Active Recombinant Full Length Human Peroxisome Proliferator-activated Receptor Alpha/PPARA, His-tagged
| Cat.No. : | PPARA-1083H |
- Specification
- Gene Information
- Related Products
- Citation
- Download
| Species : | Human |
| Source : | E.coli |
| Tag : | His |
| Protein Length : | 1-468 a.a. |
| Description : | Recombinant His tagged PPARα(52 kDa) is isolated from an E.coli strain that carries the coding sequence of the human PPARα under the control of a T7 promoter. There is evidence that a group of closely related nuclear receptors, called Peroxisome Proliferator-activated Receptors (PPARs), may be involved in chronic diseases such as diabetes, obesity, atherosclerosis and cancer. The PPARs were first cloned as the nuclear receptors that mediate the effects of synthetic compounds called peroxisome proliferators on gene transcription. It soon became clear that eicosanoids and fatty acids can also regulate gene transcription through PPARs. They bind a specific element in the promoter region of target genes only as a heterodimer with the receptor for 9-cis retinoic acid, RXR (retinoid X receptor). Binding of the ligand of either receptor can activate the complex, but binding of both ligands simultaneously is more potent. Three PPAR isotypes have been identified: α,β (also called NUC1) and γ. PPARα is expressed most in brown adipose tissue and liver, then kidney, heart and skeletal muscle. PPARγ is mainly expressed in adipose tissue, and to a lesser extent in colon, the immune system and the retina. PPARβ is found in many tissues but the highest expression is in the gut, kidney and heart. The target genes of PPARα are a relatively homogenous group of genes that participate in aspects of lipid catabolism such as fatty acid uptake through membranes, fatty acid binding in cells, fatty acid oxidation (in microsomes, peroxisomes and mitochondria) and lipoprotein assembly and transport. |
| Form : | Liquid. Supplied in 20 mM Tris-HCl pH 8.0, 100 Mm KCl, 0.2 mM EDTA, 1 mM DTT and 20% glycerol. |
| Purity : | > 95% by SDS-PAGE. |
| Application : | PPARα has been applied in DNA and protein-protein interaction assays. |
| Activity : | 20 ng are sufficient for a gel-mobility shift assay and 100 ng are sufficient for a protein-protein interaction assay. |
| Usage : | For in vitro use only. |
| Storage : | Quality guaranteed for 12 months store at -80°C. Avoid freeze / thaw cycles. |
| Gene Name | PPARA peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha [ Homo sapiens ] |
| Synonyms | PPARA; peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha; PPAR; NR1C1; hPPAR; MGC2237; MGC2452; PPARalpha; peroxisome proliferative activated receptor, alpha; OTTHUMP00000197740; OTTHUMP00000197741; PPAR-alpha; Nuclear receptor subfamily 1 group C member 1 |
| Gene ID | 5465 |
| mRNA Refseq | NM_001001928 |
| Protein Refseq | NP_001001928 |
| MIM | 170998 |
| UniProt ID | Q07869 |
| Chromosome Location | 22q12-q13.1 |
| Pathway | Adipocytokine signaling pathway; PAR signaling pathway; Metabolism of lipids and lipoproteins |
| Function | drug binding; ligand-regulated transcription factor activity; lipid binding; metal ion binding; protein domain specific binding; sequence-specific DNA binding; steroid hormone receptor activity; transcription activator activity; transcription factor activity; zinc ion binding |
| ◆ Recombinant Proteins | ||
| PPARA-29987TH | Recombinant Human PPARA, His-tagged | +Inquiry |
| PPARA-113H | Recombinant Human PPARA, GST-tagged | +Inquiry |
| PPARA-5939H | Recombinant Human PPARA Protein (Pro61-Ala170), His-tagged | +Inquiry |
| PPARA-1107C | Recombinant Chicken PPARA | +Inquiry |
| PPARA-28675TH | Recombinant Human PPARA | +Inquiry |
| ◆ Cell & Tissue Lysates | ||
| PPARA-2987HCL | Recombinant Human PPARA 293 Cell Lysate | +Inquiry |
Arctigenin Inhibits Liver Cancer Tumorigenesis by Inhibiting Gankyrin Expression via C/EBPα and PPARα
Journal: Frontiers in Pharmacology PubMed ID: 29636686 Data: 2018/3/27
Authors: Ying Sun, Yu-jun Tan, Jie Li
Article Snippet:Horseradish peroxidase (HRP)-conjugated goat anti-rabbit immunoglobulin G (IgG) was obtained from Santa Cruz (Santa Cruz Biotechnology, Santa Cruz, CA, United States).Horseradish peroxidase (HRP)-conjugated goat anti-rabbit immunoglobulin G (IgG) was obtained from Santa Cruz (Santa Cruz Biotechnology, Santa Cruz, CA, United States).. C/EBPα proteins were obtained from ORIGENE (Rockville, MD, United States), and PPARα was obtained from Creative BioMart (Shirley, NY, United States).
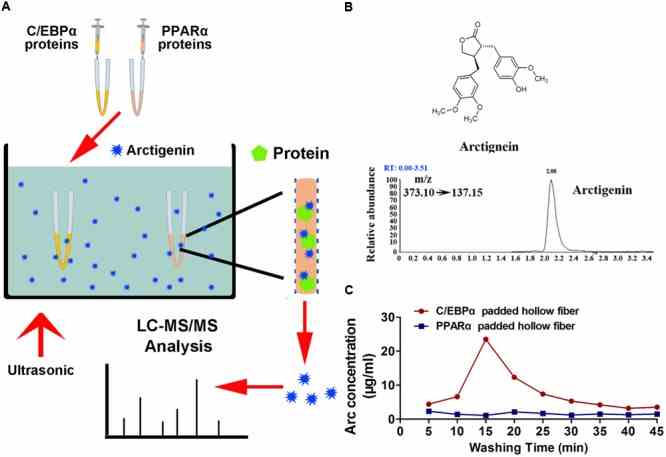
Arctigenin binds
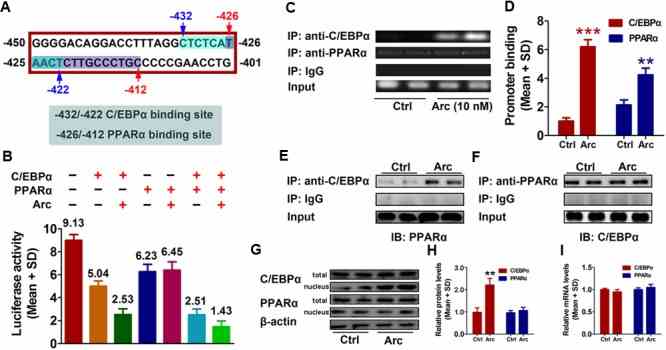
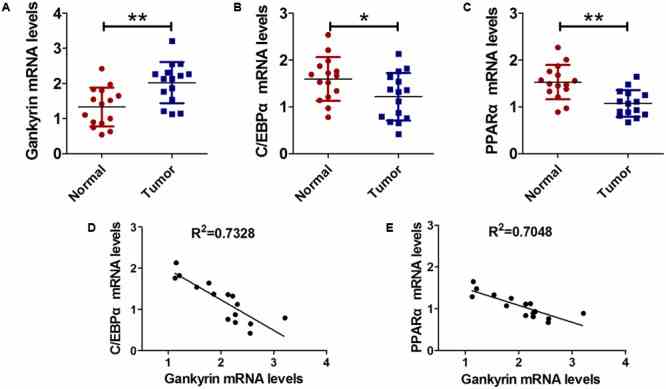
Gankyrin expression was increased and negatively correlated
Not For Human Consumption!
Inquiry
- Reviews (0)
- Q&As (0)
Ask a Question for All PPARA Products
Required fields are marked with *
My Review for All PPARA Products
Required fields are marked with *



