SLC2A4
-
Official Full Name
solute carrier family 2 (facilitated glucose transporter), member 4 -
Overview
This gene is a member of the solute carrier family 2 (facilitated glucose transporter) family and encodes a protein that functions as an insulin-regulated facilitative glucose transporter. In the absence of insulin, this integral membrane protein is sequestered within the cells of muscle and adipose tissue. Within minutes of insulin stimulation, the protein moves to the cell surface and begins to transport glucose across the cell membrane. Mutations in this gene have been associated with noninsulin-dependent diabetes mellitus (NIDDM). -
Synonyms
SLC2A4;solute carrier family 2 (facilitated glucose transporter), member 4;GLUT4;solute carrier family 2, facilitated glucose transporter member 4;GLUT-4;OTTHUMP00000128376;insulin-responsive glucose transporter type 4;glucose transporter type 4, insulin-responsive
Recombinant Proteins
- Human
- Mouse
- Rat
- Dog
- Sus scrofa (Pig)
- E.coli
- HEK293
- Wheat Germ
- Mammalian Cells
- In Vitro Cell Free System
- GST
- Non
- His
- Avi
- Fc
- DDK
- Myc
- SUMO
- Flag
Background
What is SLC2A4 Protein?
SLC2A4 gene (solute carrier family 2 member 4) is a protein coding gene which situated on the short arm of chromosome 17 at locus 17p13. This gene is a member of the solute carrier family 2 (facilitated glucose transporter) family and encodes a protein that functions as an insulin-regulated facilitative glucose transporter. In the absence of insulin, this integral membrane protein is sequestered within the cells of muscle and adipose tissue. Within minutes of insulin stimulation, the protein moves to the cell surface and begins to transport glucose across the cell membrane. The SLC2A4 protein is consisted of 509 amino acids and SLC2A4 molecular weight is approximately 54.8 kDa.
What is the Function of SLC2A4 Protein?
SLC2A4 protein, also known as glucose transporter 4 (GLUT4), is an important transmembrane transporter whose main function is to regulate the absorption of glucose by cells. GLUT4 is expressed in a variety of cell types, especially in fat and muscle cells, where it is stimulated by insulin to move from the cell's internal vesicles to the membrane, thereby increasing the cell's uptake of glucose, a key step in regulating blood sugar levels. The function of SLC2A4 is essential for maintaining energy balance and blood glucose homeostasis. In diseases such as insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes, the transport function of GLUT4 is often impaired, resulting in abnormal blood sugar control.
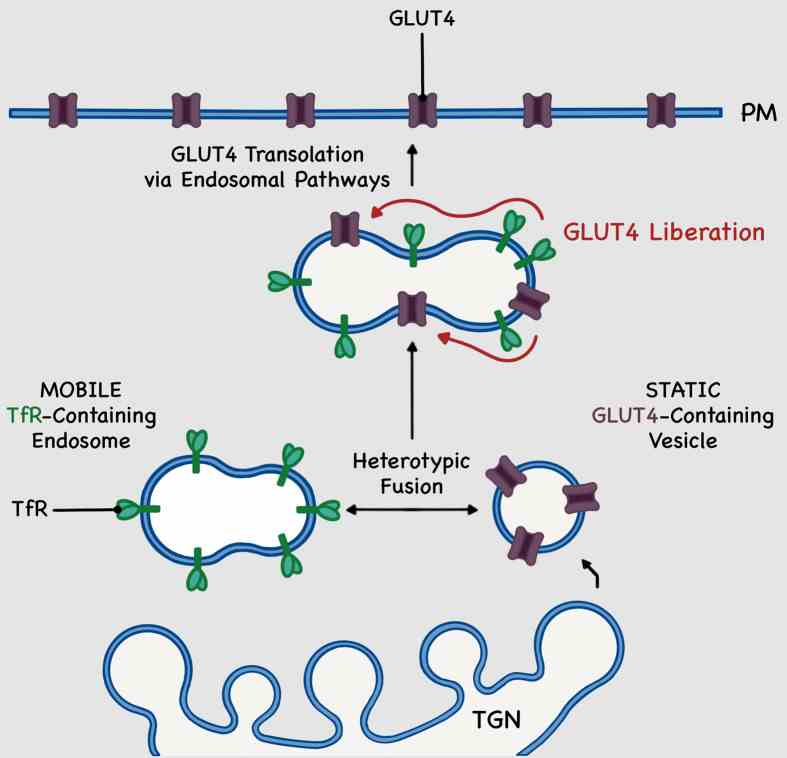
Fig1. Endosomal-dependant model of insulin-stimulated GLUT4 trafficking to the plasma membrane. (Angéline Geiser, 2023)
SLC2A4 Related Signaling Pathway
Insulin activates the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway by binding to its receptor, which in turn promotes the transfer of GLUT4 from intracellular vesicles to the cell membrane and increases glucose uptake. AMPK activation can increase GLUT4 expression and activity in muscle cells, promote glucose uptake and utilization, and thus play a role in energy balance and metabolic regulation. An increase in calcium ions (Ca2+) can activate GLUT4 transport activity, which is particularly important in glucose uptake after muscle contraction. GLUT4 transport and localization are regulated by cytoskeleton, and dynamic changes in microtubules and microfilaments can affect GLUT4 cell membrane localization.
SLC2A4 Related Diseases
Glucose transporter 4 (GLUT4) encoded by the SLC2A4 gene plays a key role in regulating the absorption of glucose by cells, and its abnormal function has been associated with a variety of diseases. Type 2 diabetes is one of the diseases closely related to SLC2A4, because the expression or function of GLUT4 is impaired, resulting in blocked insulin signaling, which in turn causes elevated blood sugar levels. In addition, insulin resistance is also a result of abnormal functioning of SLC2A4, which may further increase the risk of cardiovascular disease. Obesity is also associated with SLC2A4 because decreased GLUT4 activity in muscle and adipose tissue may lead to an imbalance in energy metabolism. In muscle atrophy and certain neurodegenerative diseases, SLC2A4 expression may also be affected, affecting the energy supply and function of cells.
Bioapplications of SLC2A4
Off-the-shelf applications related to SLC2A4 are mainly in the field of diagnosis and treatment of diabetes and other metabolic diseases. For example, measuring the expression level of SLC2A4 or the function of the GLUT4 protein it encodes can help diagnose insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes. In addition, the development of drugs that target SLC2A4 or its regulatory pathways, such as drugs that increase the efficiency of GLUT4 transport, may help improve insulin sensitivity and lower blood sugar levels, although these treatments may still be in the research and development phase at present. In addition, understanding the expression and function of SLC2A4 in different tissues could also help develop intervention strategies that target specific metabolic pathways.
Case Study
Case Study 1: Stéphane M Camus, 2020
Glucose transporter 4 (GLUT4) is sequestered inside muscle and fat and then released by vesicle traffic to the cell surface in response to postprandial insulin for blood glucose clearance. Here, researchers map the biogenesis of this GLUT4 traffic pathway in humans, which involves clathrin isoform CHC22. GLUT4 transits through the early secretory pathway more slowly than the constitutively secreted GLUT1 transporter and localize CHC22 to the ER-to-Golgi intermediate compartment (ERGIC). CHC22 functions in transport from the ERGIC, as demonstrated by an essential role in forming the replication vacuole of Legionella pneumophila bacteria, which requires ERGIC-derived membrane. CHC22 complexes with ERGIC tether p115, GLUT4, and sortilin, and downregulation of either p115 or CHC22, but not GM130 or sortilin, abrogates insulin-responsive GLUT4 release.
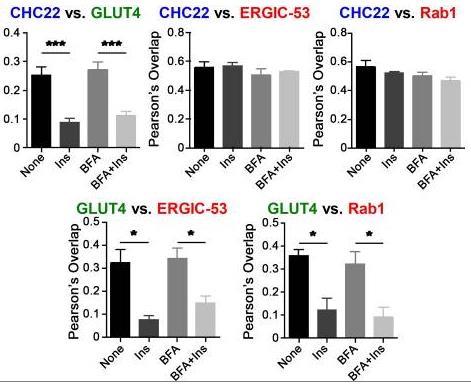
Fig1. Quantification of Pearson's overlap values between CHC22, GLUT4, ERGIC-53, and Rab1.
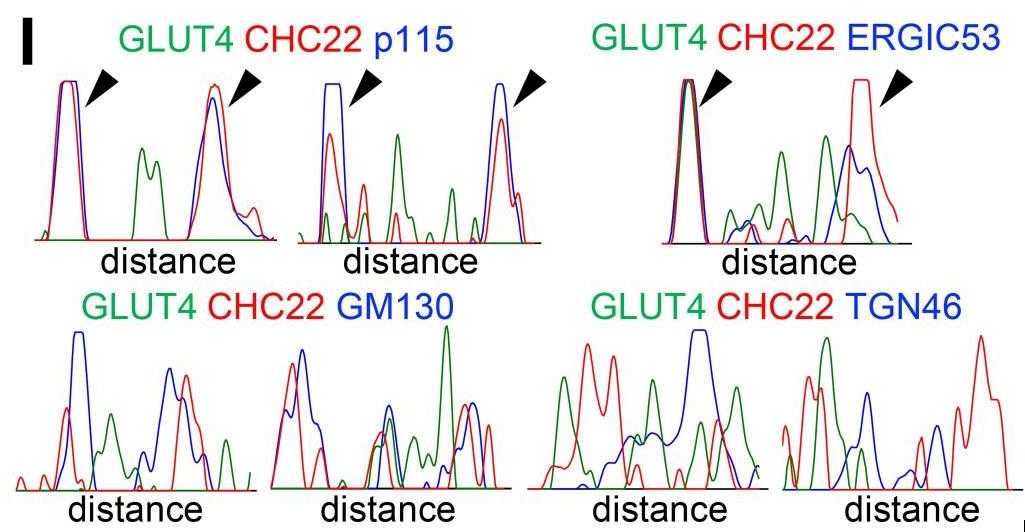
Fig2. Representative fluorescence intensity plots for GLUT4 (green), CHC22 (red), and p115, ERGIC-53, GM130, or TGN46 (blue).
Case Study 2: Jingya Liao, 2022
Glucose transporter 4 (GLUT4) is a membrane protein that regulates blood glucose balance and is closely related to type 2 diabetes. Andrographolide (AND) is a diterpene lactone extracted from herbal medicine Andrographis paniculata, which has a variety of biological activities. In this study, the antidiabetic effect of AND in L6 cells and its mechanism were investigated. The uptake of glucose of L6 cells was detected by a glucose assay kit. The expression of GLUT4 and phosphorylation of protein kinase B (PKB/Akt), AMP-dependent protein kinase (AMPK), and protein kinase C (PKC) were detected by Western blot. At the same time, the intracellular Ca2+ levels and GLUT4 translocation in myc-GLUT4-mOrange-L6 cells were detected by confocal laser scanning microscopy. The results showed that AND enhanced the uptake of glucose, GLUT4 expression and fusion with plasma membrane in L6 cells. In addition, in the case of 0 mM extracellular Ca2+ and 0 mM extracellular Ca2+ + 10 μM BAPTA-AM (intracellular Ca2+ chelator), AND induced the translocation of GLUT4, and the uptake of glucose was significantly inhibited.
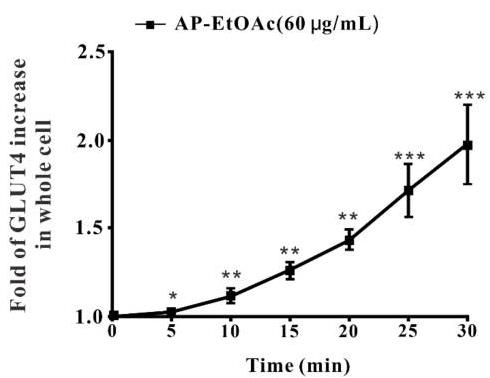
Fig3. Calculation of fluorescence intensity in myc-GLUT4-mOrange-L6 cells.
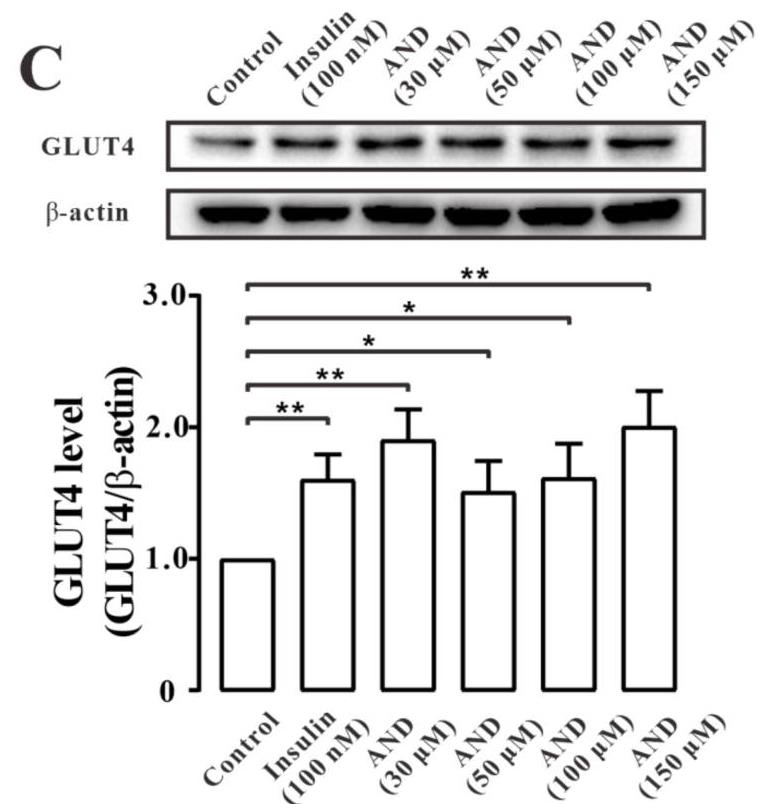
Fig4. The expression level of GLUT4 after treatment with 100 nM insulin or different concentrations of AND.
Quality Guarantee
Involved Pathway
SLC2A4 involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways SLC2A4 participated on our site, such as FoxO signaling pathway,AMPK signaling pathway,Insulin signaling pathway, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with SLC2A4 were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| Adipocytokine signaling pathway | IRS4,RXRG,PRKAG3B,ACSL3,RELA,POMCA,ACSL3B,PRKAB1,ADIPOR1B,PTPN11A |
| Insulin resistance | PTPRF,PYGB,PTPN11A,MGEA5,SLC2A2,ACACB,PPP1R3CB,RPS6KA6,FOXO1A,PRKCD |
| Insulin signaling pathway | NRAS,PYGMA,PRKAA2,PPP1R3D,MTOR,MAPK3,CALM4,IRS1,IRS2,GRB2B |
| Type II diabetes mellitus | TNF,PRKCD,SOCS4,SOCS1,PIK3CA,SLC2A2,PKLR,MAPK1,PIK3CG,MAPK8 |
| AMPK signaling pathway | CFTR,EIF4EBP1,PFKFB3,ADIPOQ,PIK3CB,RPTOR,ULK1,CD36,PRKAB1,PPP2R2B |
| FoxO signaling pathway | MAPK8,PDPK1,GRB2A,PCK2,PRKAG3,CDKN2D,PTENA,CCND2A,TGFBR1A,MAPK8B |
Protein Function
SLC2A4 has several biochemical functions, for example, D-glucose transmembrane transporter activity,glucose transmembrane transporter activity,protein binding. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by SLC2A4 itself. We selected most functions SLC2A4 had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with SLC2A4. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| D-glucose transmembrane transporter activity | SLC2A2,SLC2A13B,SLC2A1 |
| protein binding | TXNRD3,LLGL2,TAOK1,URI1,CTIF,RIPK1,AVPI1,SETBP1,GAS1,P2RY1 |
| glucose transmembrane transporter activity | SLC2A6,SLC2A8,SLC2A3A,SLC2A2,SLC2A3,SLC2A9L1,PPBP,SLC2A11B,SLC2A1A,SLC2A15A |
Interacting Protein
SLC2A4 has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with SLC2A4 here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of SLC2A4.
DAXX;tax
Resources
Research Area
Related Services
Related Products
References


.jpg)
.jpg)

