CD1D
-
Official Full Name
CD1d molecule -
Overview
This gene encodes a divergent member of the CD1 family of transmembrane glycoproteins, which are structurally related;to the major histocompatibility complex (MHC) proteins and form heterodimers with beta-2-microglobulin. The CD1;proteins mediate the presentation of primarily lipid and glycolipid antigens of self or microbial origin to T cells.;The human genome contains five CD1 family genes organized in a cluster on chromosome 1. The CD1 family members are;thought to differ in their cellular localization and specificity for particular lipid ligands. The protein encoded by;this gene localizes to late endosomes and lysosomes via a tyrosine-based motif in the cytoplasmic tail. This gene encodes a divergent member of the CD1 family of transmembrane glycoproteins, which are structurally related to the major histocompatibility complex (MHC) proteins and form heterodimers with beta-2-microglobulin. The CD1 proteins mediate the presentation of primarily lipid and glycolipid antigens of self or microbial origin to T cells. The human genome contains five CD1 family genes organized in a cluster on chromosome 1. The CD1 family members are thought to differ in their cellular localization and specificity for particular lipid ligands. The protein encoded by this gene localizes to late endosomes and lysosomes via a tyrosine-based motif in the cytoplasmic tail. -
Synonyms
CD1D;CD1d molecule;CD1d antigen , CD1D antigen, d polypeptide;antigen-presenting glycoprotein CD1d;R3G1;thymocyte antigen CD1D;CD1D antigen, d polypeptide;T-cell surface glycoprotein CD1d;differentiation antigen CD1-alpha-3;HMC class I antigen-like glycoprotein CD1D;R3;CD1A;MGC34622
Recombinant Proteins
- Human
- Rabbit
- Rhesus macaque
- Sheep
- Human Cells
- E.coli
- Wheat Germ
- E.Coli/Yeast
- Mammalian Cells
- HEK293
- Insect Cells
- In Vitro Cell Free System
- His
- Non
- Fc
- SUMO
- Avi
Background
What is CD1D protein?
CD1D (CD1d molecule) gene is a protein coding gene which situated on the long arm of chromosome 1 at locus 1q23. This gene encodes a divergent member of the CD1 family of transmembrane glycoproteins, which are structurally related to the major histocompatibility complex (MHC) proteins and form heterodimers with beta-2-microglobulin. The CD1 proteins mediate the presentation of primarily lipid and glycolipid antigens of self or microbial origin to T cells. The human genome contains five CD1 family genes organized in a cluster on chromosome 1. The CD1 family members are thought to differ in their cellular localization and specificity for particular lipid ligands. The protein encoded by this gene localizes to late endosomes and lysosomes via a tyrosine-based motif in the cytoplasmic tail. The CD1D protein is consisted of 335 amino acids and its molecular mass is approximately 37.7 kDa.
What is the function of CD1D protein?
CD1d functions as an antigen-presenting protein that binds to self and non-self glycolipids and presents them to T-cell receptors on natural killer T-cells (NKT cells). CD1d is involved in the regulation of the immune response, particularly in the activation of invariant NKT cells. It plays a role in presenting glycolipid antigens to these cells, which are equipped with natural killer receptors and an invariant T-cell receptor-alpha chain. Recent studies have shown that CD1d has a function in the control of lipid metabolism, with CD1d-deficient macrophages exhibiting altered metabolic profiles. The acquisition of glycolipid antigens by CD1d occurs in part in endosomes through the function of resident lipid transfer proteins, such as saposins.
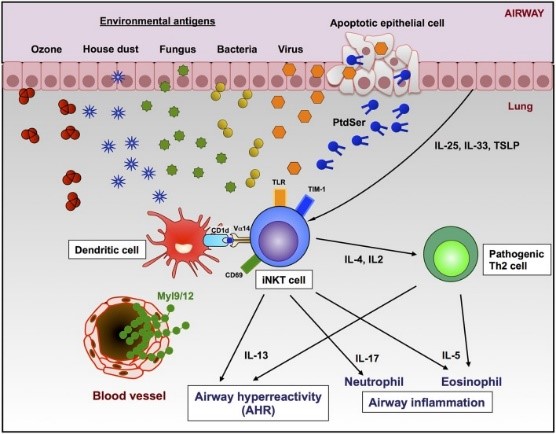
Fig1. Roles of iNKT cells and Th2 cells in the development of AHR and airway inflammation. (Chiaki Iwamura, 2018)
CD1D Related Signaling Pathway
CD1d can mediate reverse signaling in antigen-presenting cells (APCs), which may influence the activation and function of these cells. CD1d presents lipid antigens to natural killer T cells (NKT cells), which are equipped with an invariant T-cell receptor (TCR). This interaction is crucial for the activation of NKT cells, which play a role in autoimmune diseases, tumor rejection, and certain microbial infections. CD1d regulates the internalization of the lipid transporter CD36, which is involved in lipid uptake and metabolism in macrophages. This regulation by CD1d affects the inflammatory-metabolic circuit in these cells.
CD1D Related Diseases
CD1d has been implicated in the regulation of tumor growth. In some studies, CD1d deficiency has been associated with increased tumor growth, while in others, it has been shown to inhibit tumor progression. The specific role of CD1d in cancer appears to be context-dependent and may involve the activation of NKT cells and their influence on the immune response to tumors. CD1d is involved in the regulation of immune responses, and dysregulation of CD1d expression or function could contribute to autoimmune diseases. CD1d and NKT cells can influence the immune response to infections. CD1d has been shown to play a role in the control of lipid metabolism in macrophages, which could have implications for metabolic diseases. CD1d deficiency in macrophages leads to metabolic reprogramming, which primes these cells for enhanced responses to innate signals.
Bioapplications of CD1D
The CD1d protein is able to activate NKT cells, which play a role in immune regulation, anti-tumor and anti-pathogen activity. iNKT cell-based therapies have shown safety and clinical activity in some cancers. Tri-specific CD1d-Vd2 bsTCE (LAVA-051) is being tested in Phase 1/2a clinical trials for the treatment of patients with AML, CLL, and MM. In addition, the CD1d recombinant protein has the potential to regulate immunity and may be used to develop new immunotherapeutic strategies.
Case Study
Case Study 1: Xingguang Liu, 2019
The cross-talk between cellular lipid metabolism and the innate immune responses remains obscure. In addition to presenting lipid antigens to Natural Killer T-cells (NKT cells), the Cluster of Differentiation 1D Glycoprotein (CD1d) might mediate reverse signaling in antigen-presenting cells (APCs). Here the researchers found CD1d deficiency attenuated Toll-like receptor (TLR)-triggered inflammatory innate responses in macrophages and dendritic cells, protecting mice from endotoxin shock. TLR activation in macrophages induced metabolic changes of glycosphingolipids (GSLs), among which glycolipid isoglobotrihexosylceramide (iGb3) was rapidly produced. The endogenously generated iGb3 bound CD1d in endosomal compartments and then synergized with the initially activated TLR signal to induce Tyr332 phosphorylation of CD1d intracellular domain. This led to the recruitment and activation of proline-rich tyrosine kinase 2 (Pyk2). Pyk2 interacted with IκB kinase β (IKKβ) and TANK-binding kinase 1 (TBK1), and enhanced tyrosine phosphorylation of Tyr188/199 of IKKβ and Tyr179 of TBK1 and thus, their activation to promote full activation of TLR signaling. Thus, intracellular CD1d reverse signaling, triggered by endogenous iGb3, amplifies inflammatory innate responses in APCs.
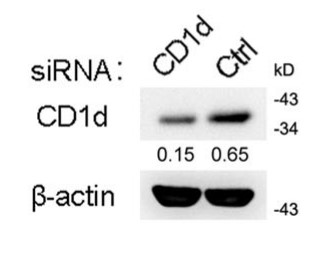
Fig1. Immunoblot of CD1d expression in macrophages.
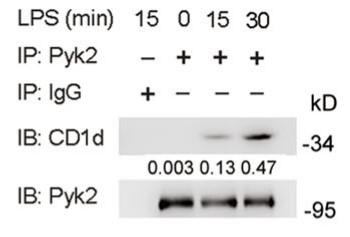
Fig2. IB analysis of CD1d and Pyk2.
Case Study 2: Zhigang Lei, 2024
Hepatocyte apoptosis, a well-defined form of cell death in non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), is considered the primary cause of liver inflammation and fibrosis. However, the mechanisms underlying the regulation of hepatocyte apoptosis in NASH remain largely unclear. Hepatocyte CD1d expression was analyzed in patients with NASH and mouse models. Hepatocyte-specific gene overexpression or knockdown and anti-CD1d crosslinking were used to investigate the anti-apoptotic effect of hepatocyte CD1d on lipotoxicity-, Fas-, and concanavalin (ConA)-mediated liver injuries. The researchers identified a dramatic decrease in CD1d expression in hepatocytes of patients with NASH and mouse models. Hepatocyte-specific CD1d overexpression and knockdown experiments collectively demonstrated that hepatocyte CD1d protected against hepatocyte apoptosis and alleviated hepatic inflammation and injuries in NASH mice. Furthermore, decreased JAK2-STAT3 signaling was observed in NASH patient livers. Mechanistically, anti-CD1d crosslinking on hepatocytes induced tyrosine phosphorylation of the CD1d cytoplasmic tail, leading to the recruitment and phosphorylation of JAK2. Phosphorylated JAK2 activated STAT3 and subsequently reduced apoptosis in hepatocytes.
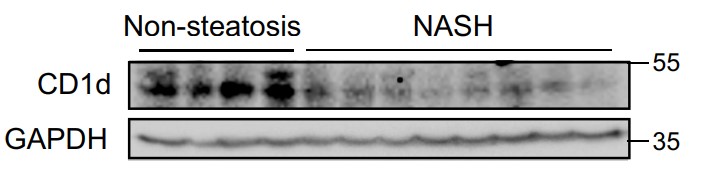
Fig3. CD1d protein levels were normalized to GAPDH.
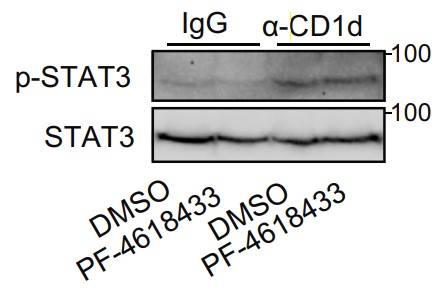
Fig4. Shown are representative immunoblots of p-STAT3 in cell lysates.
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
.jpg)
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (CD1D-166H)
.
.jpg)
Fig2. SDS-PAGE (CD1D-5279H)
Involved Pathway
CD1D involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways CD1D participated on our site, such as Hematopoietic cell lineage,Amoebiasis, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with CD1D were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| Hematopoietic cell lineage | IL3,CD37,Fcer2a,IL6,GM2002,IL9R,CD59,CD19,CD44,GM-CSF |
| Amoebiasis | RAB5C,GM-CSF,GNAL,PRKCG,TLR2,HSPB1,C8B,COL27A1,RELA,ITGB2L |
Protein Function
CD1D has several biochemical functions, for example, beta-2-microglobulin binding,cell adhesion molecule binding,endogenous lipid antigen binding. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by CD1D itself. We selected most functions CD1D had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with CD1D. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| beta-2-microglobulin binding | CD1d1,CD1C,CD1A,HLA-E,FCGRT,HFE,CD1B,CD1D2,H2-Q10,CD1E |
| histone binding | PRMT6,ZMYND11,WDTC1,L3MBTL1,HIST1H3F,BRD7,NOC2L,SFMBT1,HJURP,PHF21B |
| exogenous lipid antigen binding | CD1A,CD1C,CD1B,CD1E,CD1D2,CD1d1 |
| lipopeptide binding | CD1B,CD1D2,CD1E,TLR6,CD1C,CD1A,CD1d1 |
| endogenous lipid antigen binding | CD1D2,CD1B,CD1d1,CD1C,CD1A,CD1E |
| receptor activity | NOTCH4,TLR6,VMN1R49,CD4,MED12,SIGLEC7,RAMP3,CADM1,STRA6,VMN1R47 |
| lipid antigen binding | CD1d1 |
| cell adhesion molecule binding | TENM2,DSG2,ADAM8,NRXN1,SMAGP,CADM3,CD200,PVRL2,EZR,POSTNB |
Interacting Protein
CD1D has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with CD1D here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of CD1D.
Resources
Research Area
Related Services
Related Products
References
- Rosales, C; Tang, DM; et al. CD1d serves as a surface receptor for oxidized cholesterol induction of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma. ATHEROSCLEROSIS 239:224-231(2015).
- Matsuda, T; Yanase, S; et al. The immunosenescence-related gene Zizimin2 is associated with early bone marrow B cell development and marginal zone B cell formation. IMMUNITY & AGEING 12:-(2015).



