What is L1CAM Protein
The L1 cell adhesion molecule, or L1CAM, is a transmembrane glycoprotein that plays a crucial role in various cellular processes. Also known by its official full name CD171, L1CAM is often referred to by synonyms such as Neural Cell Adhesion Molecule L1 and N-CAM-L1. Belonging to the immunoglobulin superfamily, L1CAM is a type I integral membrane protein that is primarily expressed in the nervous system. Recent research advances have shed light on its multifaceted functions and implications in various physiological and pathological conditions.
L1CAM Protein Structural Characteristics and Classification
Structurally, L1CAM is characterized by six immunoglobulin-like domains, five fibronectin type III repeats, a transmembrane domain, and a cytoplasmic tail. The extracellular region is involved in cell adhesion, while the cytoplasmic tail interacts with the cellular cytoskeleton, contributing to its diverse functions. Within the immunoglobulin superfamily, L1CAM is a member of the L1 subfamily, which includes closely related cell adhesion molecules.
L1CAM Biological Functions and Molecular Mechanisms
The biological functions of L1CAM are broad and pivotal, encompassing cell adhesion, migration, neurite outgrowth, and signal transduction. L1CAM is particularly crucial in neural development, where it promotes neurite outgrowth and guides axon pathfinding. Additionally, L1CAM facilitates cell-cell adhesion in various tissues, influencing tissue architecture and organ development. The molecular mechanisms underlying L1CAM's functions involve interactions with other cell adhesion molecules, cytoskeletal elements, and intracellular signaling pathways.
L1CAM Related Signaling Pathway
The signaling pathways activated by L1CAM are diverse and context-dependent. In neural development, L1CAM interacts with various receptors, including integrins and fibroblast growth factor receptors, triggering downstream signaling cascades that regulate neurite outgrowth and axon guidance. In cancer, L1CAM promotes tumor progression by activating pathways such as PI3K/Akt and MAPK, enhancing cell survival, migration, and invasion. Elucidating these signal pathways is crucial for developing targeted therapies to modulate L1CAM-mediated signaling in pathological conditions.
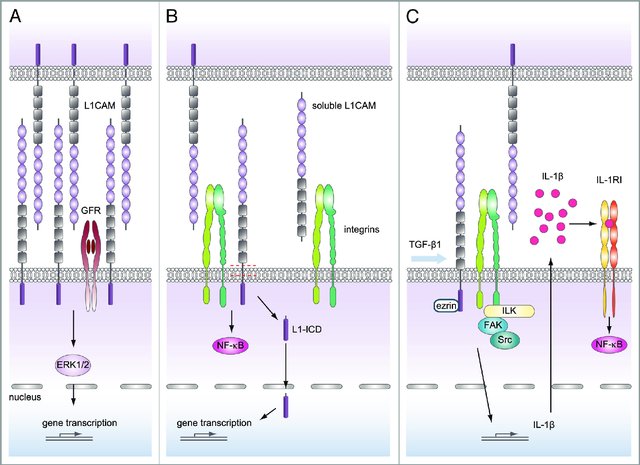
Figure 1. L1CAM can trigger different signaling pathways. (Kiefel H, et al., 2012)
L1CAM Related Diseases
Despite its essential role in normal physiological processes, dysregulation of L1CAM has been implicated in several diseases. Mutations or abnormal expression of L1CAM have been associated with neurological disorders, including X-linked hydrocephalus and mental retardation. Moreover, aberrant L1CAM expression has been observed in various cancers, promoting tumor invasion and metastasis. Understanding the involvement of L1CAM in disease pathogenesis provides valuable insights for potential therapeutic interventions.
L1CAM's Applications in Biomedicine
The unique properties and functions of L1CAM make it a promising target for biomedical applications. In diagnostic development, L1CAM is being explored as a biomarker for certain cancers, aiding in early detection and prognosis assessment. Additionally, L1CAM's involvement in neural development positions it as a potential target for therapeutic interventions in neurological disorders. In vaccine development, researchers are investigating L1CAM-derived peptides to stimulate immune responses against cancer cells expressing aberrant L1CAM. These applications underscore the potential of L1CAM as a versatile tool in advancing biomedical research and clinical practices.
Recommended Products
Reference
- Kiefel H, et al. L1CAM: a major driver for tumor cell invasion and motility. Cell Adhesion & Migration. 2012, 6(4): 374-384.

