MMP1
-
Official Full Name
matrix metallopeptidase 1 (interstitial collagenase) -
Overview
Proteins of the matrix metalloproteinase (MMP) family are involved in the breakdown of extracellular matrix in normal physiological processes, such as embryonic development, reproduction, and tissue remodeling, as well as in disease processes, such as arthritis and metastasis. Most MMPs are secreted as inactive proproteins which are activated when cleaved by extracellular proteinases. This gene encodes a secreted enzyme which breaks down the interstitial collagens, types I, II, and III. The gene is part of a cluster of MMP genes which localize to chromosome 11q22.3. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants.[provided by RefSeq, Mar 2009] -
Synonyms
MMP1;matrix metallopeptidase 1 (interstitial collagenase);CLG;CLGN;interstitial collagenase;fibroblast collagenase;matrix metalloprotease 1;matrix metalloproteinase 1
Recombinant Proteins
- Human
- Cattle
- Rat
- Rabbit
- Pig
- Bovine
- Sheep
- E.coli
- HEK293
- Insect Cells
- Mammalian Cells
- Human Cells
- CHO
- Human Fibroblasts
- Wheat Germ
- In Vitro Cell Free System
- His
- Non
- DDK
- Myc
- T7
- Flag
- MBP
- Avi
- Fc
- GST
Background
What is mmp1 protein?
The MMP1 protein, also known as matrix metalloproteinase 1, is an enzyme that belongs to the matrix metalloproteinase family. It is produced by various cells in the body, including fibroblasts, macrophages, and endothelial cells. MMP1 is involved in the breakdown and remodeling of the extracellular matrix, which is the structural framework of tissues.
The main function of MMP1 is to degrade the collagens present in the extracellular matrix, specifically type I, II, and III collagens. This allows for tissue remodeling during normal physiological processes such as development, wound healing, and tissue repair. MMP1 plays a critical role in maintaining tissue homeostasis by controlling cell migration, tissue morphogenesis, and angiogenesis.
However, overexpression and dysregulation of MMP1 have been associated with various pathological conditions. Excessive MMP1 activity can lead to abnormal tissue remodeling, tissue degradation, and disease progression. It has been implicated in several diseases, including cancer, arthritis, cardiovascular diseases, and chronic lung diseases.
What is the function of mmp1 protein?
MMP1 is secreted as an inactive zymogen and requires activation to become enzymatically active. Once activated, MMP1 can initiate the breakdown of collagen fibers, thereby facilitating tissue remodeling and turnover. It is involved in normal physiological processes such as development, wound healing, and tissue repair. However, excessive MMP1 activity has been associated with pathological conditions such as tissue degradation in arthritis, cancer invasion and metastasis, and fibrosis.
In addition to its role in collagen degradation, MMP1 can also cleave other ECM components, growth factors, cytokines, and cell adhesion molecules, thereby influencing various cellular processes such as cell migration, angiogenesis, and immune response.
Mmp1 related signaling pathway
The signaling pathway related to Mmp1 involves the activation of certain transcription factors such as AP-1 (activator protein 1) and NF-κB (nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells). These transcription factors regulate the expression of Mmp1 gene and promote the production of Mmp1 protein.
Mmp1 Related Diseases
- Cancer therapy: MMP1 is a promising target for developing anticancer drugs and blocking tumor growth and metastasis.
- Arthritis treatment: Inhibiting MMP1 activity can slow cartilage and bone degradation in arthritis.
- Neurodegenerative diseases: MMP1 inhibition could reduce amyloid plaque formation and neuronal damage in Alzheimer's.
- Neurodegenerative diseases: MMP1 inhibition could reduce amyloid plaque formation and neuronal damage in Alzheimer's.
Biomedical Application of mmp1 Protein
In terms of biomedical applications, Mmp1 protein and its inhibitors have been explored as potential therapeutic targets for various diseases. In conditions characterized by excessive tissue remodeling, such as fibrosis, the inhibition of Mmp1 activity can prevent the degradation of extracellular matrix and tissue damage. On the other hand, promoting Mmp1 activity can be beneficial in wound healing and tissue regeneration processes.
Furthermore, Mmp1 has been studied as a potential biomarker for certain diseases, particularly in cancer. Elevated levels of Mmp1 have been associated with tumor progression, invasion, and metastasis, making it a potential diagnostic and prognostic marker for cancer.
Case Study
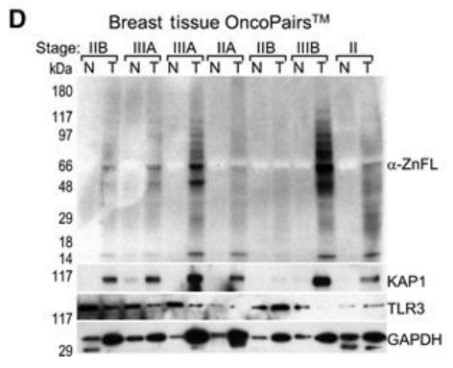
(Joseph B. Addison, 2015)
Fig2. KAP1 and KRAB-ZNFs are overexpressed in breast tumors. Western blot analysis of KAP1 and KRAB-ZNFs in biopsy samples of matched normal(N)–tumor(T) pairs. TLR3 and GAPDH are shown for comparison.
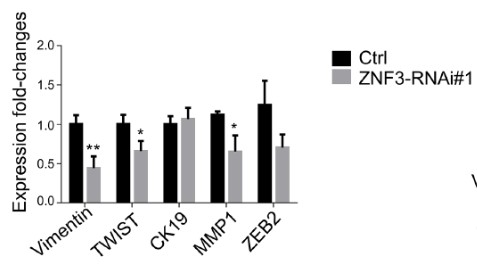
(Le Du, 2022)
Fig3. ZNF3 regulates the expressions of EMT-related markers. The mRNA expression levels of EMT-related markers ( Vimentin, TWIST, CK19, MMP1, and ZEB2) were decreased in ZNF3-silenced SW480 cells.
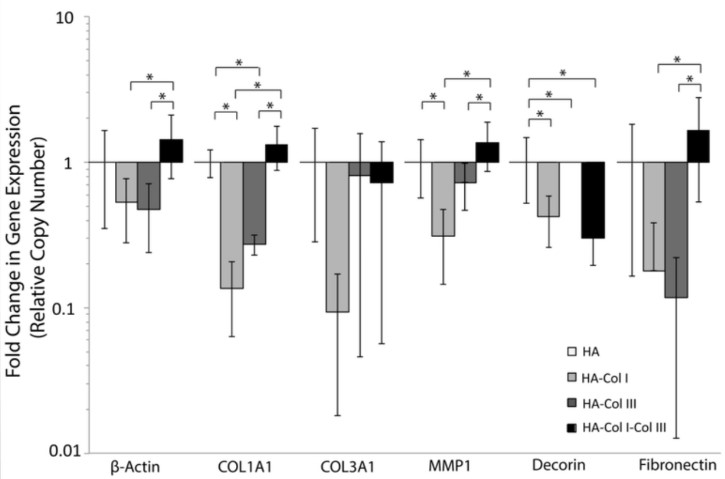
(Le Du, 2022)
Fig4. Gene Expression of Fibroblasts Encapsulated in Different Hydrogel Blends. Fold changes in fibroblast ECM related genes when normalized to HA alone gels show that cells respond differently to their microenvironments. One way ANOVA with Tukey's post-hoc test was used to determine differences in gene expression between cells encapsulated in different hydrogel blends.
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
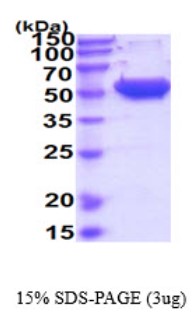
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (MMP1-26H)
Involved Pathway
MMP1 involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways MMP1 participated on our site, such as PPAR signaling pathway,Pathways in cancer,Bladder cancer, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with MMP1 were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| Bladder cancer | SRC,RB1,RPS6KA5,BRAF,TP53,MAP2K1,MAPK1,THBS1,HBEGF,E2F2 |
| PPAR signaling pathway | RXRGA,SCD,PDPK1B,CYP27A1,ACSBG1,PCK2,SCDB,PPARA,AQP7,PPARAB |
| Pathways in cancer | DAPK3,AGTR1B,HGF,ITGAV,PTEN,FGF20,GNG12,MSH2,MTOR,PGF |
| Rheumatoid arthritis | ATP6V0A2,IL15,ICAM1,ATP6V0E1,TGFB2,IL-8,ATP6V1E1,ATP6V1G1,ATP6V0A4,HLA-DOB |
Protein Function
MMP1 has several biochemical functions, for example, calcium ion binding,endopeptidase activity,metalloendopeptidase activity. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by MMP1 itself. We selected most functions MMP1 had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with MMP1. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| zinc ion binding | NR2C2,DUSP12,RING1,RABGGTA,FBXO11A,RP9,RFPL4B,ZNF205,ZMAT2,KLF4 |
| metalloendopeptidase activity | Adamts19,GM12824,MMP28,SPG7,ADAM8,UQCRC2,ADAMTS15,ADAM7,MMP14B,ADAMTS10 |
| calcium ion binding | SCUBE1,AIF1L,PRF1,CALM,EFEMP2,LTBP2,SCIN,TMPRSS6,C1R,EHD2B |
| endopeptidase activity | TPP1,NAPSA,SENP3B,PSMB11,NCSTN,PSMB6,PSEN2,KLK1B4,SENP5,PSMA3 |
Interacting Protein
MMP1 has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with MMP1 here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of MMP1.
F2R;SOX8
Resources
Gene Families
Research Area
Related Services
Related Products
References
- Addison, JB; Koontz, C; et al. KAP1 Promotes Proliferation and Metastatic Progression of Breast Cancer Cells. CANCER RESEARCH 75:344-355(2015).
- Kumar, D; Moore, RM; et al. Decidual GM-CSF is a critical common intermediate necessary for thrombin and TNF induced in-vitro fetal membrane weakening. PLACENTA 35:1049-1056(2014).
Reviews
Regarding the MMP1 enzyme. I tested the activity in our assay last week and everything works fine.


