What is JAG1 Protein
JAG1, or Jagged-1, is a crucial protein encoded by the JAG1 gene, officially known as "Jagged Canonical Notch Ligand 1." This protein is also recognized by its synonyms, including CD339 antigen, Alagille syndrome 1 protein, and HJ1. Belonging to the Serrate/Jagged/DSL (Delta/Serrate/Lag-2) family, JAG1 plays a pivotal role in cell signaling and development. Structurally, JAG1 is characterized by a DSL domain (Delta/Serrate/Lag-2), cysteine-rich region, and multiple EGF-like repeats.
Recent research advances in JAG1 have shed light on its significance in various cellular processes, influencing embryonic development, tissue homeostasis, and cell fate determination. The exploration of JAG1's structural characteristics has paved the way for a deeper understanding of its functional intricacies.
JAG1 Biological Functions and Molecular Mechanisms
JAG1 orchestrates essential biological functions by serving as a ligand for the Notch receptor. The interaction between JAG1 and Notch receptors triggers a series of molecular events, culminating in the activation of downstream signaling pathways. This intricate cascade plays a pivotal role in cell differentiation, proliferation, and apoptosis during development and adulthood.
At the molecular level, JAG1-Notch signaling influences various cellular processes, including neurogenesis, angiogenesis, and immune system modulation. The binding of JAG1 to Notch receptors initiates a cleavage process, releasing the Notch intracellular domain (NICD), which translocates to the nucleus. In the nucleus, NICD acts as a transcriptional regulator, modulating the expression of target genes that govern cell fate and function.
JAG1 Related Signaling Pathway
The JAG1-Notch signaling pathway is a highly conserved mechanism that regulates cell fate decisions and tissue development. Upon JAG1-Notch receptor interaction, the activation of downstream effectors, such as HES and HEY transcription factors, orchestrates a cascade of events. This pathway is crucial for maintaining tissue homeostasis and ensuring proper cellular responses to external cues.
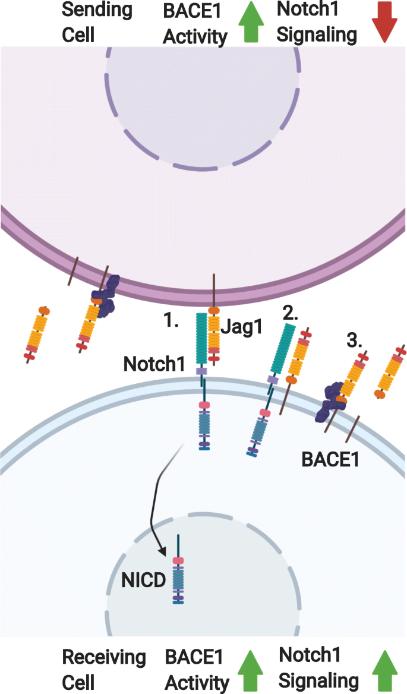
Figure 1. Jagged-1/Notch signaling and regulation in the context of BACE1 activity. (Fissel J A, et al., 2021)
Understanding the intricacies of the JAG1-related signal pathway provides valuable insights into the molecular basis of developmental processes and disease pathogenesis. Targeting specific components of this pathway holds promise for therapeutic interventions in conditions where JAG1 dysregulation is implicated.
JAG1 Related Diseases
The dysregulation of JAG1 has been implicated in several diseases, with Alagille syndrome being a notable example. Alagille syndrome is a rare genetic disorder characterized by liver, heart, and other organ abnormalities. Mutations in the JAG1 gene can disrupt normal Notch signaling, contributing to the diverse symptoms observed in affected individuals.
Additionally, aberrant JAG1 expression has been linked to certain cancers, emphasizing its role in tumorigenesis. The intricate involvement of JAG1 in disease pathogenesis underscores its potential as a therapeutic target for various conditions.
JAG1's Applications in Biomedicine
The versatile nature of JAG1 extends beyond its role in normal development and disease. In the realm of biomedical research, JAG1 has garnered attention for its potential applications in diagnostic development, vaccine design, and therapeutics.
Researchers are exploring the use of JAG1 as a diagnostic marker for diseases associated with Notch pathway dysregulation. The detection of JAG1 expression levels in clinical samples could serve as a valuable indicator of disease progression and prognosis.
In vaccine development, JAG1's involvement in immune system modulation opens avenues for novel strategies. Utilizing JAG1-derived peptides or mimetics in vaccine formulations could enhance immune responses, offering new possibilities for vaccine design and optimization.
Furthermore, the therapeutic potential of targeting JAG1-Notch signaling is being actively explored. Small molecules, antibodies, and gene therapies aimed at modulating JAG1 activity hold promise for treating conditions ranging from developmental disorders to cancer.
Recommended Products
| Cat.# | Product name | Species | Source (Host) | Tag |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JAG1-3226H | Active Recombinant Human JAG1 protein, His-tagged | Human | HEK293 | His |
| JAG1-344H | Recombinant Human JAG1 Protein, MYC/DDK-tagged, C13 and N15-labeled | Human | HEK293 | C-Myc/DDK |
| JAG1-3138H | Active Recombinant Human JAG1, Fc tagged | Human | HEK293 | Fc |
| JAG1-1226H | Recombinant Human JAG1 Protein, His (Fc)-Avi-tagged | Human | HEK293 | His (Fc)-Avi |
| JAG1-792H | Recombinant Human JAG1 Protein, MYC/DDK-tagged | Human | HEK293 | Myc/DDK |
| JAG1-1115HFL | Recombinant Full Length Human JAG1 Protein, C-Flag-tagged | Human | Mammalian cells | Flag |
| JAG1-379H | Active Recombinant Human JAG1 protein, Fc-tagged | Human | CHO | Fc |
| JAG1-4065H | Recombinant Human JAG1 Protein (Met1-Ser1046), C-His tagged | Human | Mammalian cells | C-His |
| JAG1-5856H | Recombinant Human JAG1 protein, hFc-Myc-tagged | Human | HEK293 | hFc-Myc |
| JAG1-338H | Recombinant Human JAG1 Protein, His-tagged | Human | HEK293 | His |
Reference
- Fissel J A, Farah M H. The influence of BACE1 on macrophage recruitment and activity in the injured peripheral nerve. Journal of Neuroinflammation. 2021, 18(1): 1-14.

