Jag1
-
Official Full Name
jagged 1 -
Overview
The jagged 1 protein encoded by JAG1 is the human homolog of the Drosophilia jagged protein. Human jagged 1 is the ligand for the receptor Notch-1, the latter a human homolog of the Drosophilia jagged receptor notch. Mutations that alter the jagged 1 protein cause Alagille syndrome. Jagged 1 signalling through notch 1 has also been shown to play a role in hematopoiesis. -
Synonyms
Jagged1;JAG1;AGS;AHD;AWS;CD339;HJ1;JAGL1;jagged 1
Recombinant Proteins
- Human
- Rat
- Mouse
- Rhesus macaque
- HEK293
- CHO
- E.coli
- Mammalian Cells
- Human Cells
- NS0
- His
- Fc
- Avi
- Myc
- SUMO
- Non
- hIgG4
- Flag
- DDK
- GST
Background
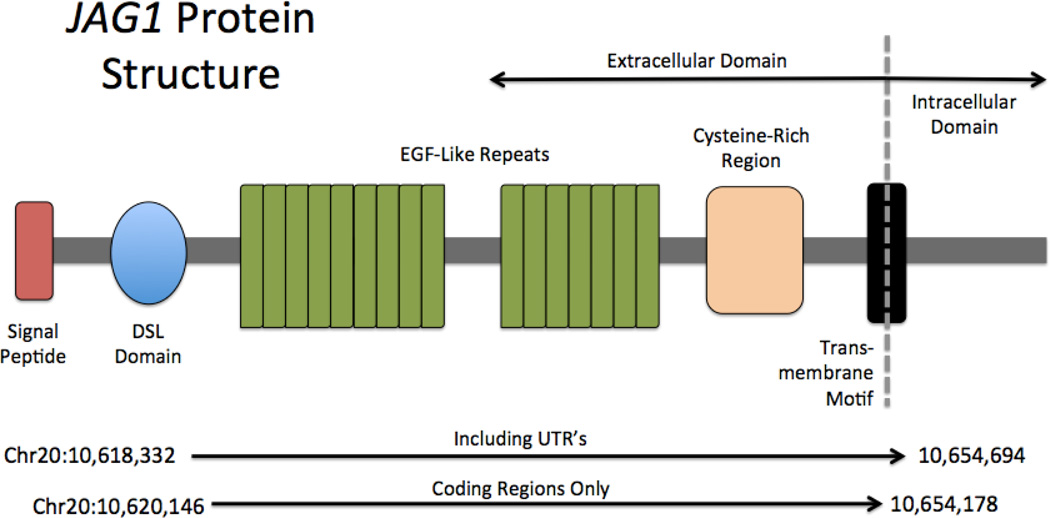
Fig1. JAG1 protein structure. (Christopher M Grochowski, 2016)
What is JAG1 protein?
JAG1 gene (jagged canonical Notch ligand 1) is a protein coding gene which situated on the short arm of chromosome 20 at locus 20p12. JAG1 is a cell surface ligand that primarily plays a role in the highly conserved Notch signaling pathway. Notch signaling plays a critical role in cell fate determination and is active during development as well as in multiple organ systems. Typical interactions between JAG1 and Notch result in a series of proteolytic cleavages, with the result that the Notch intracellular domain is transported into the nucleus, where it activates transcription of downstream target genes. The JAG1 protein is consisted of 1218 amino acids and JAG1 molecular weight is approximately 133.8 kDa.
What is the function of JAG1 protein?
JAG1 protein is a type I transmembrane protein that belongs to the Notch family of receptors. It is involved in the development and maintenance of the nervous system, as well as in the regulation of cell proliferation, differentiation, and apoptosis. JAG1 protein interacts with the NOTCH receptor to activate the NOTCH signaling pathway, which is important for regulating cell fate decisions during embryonic development. In addition, JAG1 protein has been implicated in a number of human diseases, including cancer, Alzheimer's disease, and schizophrenia.
JAG1 related signaling pathway
By binding to the Notch receptor, JAG1 triggers a series of proteolytic cleavage processes, resulting in the transport of the Notch intracellular domain (NICD) into the nucleus and activation of transcription of downstream target genes. This signaling pathway plays a crucial role in cell fate determination, cell proliferation, differentiation, migration and apoptosis.
In tumors, the formation of JAG1's intracellular domain (JICD1) is enhanced by carcinogenic signals including IL-4-PI3Kd/AKT or KRAS/ERK/ADAM17 signaling. JICD1 enhances tumor formation by forming transcription complex with DEAD-box helicase 17 (DDX17)/SMAD family member 3 (SMAD3)/ TGF-β-induced factor homeobox 2 (TGIF2).
JAG1 related diseases
JAG1 protein (Jagged1) is a cell surface ligand that is mainly involved in the Notch signaling pathway. This signaling pathway plays a key role in cell fate determination, tissue development and maintenance of tissue homeostasis. Mutations in JAG1 have been linked to a variety of diseases, notably Alagille syndrome, a multisystem dominant genetic disorder affecting the liver, heart, bones, eyes, face, kidneys, and vascular systems. In addition, mutations in the JAG1 gene have also been linked to several types of cancer, including breast cancer and adrenal cortical cancer. In cancer, JAG1 overexpression is associated with tumor aggressiveness, metastasis and poor prognosis, and it promotes tumor cell proliferation, survival, chemotherapy resistance and cancer stem cell characteristics by activating Notch signaling pathway.
Bioapplications of JAG1
Practical applications related to JAG1 are mainly in the fields of medicine and biotechnology, especially its potential in tumor therapy, neurodegenerative disease research and drug development. Since the JAG1 protein is involved in the regulation of the NOTCH signaling pathway, which is often malregulated in a variety of cancers, JAG1 has become a potential anticancer therapeutic target. By developing inhibitors or antibodies against JAG1, abnormal NOTCH signaling can be blocked, thereby inhibiting tumor growth. In addition, JAG1 also plays an important role in nervous system development and disease, and studying the function of JAG1 can help to understand and treat neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer's disease. In drug development, small molecules or biologics that regulate JAG1 expression or function are being investigated to explore their application value in clinical therapy.
Case Study
Case Study 1: Archana Kamalakar, 2021
JAG1, a protein involved in craniofacial bone development, shows promise as a regenerative therapy for pediatric bone loss, where current BMP2 treatment is unsafe. This study demonstrates that JAG1, delivered via synthetic hydrogels with O9-1 CNC cells, effectively regenerates bone in C57BL/6 mice calvarial defects. JAG1 activates both canonical (Hes1/Hey1) and non-canonical (JAK2) NOTCH pathways, inducing osteoblast commitment and proliferation, as well as upregulating bone-related genes and inhibiting osteoclasts. This approach could improve upon existing autologous bone graft techniques and provide a safer alternative for children.
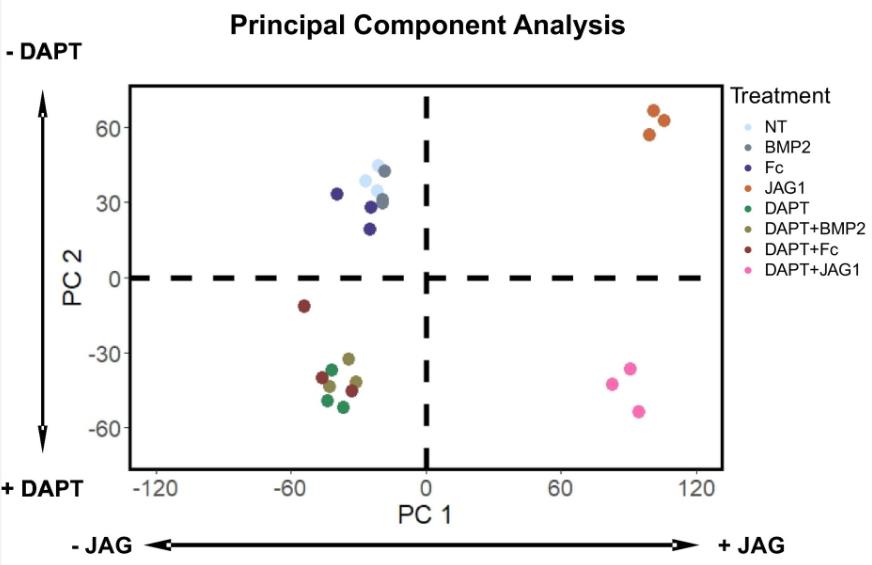
Fig1. PC1 distinguished JAG1-treated cells to the right from non-JAG1 treated cells to the left along the horizontal axis.
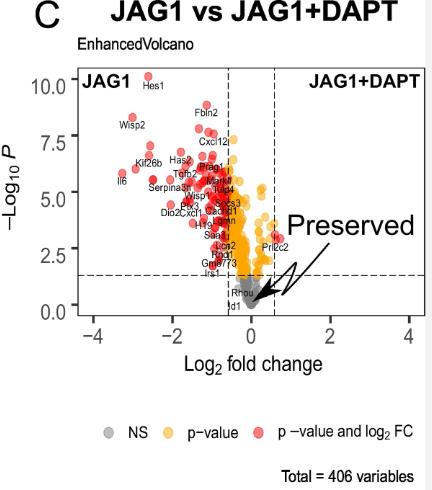
Fig2. Subsequent comparison of the JAG1 and JAG1 + DAPT treatment groups for genes.
Case Study 2: Archana Kamalakar, 2019
In craniofacial development, JAG1 signaling is crucial for CNC cell migration and intramembranous ossification, essential for maxillary bone formation. This study shows that JAG1 promotes osteoblast differentiation in CNC cells, as indicated by increased Runx2, Ocn, and ALP levels, independent of the canonical NOTCH pathway. Instead, JAG1 activates the non-canonical NOTCH pathway via JAK2 phosphorylation, which is essential for osteoblast commitment and maturation.
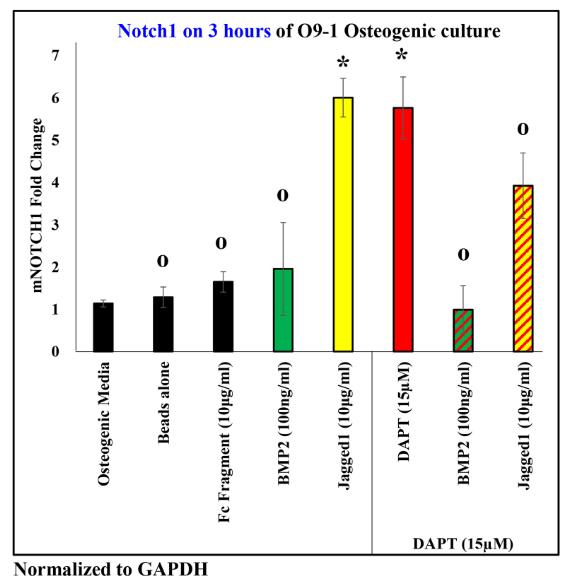
Fig3. The expression of all genes induced by JAG1 was observed to be inhibited by a canonical NOTCH pathway inhibitor, DAPT.
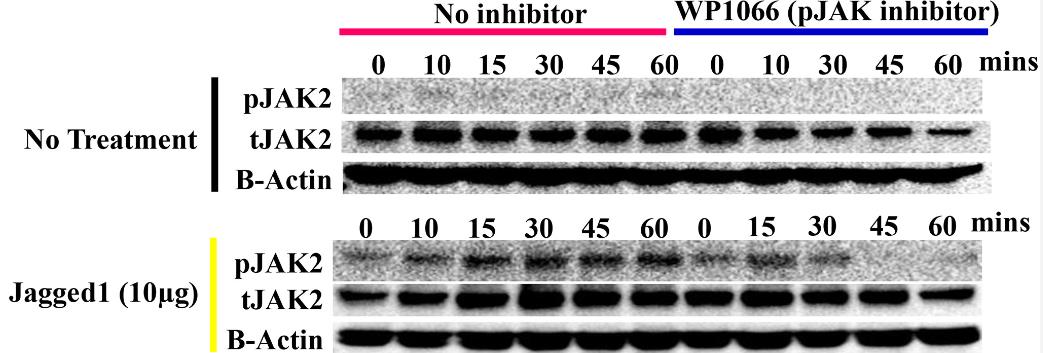
Fig4. Dynabeads bound recombinant JAG1-Fc fragment, were probed for phosphorylated JAK2.
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
.jpg)
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (JAG1-2348H)
.
.jpg)
Fig2. SDS-PAGE (JAG1-4065H)
Involved Pathway
Jag1 involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways Jag1 participated on our site, such as Activated NOTCH1 Transmits Signal to the Nucleus,Constitutive Signaling by NOTCH1 HD Domain Mutants,Constitutive Signaling by NOTCH1 HD+PEST Domain Mutants, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with Jag1 were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| Disease | FKBP1A,ARF1,PSIP1,ANTXR2,DERL2,KPNA5,LRRFIP1,LTF,FMOD,CPSF6 |
| Constitutive Signaling by NOTCH1 t(7 | JAG2 |
| 9)(NOTCH1:M1580_K2555) Translocation Mutant | JAG2 |
| Constitutive Signaling by NOTCH1 PEST Domain Mutants | ADAM10,MIB1,HEY1,HEY2,CDK8,HDAC5,HDAC6,JAG2,HEYL,CCNC |
| Diseases of signal transduction | FGFR1OP,HEY2,CDK8,FGFR1OP2,RBP4,HEYL,OPN1MW2,OS9,KREMEN2,OPN1MW |
| Delta-Notch Signaling Pathway | HIVEP3,CNTF,CNTFR,TLE1,TCF3B,ADAM10A,WDR12,CNTN1,TUBB3,ZFPM1 |
| Constitutive Signaling by NOTCH1 HD+PEST Domain Mutants | HEY2,HEY1,HDAC5,MIB1,HDAC6,HEYL,CCNC,ADAM10,CDK8,JAG2 |
| Activated NOTCH1 Transmits Signal to the Nucleus | MIB1,ADAM10,DTX2,DLK1,CNTN1,DNER,JAG2 |
| Constitutive Signaling by NOTCH1 HD Domain Mutants | JAG2,MIB1,ADAM10 |
Protein Function
Jag1 has several biochemical functions, for example, Notch binding,calcium ion binding,growth factor activity. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by Jag1 itself. We selected most functions Jag1 had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with Jag1. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| calcium ion binding | PCDHB14,SLIT3,KCNIP4,PCDH2AB9,EHD3,SLIT1B,MBL2,SYTL1,FKBP7,PCDH2G17 |
| protein binding | SRRT,TCF25,MCM6,RBCK1,NCOA3,LMF2,SMARCD1,ABCF1,MTAP1B,GABPB2 |
| structural molecule activity | KRT77,CLDN1,ISCA1,SEPT5,CLDN15LB,MAP7D1,EVPLA,CLDNB,NEFLB,COL15A1B |
| Notch binding | SNW1,NOTCH4,HIF1AN,ADAM17,GALNT11,JAG1A,NCOR2,DNER,JAG2,DTX1 |
| growth factor activity | NRG3,IL3,BMP6,FGF1,OGN,AGT,CSF1A,PROK1,MDK,PDGFAB |
Interacting Protein
Jag1 has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with Jag1 here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of Jag1.
CD46;NOTCH1;ADAM17;NOTCH3;mdtB;argS;CALR;CANX
Resources
Research Area
Related Services
Related Products
References
- Huntzicker, EG; Hotzel, K; et al. Differential Effects of Targeting Notch Receptors in a Mouse Model of Liver Cancer. HEPATOLOGY 61:942-952(2015).
- Lin, YY; Chen, WL; et al. Overexpression of Jagged-1 combined with blockade of CD40 pathway prolongs allograft survival. IMMUNOLOGY AND CELL BIOLOGY 93:213-217(2015).
Reviews
Thanks for reaching out, I hope you’ve been well. Yes, your product worked as great as it always has for us, thank you for asking



