Recombinant Human TRIM72 protein, MYC/DDK-tagged
| Cat.No. : | TRIM72-12H |
| Product Overview : | Recombinant Human TRIM72 fused with MYC/DDK tag at C-terminal was expressed in HEK293. |
| Availability | February 06, 2026 |
| Unit | |
| Price | |
| Qty |
- Specification
- Gene Information
- Related Products
- Citation
- Download
| Species : | Human |
| Source : | HEK293 |
| Tag : | DDK&Myc |
| Form : | 25 mM Tris.HCl, pH 7.3, 100 mM glycine, 10% glycerol. |
| Molecular Mass : | 52.6 kDa |
| Concentration : | >50 ug/mL as determined by microplate BCA method |
| Publications : |
| Gene Name | TRIM72 tripartite motif containing 72 [ Homo sapiens ] |
| Official Symbol | TRIM72 |
| Synonyms | TRIM72; tripartite motif containing 72; tripartite motif-containing protein 72; mitsugumin-53; tripartite motif-containing 72; MG53; |
| Gene ID | 493829 |
| mRNA Refseq | NM_001008274 |
| Protein Refseq | NP_001008275 |
| MIM | 613288 |
| UniProt ID | Q6ZMU5 |
| Chromosome Location | 16p11.2 |
| Function | metal ion binding; phosphatidylserine binding; zinc ion binding; |
| ◆ Recombinant Proteins | ||
| TRIM72-156H | Recombinant Human TRIM72 protein, His/S-tagged | +Inquiry |
| TRIM72-9624M | Recombinant Mouse TRIM72 Protein, His (Fc)-Avi-tagged | +Inquiry |
| TRIM72-5943R | Recombinant Rat TRIM72 Protein, His (Fc)-Avi-tagged | +Inquiry |
| Trim72-158R | Recombinant Rat Trim72 protein, His/S-tagged | +Inquiry |
| TRIM72-12H | Recombinant Human TRIM72 protein, MYC/DDK-tagged | +Inquiry |
| ◆ Cell & Tissue Lysates | ||
| TRIM72-1835HCL | Recombinant Human TRIM72 cell lysate | +Inquiry |
MG53 anchored by dysferlin to cell membrane reduces hepatocyte apoptosis which induced by ischaemia/reperfusion injury in vivo and in vitro
Journal: Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine PubMed ID: 28401647 Data: 2017/4/12
Authors: Weifeng Yao, Haobo Li, Ziqing Hei
Article Snippet:Some of the rats received recombinant human MG53 protein (rhMG53, i.v., 5 mg/kg) or vehicle (0.9% sterile saline) 2 hrs before surgery.Some of the rats received recombinant human MG53 protein (rhMG53, i.v., 5 mg/kg) or vehicle (0.9% sterile saline) 2 hrs before surgery.. The rhMG53 protein was obtained from Creative BioMart Company (Cat#. TRIM72‐156H).. DNA sequence encoding the human MG53 (Gene ID: 493829) was fused with a polyhistidine tag at the C‐terminus.DNA sequence encoding the human MG53 (Gene ID: 493829) was fused with a polyhistidine tag at the C‐terminus.
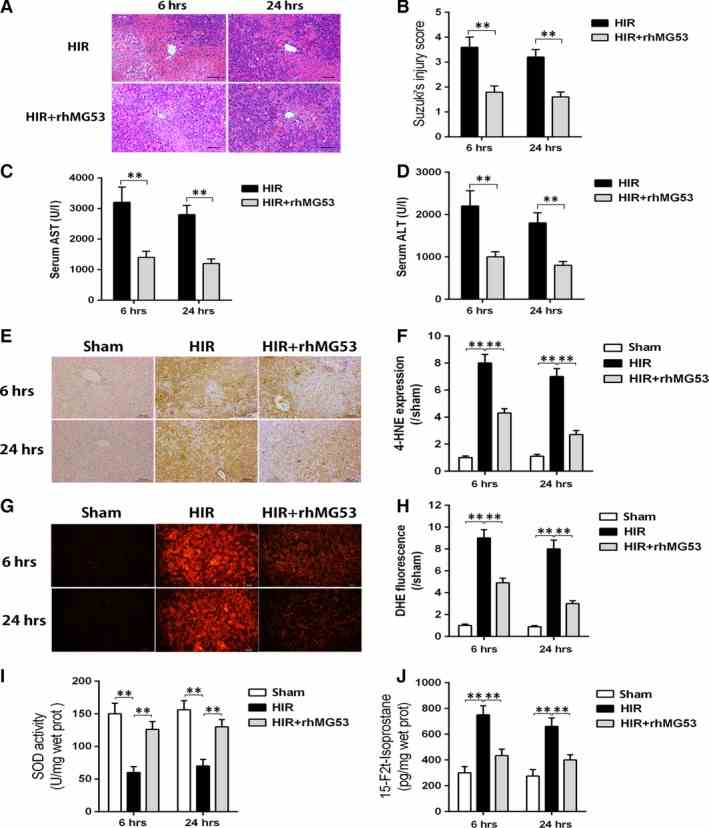
MG53 administration reduced hepatic injury and oxidative stress during ischaemia/reperfusion. Rats were subjected to HIR or sham operation with or without administration of
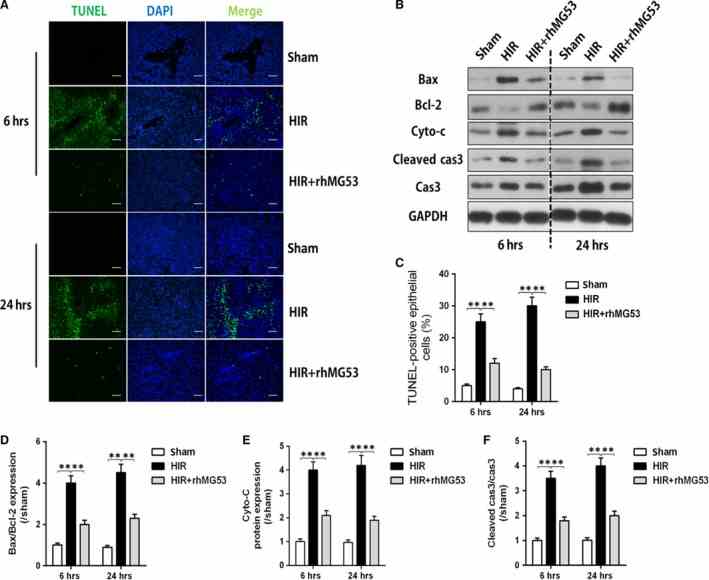
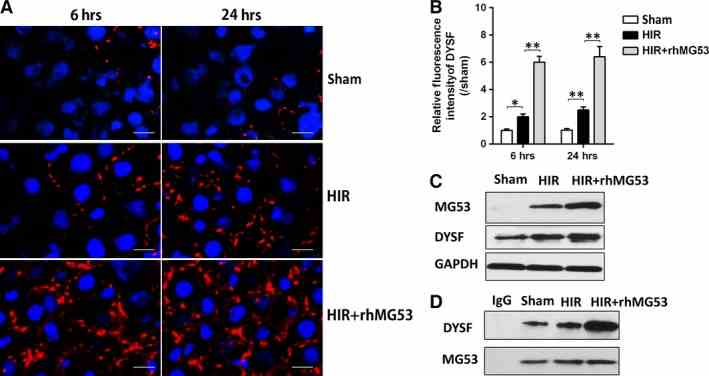
Protective effects of
Not For Human Consumption!
Inquiry
- Reviews (0)
- Q&As (0)
Ask a Question for All TRIM72 Products
Required fields are marked with *
My Review for All TRIM72 Products
Required fields are marked with *



