Recombinant Human SMPDL3B protein, His-tagged
| Cat.No. : | SMPDL3B-2822H |
| Product Overview : | Recombinant Human SMPDL3B protein(1-336 aa), fused with N-terminal His tag, was expressed in E.coli. |
| Availability | January 27, 2026 |
| Unit | |
| Price | |
| Qty |
- Specification
- Gene Information
- Related Products
- Citation
- Download
| Species : | Human |
| Source : | E.coli |
| Tag : | His |
| Protein Length : | 1-336 aa |
| Form : | The purified protein was lyophilized from sterile phosphate-buffered saline (PBS: 58 mM Na₂HPO₄, 17 mM NaH₂PO₄, 68 mM NaCl, pH 7.4). Prior to lyophilization, 5% (w/v) trehalose and 5% (w/v) mannitol were incorporated as cryoprotective excipients. The protein was eluted with a buffer containing 300 mM imidazole. |
| AASequence : | MRLLAWLIFLANWGGARAEPGKFWHIADLHLDPDYKVSKDPFQVCPSAGSQPVPDAGPWGDYLCDSPWALINSSIYAMKEIEPEPDFILWTGDDTPHVPDEKLGEAAVLEIVERLTKLIREVFPDTKVYAALGNHDFHPKNQFPAGSNNIYNQIAELWKPWLSNESIALFKKGAFYCEKLPGPSGAGRIVVLNTNLYYTSNALTADMADPGQQFQWLEDVLTDASKAGDMVYIVGHVPPGFFEKTQNKAWFREGFNEKYLKVVRKHHRVIAGQFFGHHHTDSFRMLYDDAGVPISAMFITPGVTPWKTTLPGVVNGANNPAIRVFEYDRATLSLKV |
| Purity : | 85%, by SDS-PAGE with Coomassie Brilliant Blue staining. |
| Storage : | Store at 2-8°C for 1-2 weeks. Aliquot and store at -20°C to -80°C for up to 3 months, reconstitution with sterile water and addition of an equal volume of glycerol. Avoid repeat freeze-thaw cycles. |
| Reconstitution : | Dissolve the product in 200 μl sterile water to achieve a working concentration of 0.25 µg/μl. If experimental compatibility allows, mix the aqueous solution with an equal volume of glycerol (1:1 ratio) after initial reconstitution. |
| Gene Name | SMPDL3B sphingomyelin phosphodiesterase, acid-like 3B [ Homo sapiens ] |
| Official Symbol | SMPDL3B |
| Synonyms | SMPDL3B; sphingomyelin phosphodiesterase, acid-like 3B; acid sphingomyelinase-like phosphodiesterase 3b; ASML3B; ASM-like phosphodiesterase 3b; |
| Gene ID | 27293 |
| mRNA Refseq | NM_001009568 |
| Protein Refseq | NP_001009568 |
| UniProt ID | Q92485 |
| ◆ Recombinant Proteins | ||
| SMPDL3B-2822H | Recombinant Human SMPDL3B protein, His-tagged | +Inquiry |
| Smpdl3b-159M | Recombinant Mouse Smpdl3b Protein, MYC/DDK-tagged | +Inquiry |
| Smpdl3b-3070M | Recombinant Mouse Smpdl3b, His-tagged | +Inquiry |
| Smpdl3b-5868M | Recombinant Mouse Smpdl3b protein, His&Myc-tagged | +Inquiry |
| SMPDL3B-4565C | Recombinant Chicken SMPDL3B | +Inquiry |
| ◆ Cell & Tissue Lysates | ||
| SMPDL3B-1654HCL | Recombinant Human SMPDL3B 293 Cell Lysate | +Inquiry |
SMPDL3b modulates insulin receptor signaling in diabetic kidney disease
Journal: Nature Communications PubMed ID: 31217420 Data: 2019/6/19
Authors: A. Mitrofanova, S. K. Mallela, A. Fornoni
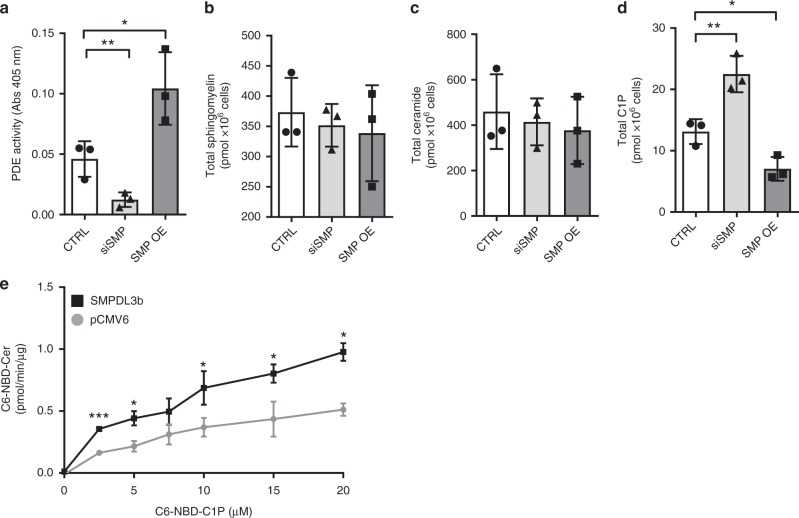
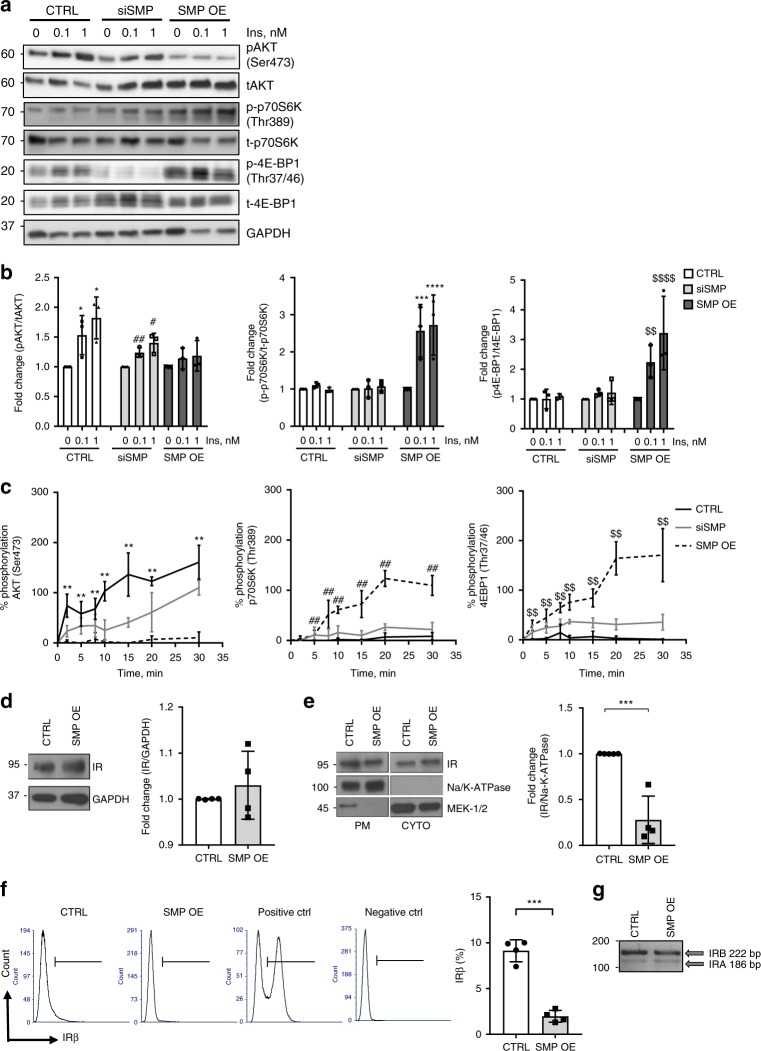
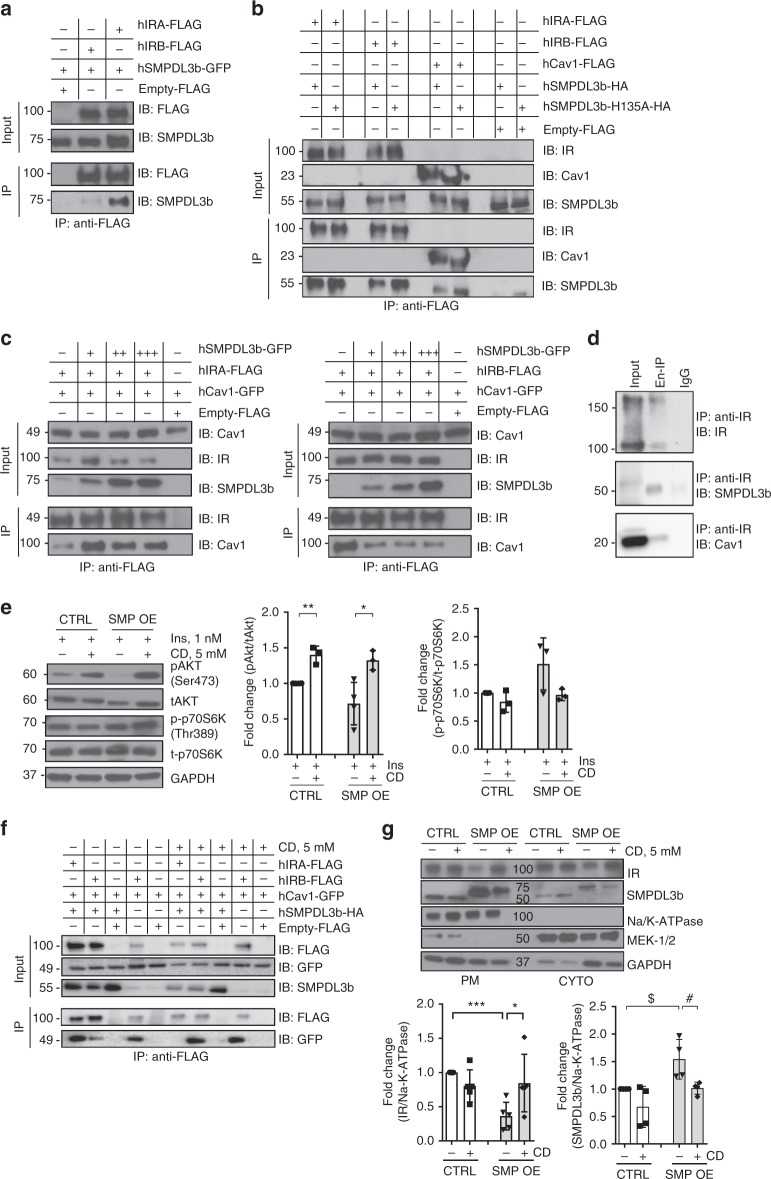
Article Snippet:C16:0 C1P (#860533) and C6-NBD-Ceramide (#810209P) were obtained from Avanti Polar Lipid (AL, USA).C16:0 C1P (#860533) and C6-NBD-Ceramide (#810209P) were obtained from Avanti Polar Lipid (AL, USA).. Recombinant human SMPDL3b protein, MYC/DDK-tagged was ordered from Creative BioMart (#SMPDL3b-2823H).. Anti-caveolin-1 (#3251 for phospho-Cav1(Tyr14), dilution 1:1000, #3267 for Cav1 (D46G3) XP TM , dilution 1:1000), anti-IR β subunit (4B8) (#3025, dilution 1:100), anti-Na/K-ATPase (#3010, dilution 1:1000), anti-MEK-1/2 (D1A5) (#8727, dilution 1:1,000), anti-AKT (#9271 for phospho-AKT (Ser473) (D9E), dilution 1:1000, #9272 for tAKT, dilution 1:1000), anti-p70S6Ke (#9234 for phosphor-p70S6K (Thr389 (108D2)), dilution 1:1000, #9202 for p70S6K, dilution 1:1000), anti-4EBP1 (#2855 for phospho-4E-BP1 (Thr37/46) (236B4), dilution 1:1000, #9644 for 4E-BP1, dilution 1:1000) primary antibodies were purchased from Cell Signaling Technology (MA, USA).Anti-caveolin-1 (#3251 for phospho-Cav1(Tyr14), dilution 1:1000, #3267 for Cav1 (D46G3) XP TM , dilution 1:1000), anti-IR β subunit (4B8) (#3025, dilution 1:100), anti-Na/K-ATPase (#3010, dilution 1:1000), anti-MEK-1/2 (D1A5) (#8727, dilution 1:1,000), anti-AKT (#9271 for phospho-AKT (Ser473) (D9E), dilution 1:1000, #9272 for tAKT, dilution 1:1000), anti-p70S6Ke (#9234 for phosphor-p70S6K (Thr389 (108D2)), dilution 1:1000, #9202 for p70S6K, dilution 1:1000), anti-4EBP1 (#2855 for..
Not For Human Consumption!
Inquiry
- Reviews (0)
- Q&As (0)
Ask a Question for All SMPDL3B Products
Required fields are marked with *
My Review for All SMPDL3B Products
Required fields are marked with *



