What is PTPN6 Protein
Protein Tyrosine Phosphatase, Non-Receptor Type 6 (PTPN6), is a protein encoded by the PTPN6 gene in humans. It is pivotal in numerous biological activities, including immune response, cellular growth and differentiation, hematopoiesis, and oncogenesis.
The PTPN6 protein was initially identified in the year 1993, as a result of a scientific investigation aiming at revealing the elemental characteristics of immune responses. The PTPN6 gene lies within a region at the long arm of human chromosome 12, specifically at position 12q24. This gene is structurally composed of 17 exons with its transcription commencing from a typical TATA-less promoter.
The PTPN6 protein consists of 597 amino acids, characterized by two Src homology 2 (SH2) domains at the amino terminal, a catalytic domain and a carboxy-terminal tail. The N-terminal SH2 domains facilitate the binding of this protein to specific phosphotyrosine residues on its target substrates, while the carboxy-terminal element is believed to be implicated in cellular localization.
Function of PTPN6 protein
The primary function of the PTPN6 protein relates to enzymatic activity. It is a key player in the regulation of numerous cell signaling mechanisms crucial for various cell functions, mainly in the immune system. This protein acts as a negative regulator of the intrinsic cell signaling, which develops through the cell receptor-antigen bond, modulating processes such as proliferation, differentiation and inflammatory reactions of cells.
PTPN6 protein related signal pathway
PTPN6 contributes to several signaling pathways, including the JAK-STAT signaling pathway, which regulates processes such as cell division, survival, and inflammation. It also interacts with signaling elements like JAKs, STATs, SOCS, and the epidermal growth factor receptor. Misregulation of PTPN6 can, therefore, lead to aberrant cytokine signaling which contributes to immune and inflammatory diseases.
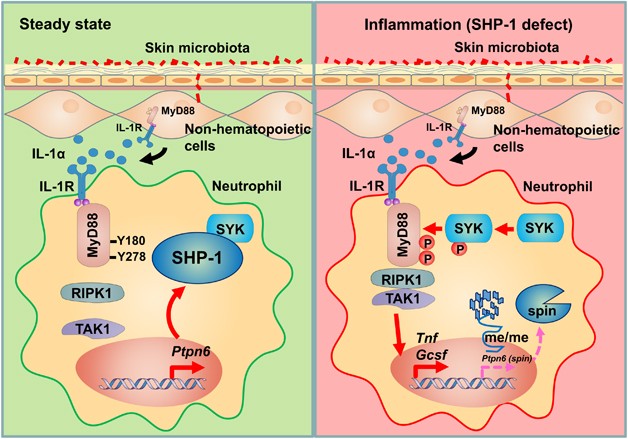
Fig1. SHP-1 (PTPN6) keeps the inflammation (You, R., et al. 2017)
PTPN6 protein modulates the growth factor-induced cell signaling pathway as well, which is vital for cell proliferation, differentiation, and migration. By specifically dephosphorylating a tyrosine residue in the EGFR, it can negatively regulate EGF-induced cell proliferation and tumorigenesis.
PTPN6 protein related diseases
Dysfunction or aberrant expression of PTPN6 contributes to several disease conditions. For instance, PTPN6 has been associated with several types of cancer such as lung, breast, and gastric cancers. In hematological malignancies, much work has particularly focused on the role of PTPN6 in leukemia immune escape, suggesting PTPN6 as a potential therapeutic target in these conditions.
In addition, several studies have implicated the PTPN6 gene in autoimmune diseases. Specific mutations in PTPN6 gene have been identified in mouse models which develop a disease similar to human systemic lupus erythematosus. It has also been linked to the susceptibility of rheumatoid arthritis in humans.
PTPN6 protein's applications in biomedical
PTPN6's clear involvement in several critical cell processes, its relation to disease, and its easily targetable nature make it a vital focus area within biomedical application development. In cancer therapy, for example, inhibitory peptides or small molecules could be designed to selectively inhibit PTPN6 activity and prevent cancer progression.
Similarly, in targeted therapy for autoimmune diseases, novel approaches to modulate PTPN6 activity could balance immune responses and prevent disease development. It's also worth noting that PTPN6 could be a potential diagnostic or prognostic marker in certain types of cancers due to its specific pattern of expression.
In conclusion, the PTPN6 protein plays essential roles in various biological processes, primarily related to immune responses. Its interactions with multiple signaling pathways place it at the juncture of many critical cell functions. While its dysfunction is implicated in several disease states, this also provides opportunities for its use in diagnostic, prognostic, and therapeutic applications, making it a significant interest in the burgeoning field of precision medicine. More research will give us a holistic understanding of its functions and applications to fully harness its potential in medical science.
Our Featured Products
| Cat.No. | Product Name | Species | Source (Host) | Tag |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PTPN6-2501H | Recombinant Human PTPN6 protein, His-tagged | Human | E.coli | His |
| PTPN6-6233H | Recombinant Human PTPN6 Protein, Myc/DDK-tagged, C13 and N15-labeled | Human | HEK293T | Myc/DDK |
| PTPN6-1360HFL | Recombinant Full Length Human PTPN6 Protein, C-Flag-tagged | Human | Mammalian cells | Flag |
| Ptpn6-1102M | Recombinant Mouse Ptpn6 Protein, MYC/DDK-tagged | Mouse | HEK293T | MYC/DDK |
| PTPN6-4494R | Recombinant Rat PTPN6 Protein, His (Fc)-Avi-tagged | Rat | HEK293 | His (Fc)-Avi |
Reference
- You, R., & Chu, C. (2017). SHP-1 (PTPN6) keeps the inflammation at bay: Limiting IL-1α-mediated neutrophilic dermatoses by preventing Syk kinase activation. Cellular & Molecular Immunology, 14(11), 881-883. https://doi.org/10.1038/cmi.2017.59

