Neurotrophin/Trk Family
Related Symbol Search List
Immunology Background
About Neurotrophin/Trk Family
The neurotrophin/Trk family refers to a group of proteins that play a crucial role in the growth, development, and maintenance of neurons in the nervous system. This family consists of neurotrophins, such as nerve growth factor (NGF), brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), neurotrophin-3 (NT-3), and neurotrophin-4/5 (NT-4/5), as well as their corresponding receptors known as tropomyosin receptor kinase (Trk) receptors.
Neurotrophins are a class of proteins that are secreted by various cells, including neurons and glial cells. They help to promote the survival and differentiation of neurons during development and throughout adulthood. In addition, neurotrophins also regulate synaptic plasticity and neuronal function.
Trk receptors are transmembrane proteins that are expressed on the surface of neurons, and they act as high-affinity receptors for neurotrophins. There are three main subtypes of Trk receptors: TrkA, TrkB, and TrkC. Each subtype has a different affinity for specific neurotrophins. For example, TrkA mainly binds to NGF, TrkB predominantly binds to BDNF and NT-4/5, while TrkC primarily binds to NT-3.
Upon binding to their respective neurotrophins, Trk receptors undergo dimerization and activation of their intracellular kinase domain. This activation triggers intracellular signaling cascades that promote cell survival, proliferation, and differentiation. Trk receptors can activate different signaling pathways, including the MAPK/ERK pathway, the PI3K/Akt pathway, and the PLCγ pathway, to regulate various cellular processes.
The neurotrophin/Trk family is crucial for the normal development and function of the nervous system. Dysregulation of this family has been associated with various neurological disorders, including neurodegenerative diseases, psychiatric disorders, and neuropathic pain. Consequently, this family of proteins and receptors has become an important target for therapeutic interventions aimed at treating these conditions.
Physiological Functions of Neurotrophin/Trk Family
Neuronal Survival and Development: Neurotrophins, such as nerve growth factor (NGF), brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), neurotrophin-3 (NT-3), and neurotrophin-4/5 (NT-4/5), promote the survival and development of neurons. They act as trophic factors by binding to their respective Trk receptors (TrkA, TrkB, and TrkC), leading to the activation of downstream signaling pathways that promote neuronal survival, prevent apoptosis, and regulate neuronal differentiation and maturation.
Synaptic Plasticity: Neurotrophins and their Trk receptors are involved in regulating synaptic plasticity, which is the ability of synapses to strengthen or weaken in response to activity. They play a role in the modulation of synaptic transmission, dendritic spine morphology, long-term potentiation (LTP), and long-term depression (LTD), which are critical for learning and memory processes.
Axonal Growth and Guidance: Neurotrophins contribute to axonal growth and guidance during neural development. They provide directional cues for axonal outgrowth, attract or repel growing axons, and promote axon branching and pathfinding. The interaction of neurotrophins with their Trk receptors and the co-receptor p75NTR helps regulate the intricate process of axonal wiring in the developing nervous system.
Pain Sensation: Neurotrophins, particularly NGF and BDNF, have been implicated in the regulation of pain sensation. They are involved in the development and plasticity of nociceptive (pain-sensing) neurons and modulate pain transmission pathways in the spinal cord and brain. Dysregulation of neurotrophin signaling has been associated with chronic pain conditions.
Neuroprotection and Regeneration: Neurotrophins have neuroprotective effects, meaning they can promote survival and protect neurons from injury or degeneration. They support the maintenance and function of neurons in various regions of the nervous system. Additionally, neurotrophins can stimulate neuronal regeneration and axonal sprouting after damage, contributing to the repair of injured neural circuits.
Neurotransmitter Regulation: Neurotrophins and Trk receptors are involved in the regulation of neurotransmitter systems. They influence the synthesis, release, and uptake of neurotransmitters, such as acetylcholine, serotonin, and dopamine, in specific neuronal populations. This modulation of neurotransmitter systems contributes to the regulation of neuronal activity and synaptic transmission.
Overall, the Neurotrophin/Trk family plays critical roles in neuronal survival, development, synaptic plasticity, axonal growth and guidance, pain sensation, neuroprotection, regeneration, and neurotransmitter regulation. Dysregulation of this family has been implicated in various neurological disorders, underscoring its significance in maintaining proper nervous system function.
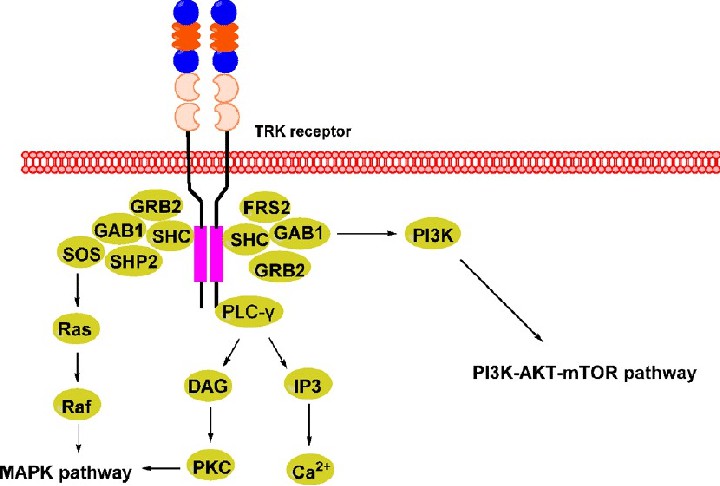 Fig.2 TRK signaling pathway. (Xie Z, et al., 2021)
Fig.2 TRK signaling pathway. (Xie Z, et al., 2021)
Neurotrophins bind to TRK receptors, leading to recruitment of adaptor proteins, including GRB2, GAB1, SHC, SHP2, FRS2, and SOS. Subsequently, Ras, PLC-γ, and PI3K are activated, triggering the MAPK pathway, calcium mobilization, and the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway. These signaling pathways regulate gene expression activation, neurite outgrowth, and neuronal survival associated with pain and cancer.
The Application Areas of Neurotrophin/Trk Family
Neurodegenerative Diseases: The neurotrophin/Trk family has been extensively studied in the context of neurodegenerative diseases, such as Alzheimer's disease, Parkinson's disease, and Huntington's disease. Understanding the role of neurotrophins and Trk receptors in neuronal survival, regeneration, and synaptic plasticity can provide insights into potential therapeutic strategies for these conditions.
Nerve Injury and Regeneration: Neurotrophins have been investigated for their potential to promote nerve regeneration and functional recovery after nerve injuries, including spinal cord injury and peripheral nerve damage. Their application may involve local delivery of neurotrophins or gene therapy approaches to enhance nerve regrowth and axonal guidance.
Mental Health Disorders: The neurotrophin/Trk family has been implicated in mental health disorders such as depression, anxiety, and post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD). Manipulating neurotrophin signaling pathways may offer novel therapeutic approaches for the treatment of these conditions.
Pain Management: Neurotrophins, particularly nerve growth factor (NGF), have been implicated in the regulation of pain sensation. Targeting NGF signaling or Trk receptors may provide opportunities for developing novel pain management strategies and therapeutics.
Neurodevelopmental Disorders: Abnormal neurotrophin signaling has been associated with neurodevelopmental disorders such as autism spectrum disorders and intellectual disabilities. Studying the Neurotrophin/Trk family can provide insights into the underlying mechanisms of these conditions and potentially identify therapeutic targets.
Neuroprotection and Stroke: Neurotrophins have neuroprotective effects and have been investigated for their potential to protect neurons from damage caused by stroke or other acute neurological insults. They may aid in reducing neuronal death and promoting recovery after stroke.
Tissue Engineering and Regenerative Medicine: The neurotrophin/Trk family has applications in tissue engineering and regenerative medicine approaches. By incorporating neurotrophins into biomaterials or stem cell-based therapies, researchers aim to enhance nerve regeneration, promote neuronal survival, and improve functional recovery in tissue engineering constructs.
Drug Development: Neurotrophins and Trk receptors are potential targets for drug development. Small molecules, antibodies, or other modulators of neurotrophin signaling pathways are being explored for their therapeutic potential in various neurological disorders.
These are just some of the application areas of the neurotrophin/Trk family. Continued research and understanding of these molecules and their signaling pathways hold promise for developing new treatments and interventions for a wide range of neurological conditions.
Available Resources for Neurotrophin/Trk Family
Creative BioMart provides a variety of products and services to support research on neurotrophin/Trk family-related molecules. Here are some of the key products and services we offer:
Diverse Product Portfolio: The products we provide include but are not limited to the following types:
- Recombinant Proteins: We offer high-quality recombinant proteins, including members of the neurotrophin/Trk family such as NGF, BDNF, NT-3, and NT-4/5. These recombinant proteins can be used for in vitro research on their functions, interactions, and signaling pathways.
- Cell and Tissue Lysates: We provide a variety of cell and tissue lysates, including lysates of molecules related to the neurotrophin/Trk family. These lysates can be used for immunohistochemistry, immunoprecipitation, and other related experimental techniques.
- Protein Pre-Coupling Beads: We offer various protein pre-coupling beads for studying the interactions between molecules related to the neurotrophin/Trk family. These pre-coupling beads can be used for immunoprecipitation, co-immunoprecipitation, affinity purification, and other experimental designs and applications.
Custom Services: Our scientific team has extensive experience and expertise and can customize specific proteins, antibodies, or experimental protocols based on your specific needs. We provide customized services to meet your specific research requirements.
Resource Support: In addition to product supply, we also provide extensive resource support. We provide neurotrophin/Trk family-related pathways, protein functions, interacting proteins, related articles, and other related resources to help you better understand and study the functions and regulatory mechanisms of these important molecules.
Click on the neurotrophin/Trk family-related molecule catalog below for a more comprehensive resource.
We are dedicated to providing you with high-quality research tools and services to help you achieve successful scientific outcomes. If you have any further questions or require custom services, please feel free to contact us at any time.
References:
- Barbacid M. The Trk family of neurotrophin receptors. J Neurobiol. 1994 Nov;25(11):1386-403.
- Barbacid M. Structural and functional properties of the TRK family of neurotrophin receptors. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1995;766:442-458.
- Xie Z, Yang X, Duan Y, Han J, Liao C. Small-Molecule Kinase Inhibitors for the Treatment of Nononcologic Diseases. J Med Chem. 2021;64(3):1283-1345.
- Haddad Y, Adam V, Heger Z. Trk Receptors and Neurotrophin Cross-Interactions: New Perspectives Toward Manipulating Therapeutic Side-Effects. Front Mol Neurosci. 2017;10:130. Published 2017 May 3.

