TNFAIP6
-
Official Full Name
tumor necrosis factor, alpha-induced protein 6 -
Overview
The protein encoded by this gene is a secretory protein that contains a hyaluronan-binding domain, and thus is a member of the hyaluronan-binding protein family. The hyaluronan-binding domain is known to be involved in extracellular matrix stability and cell migration. This protein has been shown to form a stable complex with inter-alpha-inhibitor (I alpha I), and thus enhance the serine protease inhibitory activity of I alpha I, which is important in the protease network associated with inflammation. This gene can be induced by proinflammatory cytokines such as tumor necrosis factor alpha and interleukin-1. Enhanced levels of this protein are found in the synovial fluid of patients with osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis. -
Synonyms
TNFAIP6;tumor necrosis factor, alpha-induced protein 6;tumor necrosis factor-inducible gene 6 protein;TSG 6;TSG6;Hyaluronate binding protein;TNF stimulated gene 6 protein;TNFAIP 6;Tumor necrosis factoralpha induced protein 6;Tumor necrosis factor alpha induced protein 6;Tumor necrosis factor stimulated gene 6 protein;OTTHUMP00000162710;TNF alpha-induced protein 6;hyaluronate-binding protein;TNF-stimulated gene 6 protein;tumor necrosis factor alpha-inducible protein 6;tumor necrosis factor-stimulated gene-6 protein;TSG-6
Recombinant Proteins
- Human
- Mouse
- Chicken
- Zebrafish
- Rhesus macaque
- E.coli
- Mammalian Cells
- Wheat Germ
- HEK293
- Insect Cells
- In Vitro Cell Free System
- His
- GST
- Non
- T7
- Myc
- Avi
- Fc
Background
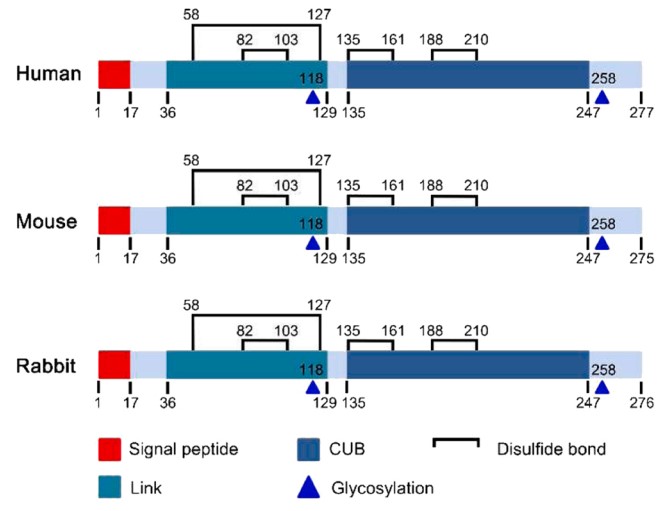
Fig1. Structure of TSG-6 in different species. (Ruomei Li, 2022)
What is TNFAIP6 protein?
TNFAIP6 (TNF alpha induced protein 6) gene is a protein coding gene which situated on the long arm of chromosome 2 at locus 2q23. The protein encoded by this gene is a secretory protein that contains a hyaluronan-binding domain, and thus is a member of the hyaluronan-binding protein family. The hyaluronan-binding domain is known to be involved in extracellular matrix stability and cell migration. This protein has been shown to form a stable complex with inter-alpha-inhibitor (I alpha I), and thus enhance the serine protease inhibitory activity of I alpha I, which is important in the protease network associated with inflammation. This gene can be induced by proinflammatory cytokines such as tumor necrosis factor alpha and interleukin-1. The TNFAIP6 protein is consisted of 277 amino acids and its molecular mass is approximately 31.2 kDa.
What is the function of TNFAIP6 protein?
TNFAIP6 plays a role in modulating the inflammatory response. It can form a stable complex with inter-alpha-inhibitor (IαI), enhancing the serine protease inhibitory activity of IαI, which is crucial in the protease network associated with inflammation. It is involved in the regulation of immune cells, helping to modulate their activation and proliferation, and enhancing the immune system's ability to clear pathogens. The hyaluronan-binding domain of TNFAIP6 is implicated in extracellular matrix stability and cell migration, which are important for tissue repair and regeneration. It has been identified as a potential cell marker for mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs), suggesting a role in stem cell biology and regenerative medicine.
TNFAIP6 Related Signaling Pathway
TNFAIP6 is associated with the NF-κB signaling pathway, which plays an important role in the spatio-temporal regulation of cell proliferation, differentiation, and apoptosis, involving immunity, inflammation, and neural function. Overexpression of TNFAIP6 can increase the distribution of β-catenin ectopic nuclei and activate the Wnt/β-Catenin signaling pathway, which plays an important role in tumor development. KEGG analysis showed that the 'p53 signaling pathway 'was associated with tumor progression, while TNFAIP6 was identified as a central gene associated with this signaling pathway, and its elevated expression level was associated with poor tumor prognosis. TNF superfamily members activate signaling pathways in cell survival, death, and differentiation, which are associated with TNFAIP6 expression and function.
TNFAIP6 Related Diseases
TNFAIP6 has anti-inflammatory effects, which can inhibit the production of cytokines in the inflammatory response and reduce pathological scarring. TNFAIP6 is expressed in some tumors and may be involved in the growth and spread of tumor cells. For example, in gastric cancer, TNFAIP6 expression is associated with tumor invasion and metastasis. TNFAIP6 may be associated with autoimmune diseases, such as rheumatoid arthritis, and its anti-inflammatory effects may be important for the treatment of such diseases. In central nervous system diseases, TNFAIP6 may play an anti-neuroinflammatory role by regulating the activation state of microglia. TNFAIP6 has a protective effect on premature infants with bronchopulmonary hypoplasia, which may be related to inhibiting the release of related inflammatory cytokines from inflammatory cells. TNFAIP6 may play a key role in the treatment of acute kidney injury induced by ischemia/reperfusion injury. TNFAIP6 may protect the body from visual defects caused by trauma through the regulation of nerves and blood vessels.
Bioapplications of TNFAIP6
Because TNFAIP6 has anti-inflammatory and immunomodulatory properties, it has potential applications in the treatment of inflammatory and autoimmune diseases. For example, TNFAIP6 may be helpful in treating inflammatory diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis. TNFAIP6 plays a role in the process of tissue repair and regeneration and may help promote the repair of damaged tissues. Tnfaip6-positive mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) show enhanced immunosuppressive activity, which may help in the development of new cell therapy strategies. TNFAIP6 has shown therapeutic efficacy in models of acute inflammation, such as in a mouse model of LPS-induced acute inflammation, where TNFAIP6+ MSCs were able to reduce serum pro-inflammatory cytokine levels, reduce neutrophil infiltration, and promote lung tissue recovery.
Case Study
Case Study 1: Li Ma, 2023
TNF-stimulated gene (TSG-6) was reported to suppress hypertrophic scar (HS) formation in a rabbit ear model, and the overexpression of TSG-6 in human HS fibroblasts (HSFs) was found to induce their apoptotic death. The molecular basis for these findings, however, remains to be clarified. HSFs were subjected to TSG-6 treatment. Treatment with TSG-6 significantly suppressed HSF proliferation and induced them to undergo apoptosis. Moreover, TSG-6 exposure led to reductions in collagen I, collagen III, and α-SMA mRNA and protein levels, with a corresponding drop in proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA) expression indicative of impaired proliferative activity. Endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress was also suppressed in these HSFs as demonstrated by decreases in Bip and p-IRE1α expression, downstream inositol requiring enzyme 1 alpha (IRE1α) -Tumor necrosis factor receptor associated factor 2 (TRAF2) pathway signalling was inhibited and treated cells failed to induce NF-κB, TNF-α, IL-1β, and IL-6 expression. Overall, ER stress was found to trigger inflammatory activity in HSFs via the IRE1α-TRAF2 axis, as confirmed with the specific inhibitor of IRE1α STF083010. Additionally, the effects of TSG-6 on apoptosis, collagen I, collagen III, α-SMA, and PCNA of HSFs were reversed by the IRE1α activator thapsigargin (TG).
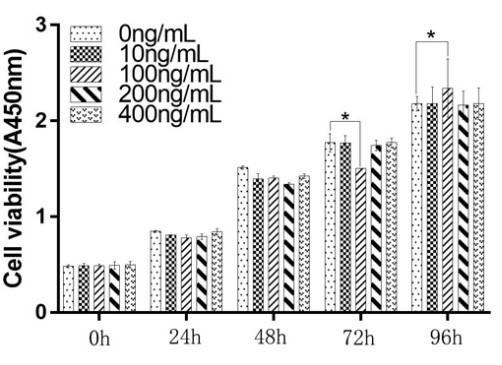
Fig1. The impact of TSG-6 on the proliferation of HFFs was assessed via CCK-8 assay.
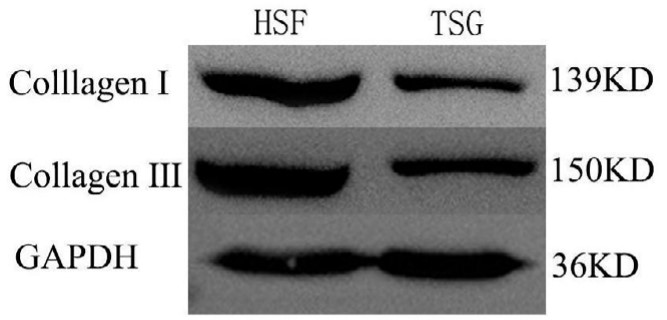
Fig2. The impact of TSG-6 on fibroblast-associated protein expression.
Case Study 2: Xiangwen Zhang, 2021
TNFα-stimulated gene-6 (TNFAIP6) plays an important role in the prognosis of many tumors. This study aims to investigate the clinical and prognostic value of TNFAIP6 expression in gastric cancer (GC) patients. Here, the researchers investigated the expression of TNFAIP6 in GC tissues using western blotting and immunohistochemistry and the association between TNFAIP6 expression and the prognosis and clinicopathological parameters of GC patients. The results revealed that the expression of TNFAIP6 was higher in GC tissue than in normal gastric tissue, and the levels were positively correlated with the depth of tumor invasion, tumors with lymph node metastasis and TNM stage of GC patients. Moreover, the results revealed that patients with high TNFAIP6 expression exhibited poorer overall survival than those with low TNFAIP6 expression. Additionally, knockdown of TNFAIP6 inhibited the proliferation, invasion and metastasis of GC cells in vitro.
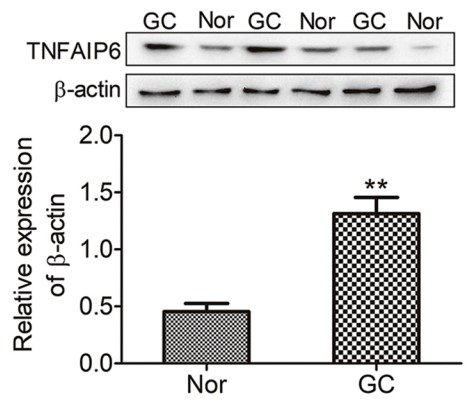
Fig3. TNFAIP6 protein expression was assayed by western blotting.
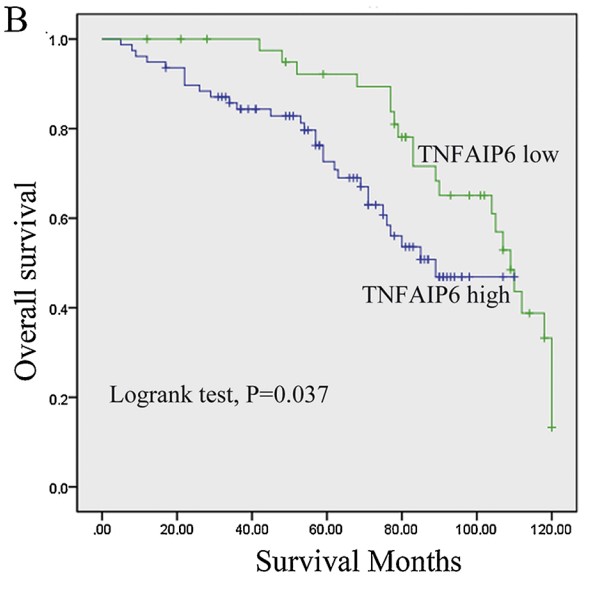
Fig4. The TNFAIP6-low group had significantly better OS outcomes than the TNFAIP6-high group.
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
.jpg)
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (Tnfaip6-1417M)
Involved Pathway
TNFAIP6 involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways TNFAIP6 participated on our site, such as , which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with TNFAIP6 were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|
Protein Function
TNFAIP6 has several biochemical functions, for example, hyaluronic acid binding. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by TNFAIP6 itself. We selected most functions TNFAIP6 had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with TNFAIP6. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| hyaluronic acid binding | LAYN,KIAA1199,CD44,HAPLN1,HAPLN2,HAPLN3,BCAN,NCAN,HMMR,C1QBP |
Interacting Protein
TNFAIP6 has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with TNFAIP6 here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of TNFAIP6.
Resources
Research Area
Related Services
Related Products
References
- Jang, YJ; Park, JI; et al. Cumulus Cell-Expressed Type I Interferons Induce Cumulus Expansion in Mice. BIOLOGY OF REPRODUCTION 92:-(2015).
- Anderson, RA; Bayne, RAL; et al. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor is a regulator of human oocyte maturation and early embryo development. FERTILITY AND STERILITY 93:1394-1406(2010).
- Nagyova, E; Camaioni, A; et al. Synthesis of tumor necrosis factor alpha-induced protein 6 in porcine preovulatory follicles: A study with A38 antibody. BIOLOGY OF REPRODUCTION 78:903-909(2008).



