What is LOXL4 Protein
In the intricate world of molecular biology, the lysyl oxidase like 4 (LOXL4) protein stands out as a fascinating and enigmatic player.
What is LOXL4 Protein?
LOXL4, a member of the lysyl oxidase (LOX) family, commands attention in the intricate landscape of molecular biology. LOXL4 stands out for its role in catalyzing the cross-linking of collagen and elastin fibers, essential for maintaining the structural integrity of connective tissues. This enzyme plays a pivotal role in the formation and stabilization of the extracellular matrix (ECM), contributing significantly to the architectural strength of various tissues.
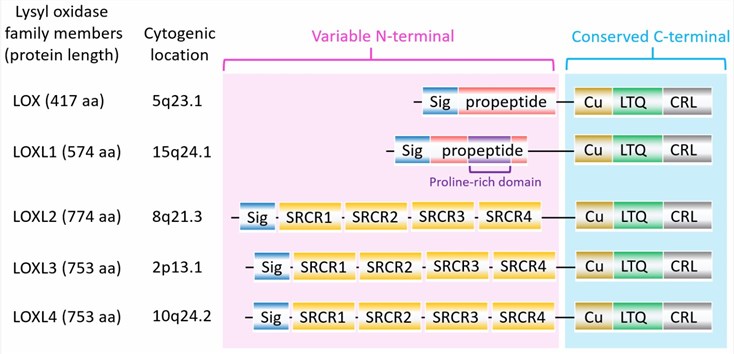
Figure 1. The structure of lysyl oxidase (LOX) family members. (Lin, H.Y., et al. 2020)
The Function of LOXL4 Protein
- Extracellular Matrix Remodeling
LOXL4's primary function lies in orchestrating the modification and restructuring of the extracellular matrix. Through oxidative deamination, LOXL4 catalyzes the cross-linking of lysine residues in collagen and elastin, promoting the formation of a robust and stable matrix. This process is indispensable for tissue development, wound healing, and maintaining tissue elasticity.
- Cell Adhesion and Migration
Beyond its role in ECM remodeling, LOXL4 influences cellular behavior by regulating adhesion molecules and interacting with integrins. This dynamic involvement contributes to cell movement during tissue repair and development, shedding light on the complex relationship between LOXL4 and cellular processes.
- Tumor Suppression and Oncogenic Roles
LOXL4's role in cancer is a paradox worth exploring. While some studies suggest its tumor-suppressive nature, inhibiting cell proliferation and promoting apoptosis, others hint at its potential oncogenic properties, fueling tumor progression and metastasis. The dual role of LOXL4 in cancer underscores its complexity and necessitates nuanced investigation for precise therapeutic interventions.
LOXL4-Related Diseases
- Connective Tissue Disorders
Dysregulation of LOXL4 manifests in various connective tissue disorders, such as Ehlers-Danlos syndrome and Marfan syndrome. These conditions, characterized by defects in collagen and elastin synthesis, underscore LOXL4's critical role in maintaining the structural integrity of tissues, and deviations from the norm contribute to pathological conditions.
- Cancer
The involvement of LOXL4 in cancer is multifaceted, with altered expression observed in breast, colorectal, and pancreatic cancer. Deciphering the exact mechanisms through which LOXL4 contributes to tumorigenesis is crucial for targeted therapeutic development, offering hope for innovative cancer treatments.
- Cardiovascular Diseases
LOXL4 extends its influence to cardiovascular health, with aberrant activity linked to atherosclerosis and cardiac fibrosis. In these contexts, LOXL4 contributes to the restructuring of vascular and cardiac tissues, implicating its role in the progression of cardiovascular diseases.
LOXL4 Related Signaling Pathways
The intricate signaling pathways associated with LOXL4 often converge with the Transforming Growth Factor-beta (TGF-β) pathway. LOXL4 expression regulation by TGF-β, coupled with its reciprocal influence on TGF-β signaling components, intricately modulates cellular processes. This interplay significantly impacts normal physiological functions and disease states, underscoring the complexity of LOXL4-associated signaling pathways.
Applications of LOXL4 in Biomedical Research
- Biomarker for Disease Diagnosis
LOXL4's dysregulation in various diseases positions it as a potential biomarker for diagnostic purposes. Monitoring LOXL4 expression levels in patient samples could provide valuable insights into the progression of connective tissue disorders, certain cancers, and cardiovascular diseases.
- Therapeutic Target in Cancer Treatment
The intricate involvement of LOXL4 in cancer progression positions it as a promising therapeutic target. Developing drugs that selectively modulate LOXL4 activity offers a novel approach to cancer treatment, exploiting its dual nature for precise intervention strategies.
- Tissue Engineering and Regenerative Medicine
Understanding LOXL4's role in ECM remodeling unveils opportunities for applications in tissue engineering and regenerative medicine. Harnessing LOXL4's ability to modify the extracellular matrix could pave the way for designing biomaterials that mimic native tissue environments, promoting better integration and functionality of engineered tissues.
The LOXL4 protein emerges as a multifaceted entity with profound implications in health and disease. From its foundational role in ECM remodeling to its intricate involvement in diseases and signaling pathways, LOXL4 captivates researchers with its potential applications in diagnostics, therapeutics, and regenerative medicine. As investigations into LOXL4 progress, the promise of transformative discoveries in the biomedical realm looms large on the horizon.
Recommended Products for LOXL4 Protein
| Cat.# | Species | Product name | Source (Host) | Tag |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LOXL4-2158H | Human | Recombinant Human LOXL4 protein, His-tagged | E.coli | His |
| LOXL4-194H | Human | Recombinant Human LOXL4 protein, GST-tagged | Insect Cell | GST |
| LOXL4-2157H | Human | Recombinant Human LOXL4 protein, GST-tagged | Wheat Germ | GST |
| LOXL4-2159H | Human | Recombinant Human LOXL4 protein, FLAG-tagged | Insect Cell | FLAG |
| LOXL4-4705H | Human | Recombinant Human LOXL4 protein, His-tagged | E.coli | His |
| LOXL4-577HF | Human | Recombinant Full Length Human LOXL4 Protein, GST-tagged | In Vitro Cell Free System | GST |
| LOXL4-280H | Human | Recombinant Human LOXL4 Protein, His-tagged | E.coli | His |
| LOXL4-5209H | Human | Recombinant Human LOXL4 Protein (Gly399-Pro552), His tagged | E.coli | His |
| LOXL4-2020M | Mouse | Recombinant Mouse LOXL4 Protein (26-757 aa), His-tagged | Yeast | His |
| Loxl4-1742M | Mouse | Recombinant Mouse Loxl4 Protein, His-tagged | E.coli | N-His |
Reference
- Lin, H.Y., et al. Roles of Lysyl Oxidase Family Members in the Tumor Microenvironment and Progression of Liver Cancer. Int J Mol Sci. 2020, 21(24): 9751.

