What is CEBPB Protein
The CEBPB protein, otherwise known as the CCAAT Enhancer Binding Protein Beta (CEBPB), has always caught the scientific community's attention due to its remarkable ability to regulate genes involved in immune and inflammatory responses, hence playing a crucial role in human health and disease.
The CEBPB protein was first discovered as a member of the CCAAT enhancer binding protein family expressing proteins involved in regulating cellular differentiation and proliferation. This protein family enriches the biology with its expansive contribution to multiple biological pathways, of which immunological and inflammatory response pathways remain the most critical.
The gene loci of CEBPB are found on chromosome 20, specifically at the position 20q13.13 in human cells. Notably, this genetic positioning plays a critical role in understanding the anomalies that may impact the CEBPB gene's structure and function, thereby leading to disease states.
The protein structure of CEBPB is as noteworthy as the gene that encodes it. This protein belongs to the basic leucine zipper (bZIP) family, characterized by a leucine zipper region and a highly conserved basic region. The basic region's task is to facilitate DNA binding, while the zipper region assists in dimerization, a process vital for the protein's functionality.
Function of CEBPB protein
The primary function of the CEBPB protein revolves around regulating the transcription of genes involved in immune and inflammatory responses. As a transcription factor, CEBPB binds to the DNA at specific sites and can stimulate or inhibit gene expression. Besides, it plays an essential role in energy balance by regulating genes involved in glucose and lipid metabolism.
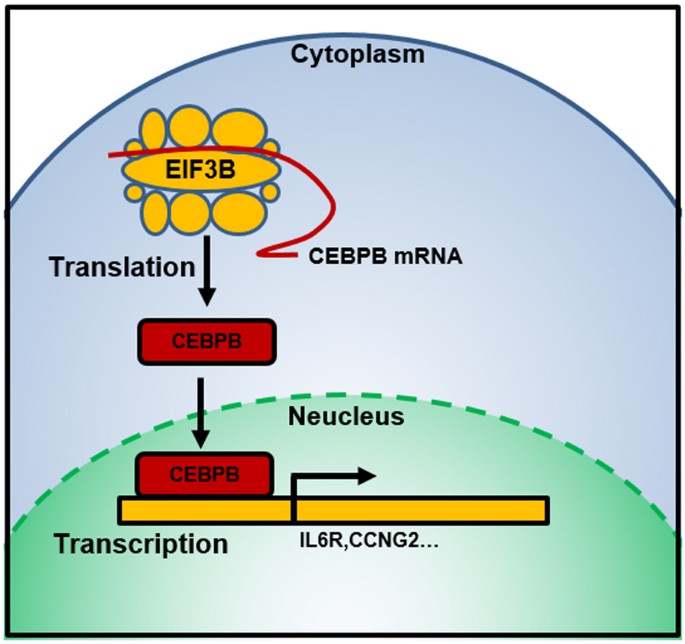
Fig1. CEBPB protein activates transcription (Xu, C., et al. 2022)
CEBPB protein related signal pathway
The CEBPB protein is involved in several signal pathways. The NF-kappa B signaling pathway remains most noteworthy, where CEBPB plays a vital role in inflammatory responses on stimulation by cytokines, bacterial or viral pathogens. Moreover, it also plays a critical role in the Janus kinase-signal transducer and activator of the transcription (JAK-STAT) signaling pathway, mediating cell growth, differentiation, and cell death.
CEBPB protein related diseases
Beyond physiological functions, the aberrations in the CEBPB protein have been linked to several diseases. Overexpression or underexpression of CEBPB can lead to chronic inflammation, one of the triggers for neurodegenerative diseases like Parkinson's and Alzheimer's. Moreover, alterations in CEBPB levels have been associated with various types of cancer, including breast cancer, colon cancer, and leukemia, because of its role in cell proliferation and differentiation.
CEBPB protein's applications in biomedical
Despite its link to several diseases, the CEBPB protein also holds potential for therapeutic intervention. Applying our understanding of CEBPB protein function and related signaling pathways can provide novel insights for medical applications in biomedicine. For instance, pharmacological modulation of CEBPB protein may serve as a therapeutic avenue in treating inflammatory conditions and cancer. Additionally, since CEBPB protein function is central to cellular energy balance, it may also pave the way for developing therapies for metabolic disorders.
In conclusion, the CEBPB protein, owing to its diverse roles, has emerged as an intriguing subject for research. Its intricate relationship with gene regulation, involvement in various signal pathways, and association with disease states make CEBPB protein a compelling candidate for further investigation. Importantly, leveraging the in-depth understanding of CEBPB protein's physiological and pathophysiological roles can open up new realms of possibilities in the world of biomedicine, thereby improving healthcare outcomes.
Our Featured Products
| Cat.No. | Product Name | Species | Source (Host) | Tag |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CEBPB-27010TH | Recombinant Human CEBPB, His-tagged | Human | E.coli | His |
| CEBPB-1101H | Recombinant Human CEBPB Protein, GST-Tagged | Human | Wheat Germ | GST |
| CEBPB-6222H | Recombinant Human CEBPB Protein, Myc/DDK-tagged, C13 and N15-labeled | Human | HEK293T | Myc/DDK |
| CEBPB-4893H | Recombinant Human CEBPB Protein, MYC/DDK-tagged | Human | HEK293T | Myc/DDK |
| CEBPB-3278HF | Recombinant Full Length Human CEBPB Protein, GST-tagged | Human | In Vitro Cell Free System | GST |
| CEBPB-543HFL | Recombinant Full Length Human CEBPB Protein, C-Flag-tagged | Human | Mammalian cells | Flag |
| CEBPB-573H | Recombinant Human CEBPB Protein, His (Fc)-Avi-tagged | Human | HEK293 | His (Fc)-Avi |
Reference
- Xu, C., Shen, Y., Shi, Y. et al. Eukaryotic translation initiation factor 3 subunit B promotes head and neck cancer via CEBPB translation. Cancer Cell Int 22, 161 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12935-022-02578-y

