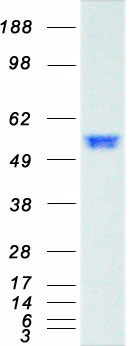
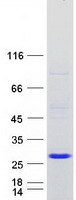
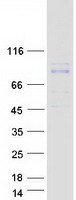
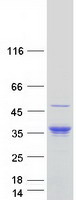
Heavy-labeled Full-length Proteins
Background
What is isotopic labeling?
Isotopic labeling is a technique used in chemistry and biology where one or more of the atoms in a molecule is replaced with an isotope of that atom - usually a radioactive or a stable isotope. This is often done to help trace the path of atoms through a chemical reaction or metabolic pathway, or to measure the movement or distribution of a substance within a system. It can also be used to gain information about the structure or function of a molecule.

Due to the costly manners of producing isotopic chemicals and heterologous proteins, an economic 15N/13C isotopic labeling strategy is critically in demand. Stable isotope labeling by amino acids in cell culture (SILAC) is a multiplexing quantitative proteomic method that incorporates isotopically (heavy) labeled amino acids metabolically into the whole proteome.
Creative BioMart now offers an extensive collection of Mass Spectrometry (MS) standards for 6,000 proteins. Produced in HEK293T cells and labeled with [U- 13C6, 15N4]-L-Arginine and [U- 13C6, 15N2]-L-Lysine, these full-length proteins with appropriate post-translational modifications are ideal identification and quantification standards.
Advantages
- Precision: Isotopic labeling allows for a very specific and precise identification and quantification of proteins.
- Stability: Isotopes are chemically identical to their non-radioactive counterparts and thus do not interfere with the normal function or behavior of the protein.
- Sensitivity: Isotopic labeling is highly sensitive and can detect even small changes in protein expression or function.
- Non-destructive
- Multiple Labeling: With isotopic labeling, multiple isotopes can be incorporated into the same protein, allowing for a detailed study of not only the protein's location but also its interactions with other proteins or molecules.
- Authentic post-translational modifications
- High data consistency
- High reproducibility
- Identifying the best SRM and MRM transitions
- Suitable for most types of MS equipment
- Over 90% incorporation efficiency
Applications
Structural Determination: NMR (nuclear magnetic resonance) spectroscopy and other techniques use isotopic labeling to determine the three-dimensional structure of proteins. Specifically labeled isotopes provide greater resolution and clarity in the data.
Reaction Tracing: Isotopic labeling can track how a protein reacts or metabolizes within a system. For example, a labeled atom could be used to trace the metabolic pathway of a protein in a biological system.
Quantification: Isotopic labeling can aid in the quantification of proteins in a complex mixture using mass spectrometry.
Enzyme/Substrate Studies: In enzyme-substrate studies, isotopic labeling helps in identifying the mechanisms and pathways.
Protein-Protein Interaction: Isotopic labeling is also used to study protein-protein interactions, protein folding, and dynamics.
Biomolecular research: Isotopic labeling is fundamental for biomolecular research, including drug discovery and development.
Protein Turnover Studies: It can be used to measure the synthesis and breakdown rates of proteins.
It also allows for kinetic studies by helping to understand reaction rates and mechanisms.