BMPR1B
-
Official Full Name
bone morphogenetic protein receptor, type IB -
Overview
Bone morphogenetic proteins (BMP); are members of the transforming growth factor beta (TGF-beta); superfamily and are involved in a wide variety of biological processes, including osteoblast differentiation and bone healing. The activities of the BMP are -
Synonyms
BMPR1B;bone morphogenetic protein receptor, type IB;bone morphogenetic protein receptor type-1B;ALK6;CDw293;BMPR-1B;BMP type-1B receptor;activin receptor-like kinase 6;serine/threonine receptor kinase;ALK-6
Recombinant Proteins
- Human
- Rhesus macaque
- Chicken
- Mouse
- E.coli
- HEK293
- Insect Cells
- Wheat Germ
- Human Cells
- Mammalian Cells
- Sf9 Cells
- Sf21 Cells
- In Vitro Cell Free System
- His
- Avi
- Fc
- GST
- Non
Background
What is bmpr1b protein?
BMPR1B (Bone morphogenetic protein receptor type-1B) is a protein that belongs to the serine/threonine kinase receptor family. It is a cell surface receptor that binds to specific growth factors called bone morphogenetic proteins (BMPs). BMPR1B plays a critical role in embryonic development, bone formation, and organogenesis.
As a receptor, BMPR1B is involved in the BMP signaling pathway, which regulates various cellular processes including cell growth, differentiation, and apoptosis. Activation of BMPR1B by binding to BMP ligands leads to the phosphorylation of downstream signaling molecules called Smads, resulting in the activation of target genes that control cell fate and tissue development.
Mutations in the BMPR1B gene have been associated with a variety of disorders and abnormalities. For example, mutations in BMPR1B can lead to acromesomelic dysplasia, a rare skeletal disorder characterized by abnormal limb development. Additionally, alterations in BMPR1B activity have been implicated in cancer progression and metastasis, highlighting the importance of this protein in both normal development and disease processes.
What is the function of bmpr1b protein?
The function of BMPR1B is to bind BMP ligands and initiate downstream signaling cascades. Upon binding to BMP ligands, BMPR1B activates the SMAD signaling pathway, leading to the phosphorylation of SMAD1/5/8 proteins. Phosphorylated SMADs then form complexes with co-SMAD and translocate into the nucleus, where they regulate the expression of target genes involved in various cellular processes.
BMPR1B is particularly involved in the regulation of skeletal development and bone formation. It plays a crucial role in the differentiation and proliferation of osteoblasts, the cells responsible for bone formation. Additionally, BMPR1B signaling is involved in the development of other tissues and organs, such as the heart, lungs, and reproductive system.
Bmpr1b related signaling pathway
The signaling pathway activated by Bmpr1b involves the phosphorylation and activation of downstream effectors, particularly SMAD proteins. Upon ligand binding, Bmpr1b phosphorylates SMAD1, SMAD5, or SMAD8, which then form complexes with SMAD4. These SMAD complexes translocate into the nucleus and regulate the expression of target genes involved in various cellular functions.
In addition to the SMAD-dependent pathway, Bmpr1b can also activate non-SMAD signaling pathways such as the MAPK/ERK, JNK, and p38 pathways, which further contribute to the diverse biological effects of BMP signaling.
Bmpr1b Related Diseases
Bmpr1b dysregulation or mutations can lead to various diseases and developmental disorders. For instance, mutations in the Bmpr1b gene have been associated with brachydactyly type A2, a genetic skeletal disorder characterized by shortened fingers or toes. Bmpr1b mutations have also been implicated in the development of pulmonary arterial hypertension, a condition characterized by increased blood pressure in the arteries of the lungs.
Biomedical Application of bmpr1b Protein
Altered expression or mutations in the Bmpr1b gene can lead to various disorders and diseases. For example, loss of Bmpr1b function in mice results in skeletal deformities and defects in limb development. Mutations in Bmpr1b have also been associated with hereditary forms of syndromic and nonsyndromic craniosynostosis, which affect skull bone fusion during development.
In terms of biomedical applications, understanding the role of Bmpr1b protein and its signaling pathway is essential for development of therapeutic interventions. Manipulating the activity of Bmpr1b or its downstream signaling components could potentially be used to modulate tissue repair and regeneration, as well as to treat bone disorders, congenital malformations, and certain types of cancers that involve dysregulated BMP signaling.
Case Study
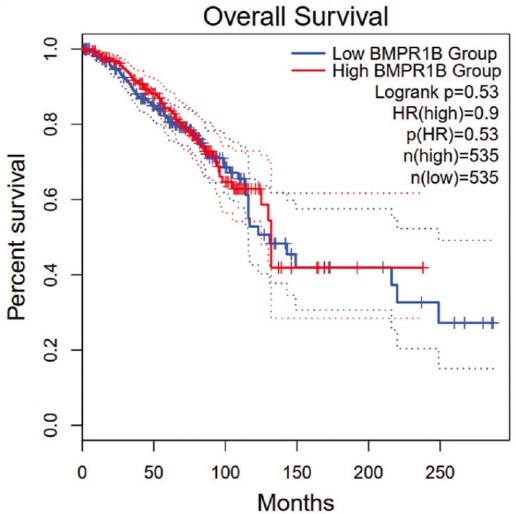
(Azadeh, Mansoureh, 2023)
Fig2. Survival analysis of BMPR1B, based on GEPIA2 online database. The x axis of this plot represents the time (month) and the y axis represents the precent survival of the patients. Red color indicates the patients with high expression level and the blue color indicates the patients with low expression level. According to this analysis, there is a non-significant correlation between the low expression of BMPR1B and low survival rate of the patients.
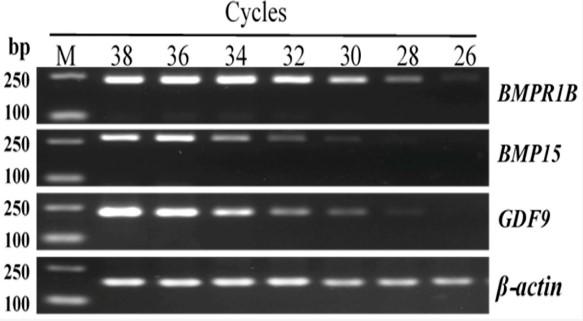
(Jishun Tang, 2018)
Fig3. Amplification results of BMPR1B, BMP15, and GDF9 in different reaction cycles.
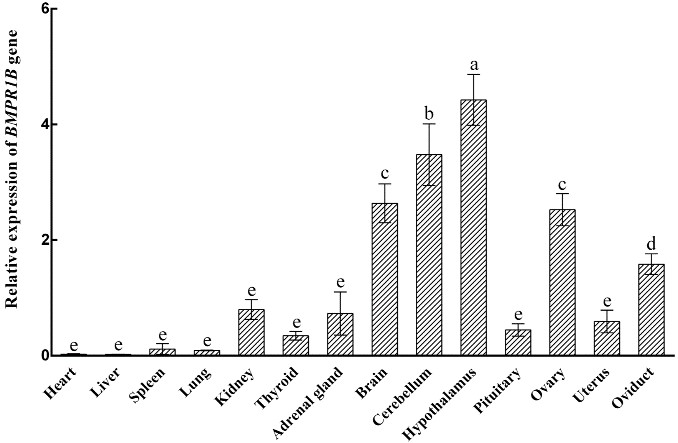
(Yu-Liang Wen, 2021)
Fig4. Relative expression of the BMPR1B gene in various tissue types in small-tail Han sheep in the follicular phase.
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (BMPR1B-283H)
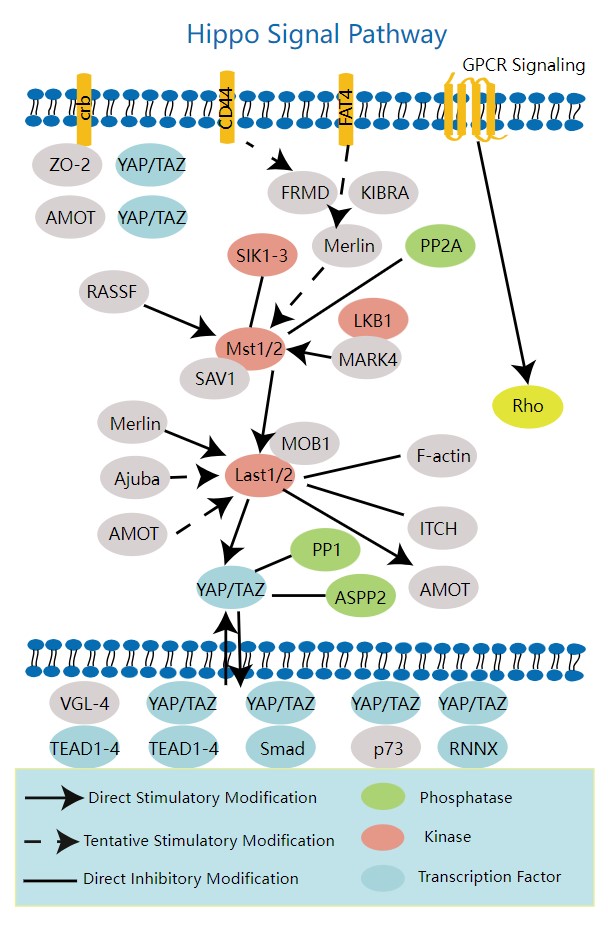
Involved Pathway
BMPR1B involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways BMPR1B participated on our site, such as Cytokine-cytokine receptor interaction,TGF-beta signaling pathway,Hippo signaling pathway, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with BMPR1B were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| Hippo signaling pathway | FZD5,WNT2B,WNT8A,SMAD3,CDH1,WNT2,TEAD2,CTNNA3,BMP8A,TEAD3 |
| TGF-beta signaling pathway | ID2,RHOA,SMAD7B,ACVR1BA,LEFTY2,ACVR1L,CHD,RHOAA,MYCB,TGFBR1B |
| Signaling pathways regulating pluripotency of stem cells | FZD3,ID3,BMI1,WNT7A,PIK3R1,REST,FGFR2,INHBB,ACVR2A,BMPR1A |
| Cytokine-cytokine receptor interaction | LTBR,EDA2R,XCL1,EDA,LOC100033925,CCL27,CCL7,CCL22,TNF,TP-1 |
Protein Function
BMPR1B has several biochemical functions, for example, ATP binding,SMAD binding,glycoprotein binding. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by BMPR1B itself. We selected most functions BMPR1B had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with BMPR1B. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| glycoprotein binding | FYN,TGFB1,SERPINA1,CALR,DNAJA2,EDEM2,FOXRED2,PLAT,LACRT,FBXO6 |
| protein binding | PPARA,IL28RA,ANXA10,ZC3H8,PEX11A,CBLB,RPL22,KHDRBS3,DMKN,FLI1 |
| ATP binding | MARK3,P2RX3B,ASNA1,ATP1A2A,NLRP14,SNRKA,MAP2K7,ULK1,CDKL5,TP53 |
| SMAD binding | PML,YY1,HIPK2,SMURF2,USP15,EID2,PRDM16,TGFBR1,FOXH1,SKOR2 |
| protein serine/threonine kinase activity | RPS6KA3B,DYRK1B,SGK3,CSNK2A2,LIMK1,DYRK2,OBSCN,RPS6KB2,SLC14A2,BMP2K |
| receptor signaling protein serine/threonine kinase activity | ACVR1C,BMPR1BA,OXSR1A,ALPK2,ACVR2AA,TGFBR1,TGFBR1A,STK24A,PAK2B,BMPR2 |
| metal ion binding | SETDB1A,TRIM35-20,CBFA2T3,ZDHHC18B,HINFP,ZNF576.2,ZEB1B,RAF1B,ACY3.2,PON2 |
| transforming growth factor beta receptor activity, type I | ACVR1,TGFBR1 |
| transmembrane receptor protein serine/threonine kinase activity | TGFBR2,BMPR1BA,BMPR2A,BMPR2B,TGFBR1A,ACVR1,BMPR1BB,BMPR1A,ACVR1B,ALPK2 |
Interacting Protein
BMPR1B has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with BMPR1B here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of BMPR1B.
GDF5;BMP2;Dlg4;Rhod;Sash3;Chn1;Ubxn1;Lztr1;Fancl;Rhebl1;Plekhb1
Resources
Gene Families
Related Services
Related Products
References