MRC1
-
Official Full Name
mannose receptor, C type 1 -
Overview
The recognition of complex carbohydrate structures on glycoproteins is an important part of several biological processes, including cell-cell recognition, serum glycoprotein turnover, and neutralization of pathogens. The protein encoded by this gene is a type I membrane receptor that mediates the endocytosis of glycoproteins by macrophages. The protein has been shown to bind high-mannose structures on the surface of potentially pathogenic viruses, bacteria, and fungi so that they can be neutralized by phagocytic engulfment.[provided by RefSeq, Apr 2011] -
Synonyms
MRC1;mannose receptor, C type 1;MMR;CD206;MRC1L1;CLEC13D;CLEC13DL;bA541I19.1;macrophage mannose receptor 1;mannose receptor, C type 1-like 1;C-type lectin domain family 13 member D;macrophage mannose receptor 1-like protein 1
Recombinant Proteins
- Mouse
- Human
- Rat
- Mammalian Cells
- E.coli
- HEK293
- Yeast
- Wheat Germ
- Non
- His
- T7
- Avi
- Fc
- rFc
- GST
- SUMO
Background
What is MRC1 protein?
MRC1 gene (mannose receptor C-type 1) is a protein coding gene which situated on the short arm of chromosome 10 at locus 10p12. The recognition of complex carbohydrate structures on glycoproteins is an important part of several biological processes, including cell-cell recognition, serum glycoprotein turnover, and neutralization of pathogens. The protein encoded by this gene is a type I membrane receptor that mediates the endocytosis of glycoproteins by macrophages. The protein has been shown to bind high-mannose structures on the surface of potentially pathogenic viruses, bacteria, and fungi so that they can be neutralized by phagocytic engulfment. The MRC1 protein is consisted of 1456 amino acids and MRC1 molecular weight is approximately 166.0 kDa.
What is the function of MRC1 protein?
MRC1 protein is a type I membrane receptor, which is mainly expressed on the surface of macrophages. It plays an important role in recognizing and binding complex carbohydrate structures on the surface of a variety of pathogens, including intercellular recognition, transformation of serum glycoproteins, and neutralization of pathogens. The MRC1 protein, which mediates the endocytosis of glycoproteins by macrophages, has been shown to bind high-mannose structures on the surface of potentially pathogenic viruses, bacteria and fungi, enabling them to be neutralized by phagocytosis.
The MRC1 protein also functions as a phagocytic receptor for a variety of pathogens, such as its ability to act as a receptor for dengue virus envelope protein E and to interact with hepatitis B virus envelope protein. In addition, the MRC1 protein is involved in the regulation of the initiation of DNA replication in the cell, in particular through the interaction with the Hsk1 kinase to regulate the activation of the replication initiation point.
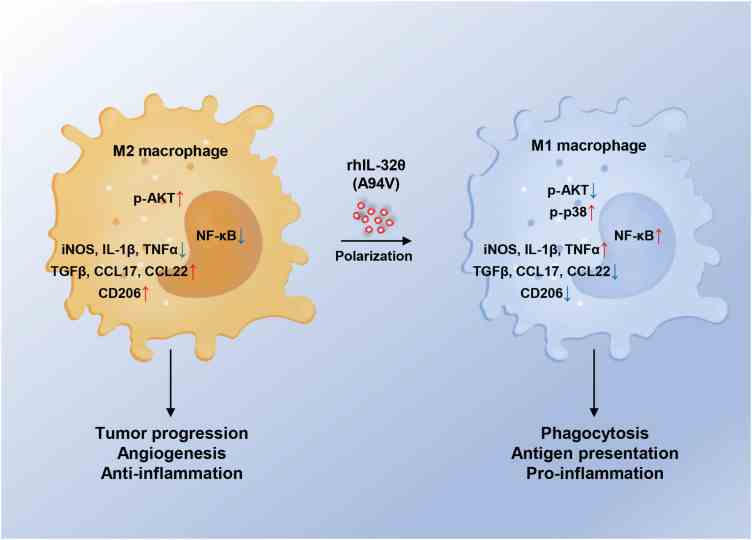
Fig1. Schematic diagram of the effect of rhIL-32θ on the macrophage polarization. (Hyo-Min Park, 2024)
MRC1 Related Signaling Pathway
The soluble form of MRC1 can alter innate and adaptive immune responses, affecting cell-cell interactions and signaling. As a pattern recognition receptor, MRC1 can recognize glycoproteins and glycolipids on the surface of pathogens, and play a role in recognizing antigens and antigen presentation. It is able to bind the high mannose structure and promote the phagocytosis of macrophages against viruses, bacteria and fungi, thus playing an important role in the innate immune response. MRC1 is involved in the clearance of sulfated glycoprotein hormones and glycoproteins in the systemic circulation. Mrc1 also plays a role in the response to DNA replication stress, working in concert with Rad53 kinase to respond to replication stress and to coordinate the replication of the leading and subsequent chains by regulating the MRC1-TOF1 complex to prevent genomic instability caused by exposure to single-stranded DNA.
MRC1 Related Diseases
MRC1 plays a key role in identifying and removing pathogens, so deficiencies in its function can lead to increased susceptibility to certain bacterial, viral, or parasitic infections. MRC1 is involved in the regulation of the immune response, and its abnormality may affect autotolerance and lead to autoimmune diseases, such as rheumatoid arthritis, systemic lupus erythematosus, etc. MRC1 is expressed on some tumor cells and may affect immune escape and metastasis of tumor cells. The abnormal function of MRC1 may be related to the occurrence and development of tumor. It is also involved in other diseases such as neurological diseases, cardiovascular diseases, metabolic diseases and many other types of diseases.
Bioapplications of MRC1
The expression level or functional status of MRC1 may be associated with certain diseases and can therefore be used as a biomarker for early diagnosis or monitoring of diseases. By harnessing MRC1's ability to recognize specific antigens, new vaccines can be designed to enhance the immune system's recognition and response to pathogens and improve vaccine protection. MRC1's role in modulating the immune response makes it a potential target for immunotherapy. By regulating the expression or function of MRC1, it may help treat certain autoimmune diseases or enhance the effectiveness of tumor immunotherapy. The ligand-binding properties of MRC1 can be used to design targeted drug delivery systems that increase drug concentration in specific tissues or cells and reduce side effects.
Case Study
Case Study 1: Abul K Azad, 2015
γ-Tilmanocept ((99m)Tc-labeled-tilmanocept or [(99m)Tc]-tilmanocept) is the first mannose-containing, receptor-directed, radiolabeled tracer for the highly sensitive imaging of sentinel lymph nodes in solid tumor staging. To elucidate the mannose-binding receptor that retains tilmanocept in this microenvironment, human macrophages were used that have high expression of the C-type lectin mannose receptor (MR; CD206). Cy3-labeled tilmanocept exhibited high specificity binding to macrophages that was nearly abolished in competitive inhibition experiments. Furthermore, Cy3-tilmanocept binding was markedly reduced on macrophages deficient in the MR by small interfering RNA treatment and was increased on MR-transfected HEK 293 cells. Finally, confocal microscopy revealed colocalization of Cy3-tilmanocept with the macrophage membrane MR and binding of labeled tilmanocept to MR(+) cells (macrophages and/or dendritic cells) in human sentinel lymph node tissues.
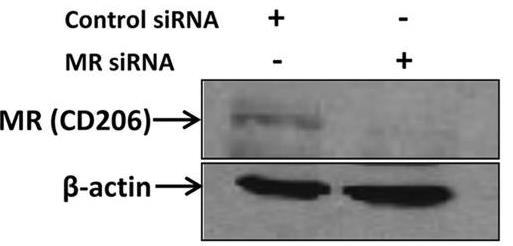
Fig1. Western blot showing siRNA-mediated knockdown of the MR protein.
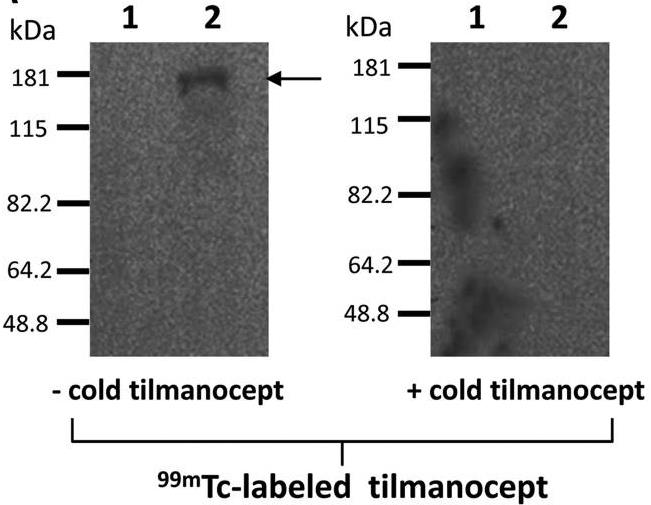

Fig2. Binding of tilmanocept to the MR protein by lectin blot.
Case Study 2: Fangyu Zhu, 2015
In the present study, researchers aimed to ascertain whether there is a correlation between CD206 expression in tumor associated-macrophages (TAMs) and the prognosis of primary hepatocellular carcinomas (HCC) and investigated the effect of GdCl3 on HCC. The expression of CD206 in HCC tumor tissues and peri-carcinoma tissues was measured using an array for liver tissues. The effects of GdCl3 on CD206 expression were examined in stimulated RAW264.7 cells. Target gene expression was evaluated by RT-PCR, western blotting and immunohistochemistry. Finally, they established a mouse model for HCC using N-nitrosodiethylamine (DEN) to determine the effect of GdCl3 on HCC. Liver tissue array analysis revealed that CD206 was highly expressed in the HCC tissues compared to the level in peri-carcinoma tissue. They found that GdCl3 suppressed the expression of CD206 in the M2 macrophage phenotype of stimulated RAW264.7 cells with an IC10 value of 0.07 μg/μl. In addition, GdCl3 also induced cell apoptosis in the RAW264.7 cells. Addition of GdCl3 into the culture medium of RAW264.7 cells markedly reduced the invasive ability of Hepa1-6 cells compared to the control cells.
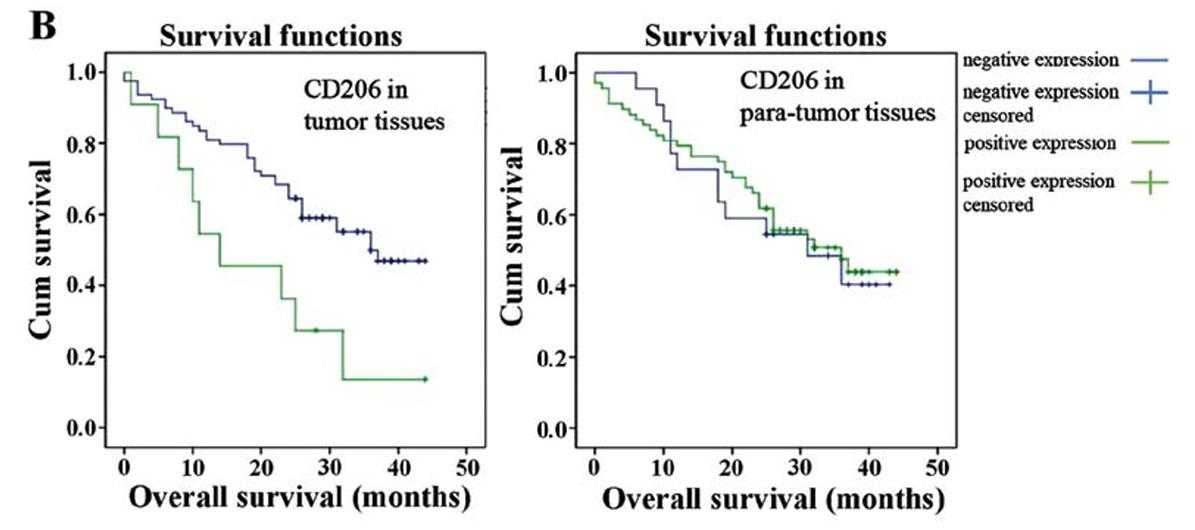
Fig3. The association between CD206 expression and overall survival time.
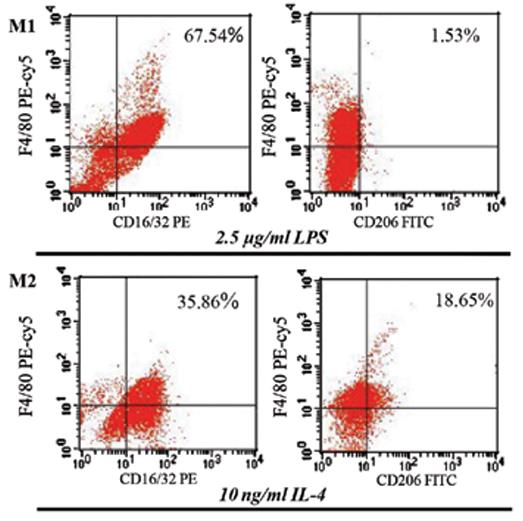
Fig4. Expression of CD16/32 and CD206 was examined by flow cytometric analysis 48 h after treatment.
Quality Guarantee
.
.jpg)
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (MRC1-5534H)
.
.jpg)
Fig2. SDS-PAGE (MRC1-1462H)
Involved Pathway
MRC1 involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways MRC1 participated on our site, such as Phagosome,Tuberculosis, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with MRC1 were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| Phagosome | MSR1,TFRC,HLA-DRB1,FCAR,HLA-E,RAB7,ATP6AP1B,ATP6V1E1B,OLR1,MRC2 |
| Tuberculosis | CAP18,CALM2,TLR9,TGFB3,HLA-DPA1,PPP3CA,NOS2,CORO1A,TLR4,MAPK1 |
Protein Function
MRC1 has several biochemical functions, for example, mannose binding,protein binding,receptor activity. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by MRC1 itself. We selected most functions MRC1 had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with MRC1. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| transmembrane signaling receptor activity | TLR10,GP1BB,LGR5,FZD7B,KIR2DL4,OR4C12,OR103-4,OR6K3,CLEC1B,ERBB2 |
| mannose binding | CD209A,MBL2,MBL1,CLN5,COLEC10,LMAN1,DPM1,Acr,MAN2B1,LMAN2 |
| virus receptor activity | SLC52A2,ITGB7,SERPINB3,NPC1,XPR1,PVR,ITGAV,ITGA5,CLEC5A,PVRL4 |
| receptor activity | GFRA1A,CADM1,VMN1R50,TNPO3,CD160,TLR1,CD93,MCC,TNFRSF13B,MED4 |
| protein binding | MC4R,NUDT16L1,RPS14,KLK15,MNDA,MAP3K7,KLHL38,LSM4,GAB1,CCNL1 |
Interacting Protein
MRC1 has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with MRC1 here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of MRC1.
rpoB;flhA
Resources
Research Area
Related Services
Related Products
References
- Cheng, L; Xing, H; et al. Lipocalin-2 Promotes M1 Macrophages Polarization in a Mouse Cardiac Ischaemia-Reperfusion Injury Model. SCANDINAVIAN JOURNAL OF IMMUNOLOGY 81:31-38(2015).
- Staines, K; Hunt, LG; et al. Evolution of an Expanded Mannose Receptor Gene Family. PLOS ONE 9:-(2014).



