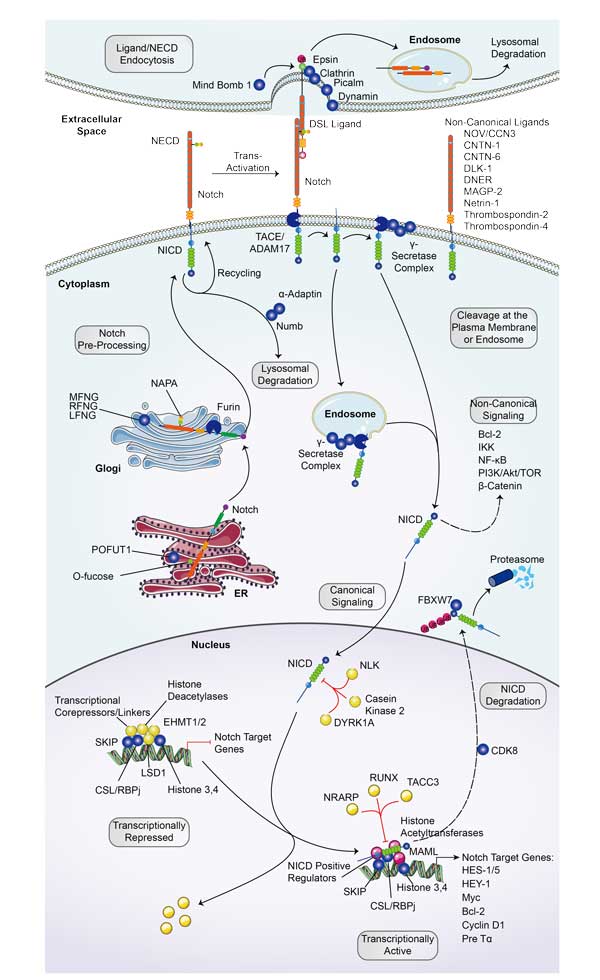
Background
 domain structure with locations of variants identified in patients.jpg)
Fig1. DNM1 protein (NP_004399) domain structure with locations of variants identified in patients. (Sarah von Spiczak, 2017)
What is DNM1 protein?
DNM1 (dynamin 1) gene is a protein coding gene which situated on the long arm of chromosome 9 at locus 9q34. This gene encodes a member of the dynamin subfamily of GTP-binding proteins. The encoded protein possesses unique mechanochemical properties used to tubulate and sever membranes, and is involved in clathrin-mediated endocytosis and other vesicular trafficking processes. Actin and other cytoskeletal proteins act as binding partners for the encoded protein, which can also self-assemble leading to stimulation of GTPase activity. The DNM1 protein is consisted of 864 amino acids and its molecular mass is approximately 97.4 kDa.
What is the function of DNM1 protein?
DNM1 is mainly involved in the remodeling process of the cell membrane, especially in endocytosis, where it helps to separate vesicles from the cell membrane by forming helical structures. In addition, DNM1 is also crucial in regulating the morphology and number of mitochondria, influencing their size and morphology by promoting their division, which in turn affects cell metabolism and energy production. DNM1 is also involved in the process of apoptosis, and changes in its activity can affect the release of apoptosis factors by mitochondria, thus participating in the regulation of cell survival and death. In nerve cells, the function of DNM1 is particularly important as it relates to the cell's response to high energy demands.
DNM1 Related Signaling Pathway
Mitochondrial dynamic signaling pathway: DNM1 is closely related to mitochondrial division, which influences the morphology, size and quantity of mitochondria by forming a helical structure around the outer membrane of mitochondria and promoting its division. Mitochondrial dynamics are essential for maintaining cellular metabolism and stress response.
Apoptosis signaling pathway: Changes in the activity of DNM1 can affect the release of apoptosis factors by mitochondria, and thus participate in the regulation of cell survival and death. The morphological changes and dysfunction of mitochondria are related to the activation of various apoptotic pathways.
Neurotransmitter receptor signaling pathway: DNM1 may be involved in endocytosis and recycling of neurotransmitter receptors, affecting neurotransmitter signal transmission, and is closely related to nervous system function.
Signaling pathway of miRNA regulation: Bioinformatics prediction and studies have shown that DNM1 may be the target gene of some mirnas (such as miR-140-3p), and miRNA is involved in regulating the expression of DNM1 by targeting the 3'UTR region, thus affecting related signaling pathways.
DNM1 Related Diseases
Variations in the DNM1 gene have been linked to developmental epileptic encephalopathy, a disorder characterized by refractory epilepsy and developmental delays. The protein encoded by the DNM1 gene plays a key role in the endocytosis and circulation of synaptic vesicles, and its abnormal function may lead to neurological diseases. Variations in the DNM1 gene may be linked to obsessive-compulsive disorder, a chronic anxiety disorder that has an important genetic basis. DNM1 is expressed at elevated levels in a variety of cancers, including acute myeloid leukemia and lung cancer. DNM1 may be involved in the occurrence and development of tumors through the influence of apoptosis, and has the potential to become a biomarker for cancer diagnosis, prognosis and treatment.
Bioapplications of DNM1
As a drug target, DNM1 inhibitors or activators may be potentially valuable for the treatment of related diseases. For example, small molecule inhibitors that target DNM1 may help treat certain types of epilepsy. Gene therapy strategies that target the DNM1 gene, such as CRISPR/Cas9 gene editing technology, may have potential applications for treating inherited diseases caused by mutations in the DNM1 gene. The change of the expression level of DNM1 may be used as a biomarker of some diseases for disease diagnosis, prognosis assessment and treatment response monitoring.
Case Study
Case Study 1: Katherine Bonnycastle, 2023
Dynamin-1 is a large GTPase with an obligatory role in synaptic vesicle endocytosis at mammalian nerve terminals. Heterozygous missense mutations in the dynamin-1 gene (DNM1) cause a novel form of epileptic encephalopathy, with pathogenic mutations clustering within regions required for its essential GTPase activity. The researchers reveal the most prevalent pathogenic DNM1 mutation, R237W, disrupts dynamin-1 enzyme activity and endocytosis when overexpressed in central neurons. To determine how this mutation impacted cell, circuit and behavioural function, they generated a mouse carrying the R237W mutation. Neurons from heterozygous mice display dysfunctional endocytosis, in addition to altered excitatory neurotransmission and seizure-like phenotypes. Importantly, these phenotypes are corrected at the cell, circuit and in vivo level by the drug, BMS-204352, which accelerates endocytosis.
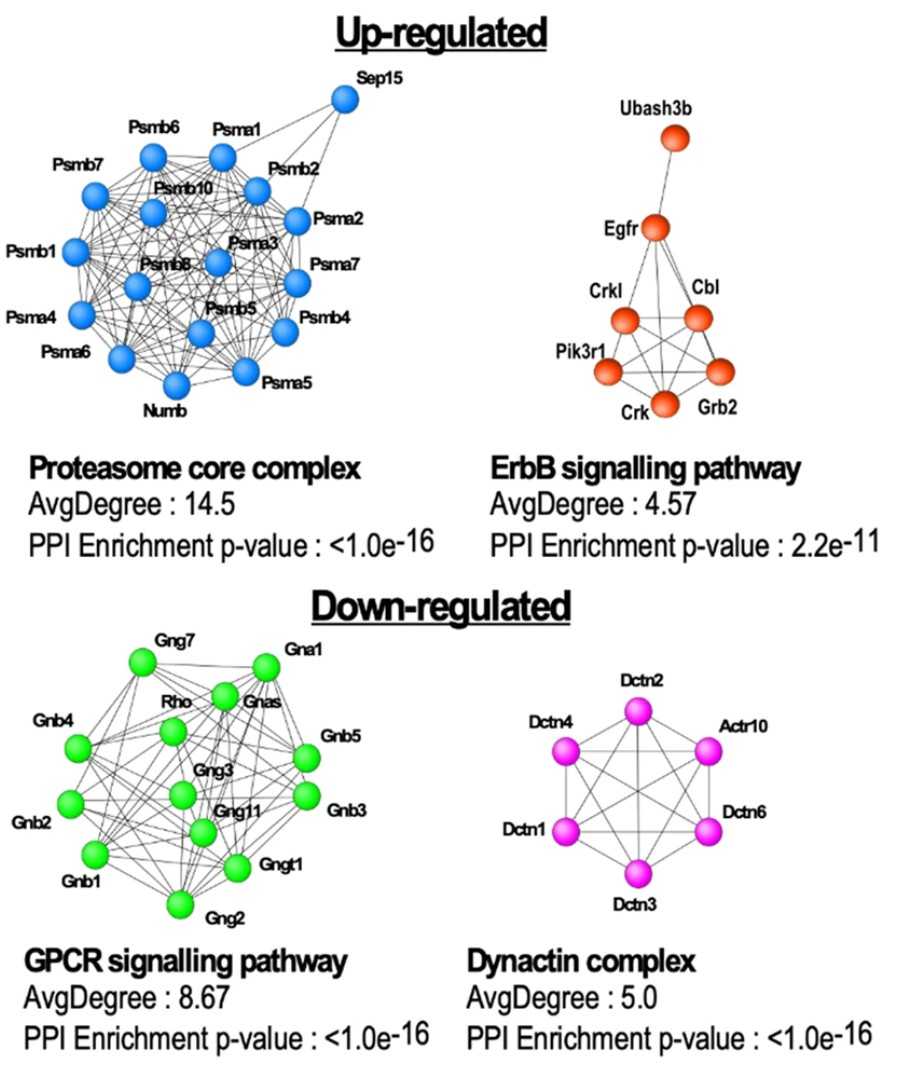
Fig1. STRING network analysis of up and down regulated proteins in Dnm1+/R237W synaptosomes.
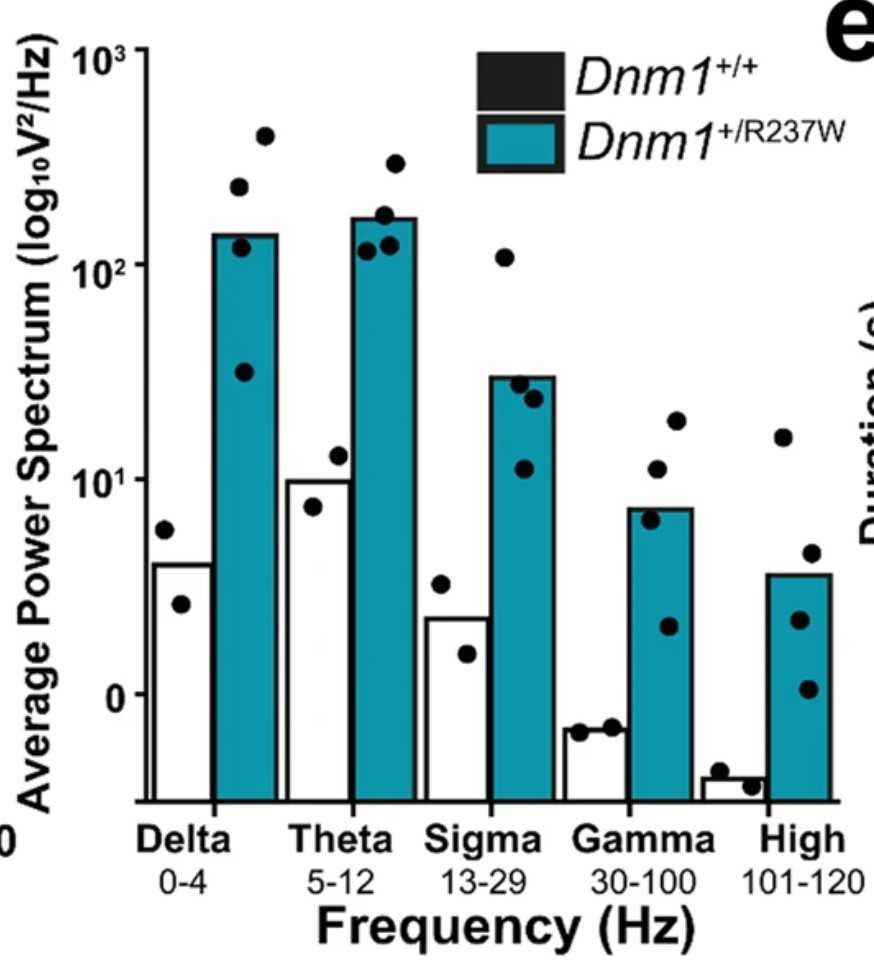
Fig2. Plot of average power in commonly used frequency bands during jumps.
Case Study 2: Abhishek Sadhu, 2023
Long-term memory formation requires anterograde transport of proteins from the soma of a neuron to its distal synaptic terminals. This allows new synaptic connections to be grown and existing ones remodeled. However, the researchers do not yet know which proteins are transported to synapses in response to activity and temporal regulation. Here, using quantitative mass spectrometry, they have profiled anterograde protein cargos of a learning-regulated molecular motor protein kinesin [Aplysia kinesin heavy chain 1 (ApKHC1)] following short-term sensitization (STS) and long-term sensitization (LTS) in Aplysia californica The results reveal enrichment of specific proteins associated with ApKHC1 following both STS and LTS, as well as temporal changes within 1 and 3 h of LTS training. A significant number of proteins enriched in the ApKHC1 complex participate in synaptic function, and, while some are ubiquitously enriched across training conditions, a few are enriched in response to specific training. For instance, factors aiding new synapse formation, such as synaptotagmin-1, dynamin-1, and calmodulin, are differentially enriched in anterograde complexes 1 h after LTS but are depleted 3 h after LTS.
 training, are validated by WB.jpg)
Fig3. Synaptotagmin-1, dynamin-1, and calmodulin, detected to be enriched in kinesin complex after LTS (1 h) training, are validated by WB.
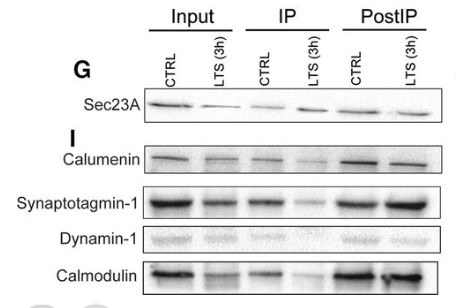
Fig4. Sec23A enrichment after 3 h of LTS was confirmed by WB.
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
.jpg)
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (DNM1-362H)
.
.jpg)
Fig2. SDS-PAGE (DNM1-458H)
Involved Pathway
DNM1 involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways DNM1 participated on our site, such as Adaptive Immune System,Axon guidance,Bacterial invasion of epithelial cells, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with DNM1 were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| Axon guidance | TRPC7,ROBO3,JAK3,PAK6,GNAI2,EPHA4A,PAK3,PPP3R1,RASGRP1,COL4A4 |
| Bacterial invasion of epithelial cells | CBL,SEPT9,PXN,CLTB,PIK3R2,ARPC5,RHOA,PTK2,CD2AP,CTTN |
| Adaptive Immune System | DCTN6,CLEC2B,CTSE,AGO2,KIF3C,FGF20A,DYNLL2,CD96,AHCYL1,SIGLEC11 |
| CXCR3-mediated signaling events | CXCL13,MAPKAP1 |
| EGFR1 Signaling Pathway | CEBPA,ZFP259,TNK2,TNIP1,RBB4L,ZNF259,REPS2,EPS8,ARF4,GRB14 |
| Developmental Biology | INSM1B,HELZ2,AP2A1,MED25,EFNA2A,COL4A4,POU5F3,EGR2,LGI2A,MYOG |
| EPH-Ephrin signaling | EFNA4,EFNA1,ACTR2,EFNA2A,EFNB2,EPHB3A,SHB,ACTR3,MYL12A,EPHB4B |
| CXCR4-mediated signaling events | BLK,CFL1,ADRBK1,GNB2L1,CSK,GNA13,ARR3,JAK2,MAPKAP1,PAG1 |
Protein Function
DNM1 has several biochemical functions, for example, GTP binding,GTPase activity,identical protein binding. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by DNM1 itself. We selected most functions DNM1 had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with DNM1. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| protein kinase binding | PTPN6,CDKN2B,PPP1CB,CAV1,RB1CC1,BCL2L1,PXN,CHRNA7,SPRED1,PTPN1 |
| identical protein binding | TPRG1L,VCP,SUN2,SLIT2,DCP1A,IFI203,DAAM1,CRYAB,EWSR1,DAPK2 |
| GTPase activity | RAB23,RAB4A,RAB12,RAB42,GTPBP4,GUF1,RRAGA,GNA11A,TUBA1L,RAB35B |
| poly(A) RNA binding | SUMO1,MAGOHB,HSP90AB1,FBL,CSTF3,WBSCR22,PUF60,HNRNPH3,EXOSC6,LARP4 |
| protein dimerization activity | ATM,HES7,MESP1,DAO,EBF3A,FBXW11B,MSC,SOHLH1,NEUROG3,MSGN1 |
| protein binding | HTR3C,TACR1,ECD,SH2D2A,NACA,ITGA4,TNFRSF1B,SALL2,LGALS13,PTPN12 |
| GTP binding | RHOC,MB21D1,SEPT8B,GTPBP1L,MXG,HHAT,RIT1,RAP2B,RAB17,RHOAB |
Interacting Protein
DNM1 has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with DNM1 here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of DNM1.
GRB2;SNX9;AMPH
DNM1 Related Signal Pathway
Resources
Research Area
Related Services
Related Products
References
- Devadas, D; Koithan, T; et al. Herpes Simplex Virus Internalization into Epithelial Cells Requires Na+/H+ Exchangers and p21-Activated Kinases but neither Clathrin-nor Caveolin-Mediated Endocytosis. JOURNAL OF VIROLOGY 88:13378-13395(2014).
- Chowdhury, SM; Manepalli, P; et al. Graphene nanoribbons elicit cell specific uptake and delivery via activation of epidermal growth factor receptor enhanced by human papillomavirus E5 protein. ACTA BIOMATERIALIA 10:4494-4504(2014).