CD Antigen (T Cell Antigen Recognition)
Related Symbol Search List
Immunology Background
Resources Available for the Study of CD Antigens (T-Cell Antigen Recognition)
Creative BioMart is the ultimate destination for your research needs related to CD antigen (T cell antigen recognition). We are committed to providing you with a comprehensive selection of products and personalized services to support your exploration of critical knowledge in the area of T cell recognition-related CD antigens.
- Our product offerings encompass a diverse range of high-quality research tools. We provide recombinant proteins, native proteins, protein pre-coupled magnetic beads, cell and tissue lysates, chromatography reagents, GMP proteins, assay kits, and more. Each product is meticulously tailored to meet your specific research requirements with unparalleled precision and expertise. We ensure the utmost quality and reliability of our products to enable accurate and reproducible results in your experiments.
- In addition to our extensive product catalog, we offer a wealth of resources on T cell recognition-related CD antigens. Our comprehensive insights cover associated pathways, protein functions, interacting proteins, relevant literature, and other valuable information. These resources serve as a valuable guide, facilitating a deeper understanding of the molecular mechanisms and biological significance of T cell recognition-related CD antigens.
Our Featured Products
| Cat.# | Product name | Species | Source (Host) | Tag |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CD1D-2188H | Recombinant Human CD1D, His tagged | Human | Human Cell | His |
| CD3E & CD3D-376H | Active Recombinant Human CD3E & CD3D protein, His-tagged | Human | HEK293 | His |
| CD4-39H | Active Recombinant human CD4 protein (26-390aa), C-hIgG/His-tagged | Human | HEK293 | C-hIgG-His |
| CD6-018H | Recombinant Human CD6 protein, His-tagged | Human | HEK293 | His |
| CD28-01H | Active Recombinant Human CD28 protein, hIgG-His-tagged | Human | Insect Cell | HIgG/His |
| CD45-10957H | Recombinant Human CD45, GST-tagged | Human | E.coli | GST |
| CD80-581H | Active Recombinant Human CD80, His-tagged, Biotinylated | Human | Human Cell | His |
| CD86-2228H | Recombinant Human CD86, His tagged | Human | Human Cell | His |
| CD160-01H | Recombinant Human CD160 Protein, His-Tagged | Human | Insect Cell | His |
| Ly9-4035M | Recombinant Mouse Ly9 protein(Met1-Arg453), His-tagged | Mouse | HEK293 | C-His |
About CD Antigen (T Cell Antigen Recognition)
The CD antigens related to T cell recognition play a crucial role in the identification, activation, and regulation of T cells, which are central players in the adaptive immune response. These CD antigens are cell surface molecules expressed on T cells and other immune cells, and they are involved in various aspects of T cell recognition and function. Here is an introduction to some key CD antigens related to T cell recognition:
- CD3 Complex: The CD3 complex is composed of CD3δ, CD3ε, CD3γ, and CD3ζ chains and is associated with the T cell receptor (TCR). It plays a critical role in transmitting signals from the TCR to the intracellular signaling machinery, initiating T cell activation upon recognition of antigens. The CD3 complex is essential for T cell development, maturation, and signal transduction.
- CD4 and CD8: CD4 and CD8 are co-receptors expressed on the surface of T cells. CD4 is primarily expressed on helper T cells (CD4+ T cells), while CD8 is expressed on cytotoxic T cells (CD8+ T cells). These co-receptors interact with the major histocompatibility complex (MHC) molecules on antigen-presenting cells (APCs) and enhance TCR signaling. CD4 interacts with MHC class II molecules, while CD8 interacts with MHC class I molecules, facilitating the recognition of antigens presented by APCs.
- CD28 and CTLA-4: CD28 and CTLA-4 are co-stimulatory molecules expressed on T cells. CD28 provides a positive co-stimulatory signal when it binds to B7-1 (CD80) or B7-2 (CD86) molecules on APCs, enhancing T cell activation, proliferation, and cytokine production. In contrast, CTLA-4 competes with CD28 for binding to B7 molecules and delivers inhibitory signals, regulating T cell responses and maintaining immune tolerance.
- CD45: CD45, also known as leukocyte common antigen (LCA), is a tyrosine phosphatase expressed on all nucleated cells of hematopoietic origin, including T cells. CD45 plays a crucial role in regulating TCR signaling by dephosphorylating tyrosine residues of intracellular signaling molecules. It helps modulate T cell activation thresholds and fine-tune T cell responses.
- CD40 Ligand (CD40L): CD40L, also known as CD154, is expressed on activated CD4+ T cells. It interacts with CD40, a molecule expressed on APCs such as B cells and dendritic cells. The interaction between CD40L and CD40 is important for B cell activation, maturation, and antibody production, facilitating effective humoral immune responses.
These CD antigens associated with T cell recognition are instrumental in the initiation, regulation, and coordination of T cell responses. They facilitate the recognition of antigens presented by APCs, provide co-stimulatory signals, regulate signal transduction, and modulate immune responses. Understanding the role of these CD antigens is essential for unraveling the mechanisms of T cell recognition and developing targeted approaches for immunotherapy, vaccine development, and the treatment of immune-related diseases.
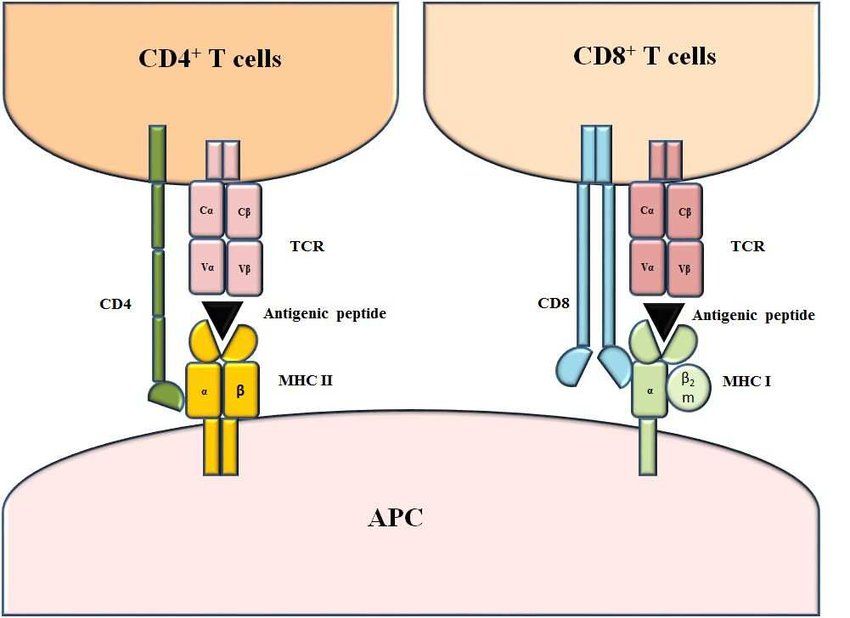 Fig.1 Structure of MHC-peptide-TCR complexes. (Majumdar, S., et al., 2018)
Fig.1 Structure of MHC-peptide-TCR complexes. (Majumdar, S., et al., 2018)
CD Antigens in T Cell Activation
T cell activation relies on the coordinated interaction of various molecules, including T cell receptors (TCR) and CD28, with their respective ligands on Antigen Presenting Cells (APCs). The process of T cell antigen recognition starts with the TCR binding to a peptide sequence presented by the Major Histocompatibility Complex (MHC) on the surface of APCs. This interaction between the TCR and MHC-peptide complex serves as the initial trigger for T cell activation.
In addition to TCR engagement, co-stimulation is crucial for the full activation of T cells. CD28, expressed on T cells, interacts with B7-1/CD80 and B7-2/CD86 proteins expressed on APCs. This co-stimulatory interaction provides an additional signal that enhances T cell activation, proliferation, and differentiation.
Within the TCR complex, CD3 proteins play a vital role. The CD3 complex, consisting of CD3δ, CD3ε, CD3γ, and CD3ζ, is associated with the TCR and is responsible for transmitting signals generated by TCR engagement. Upon TCR activation, the CD3 proteins undergo phosphorylation of immuno-receptor tyrosine-based activation motifs (ITAMs) by Lck, a tyrosine kinase. This phosphorylation event leads to the recruitment and assembly of signaling complexes, initiating further signal transduction cascades.
The phosphorylation of CD3ε ITAMs promotes the aggregation of signaling molecules, such as ZAP-70, and activates downstream signaling pathways. These signaling cascades culminate in the activation of transcription factors, such as NF-κB and AP-1, which drive T cell proliferation, cytokine production, and effector functions.
In summary, T cell activation is a multi-step process dependent on the recognition of MHC-peptide complexes by the TCR and co-stimulation through CD28-B7 interactions. The CD3 proteins within the TCR complex facilitate the transmission of signals, leading to the activation of T cells and the initiation of immune responses. Phosphorylation of CD3ε ITAMs by Lck is a critical event that triggers downstream signaling cascades, ultimately shaping the fate and function of activated T cells.
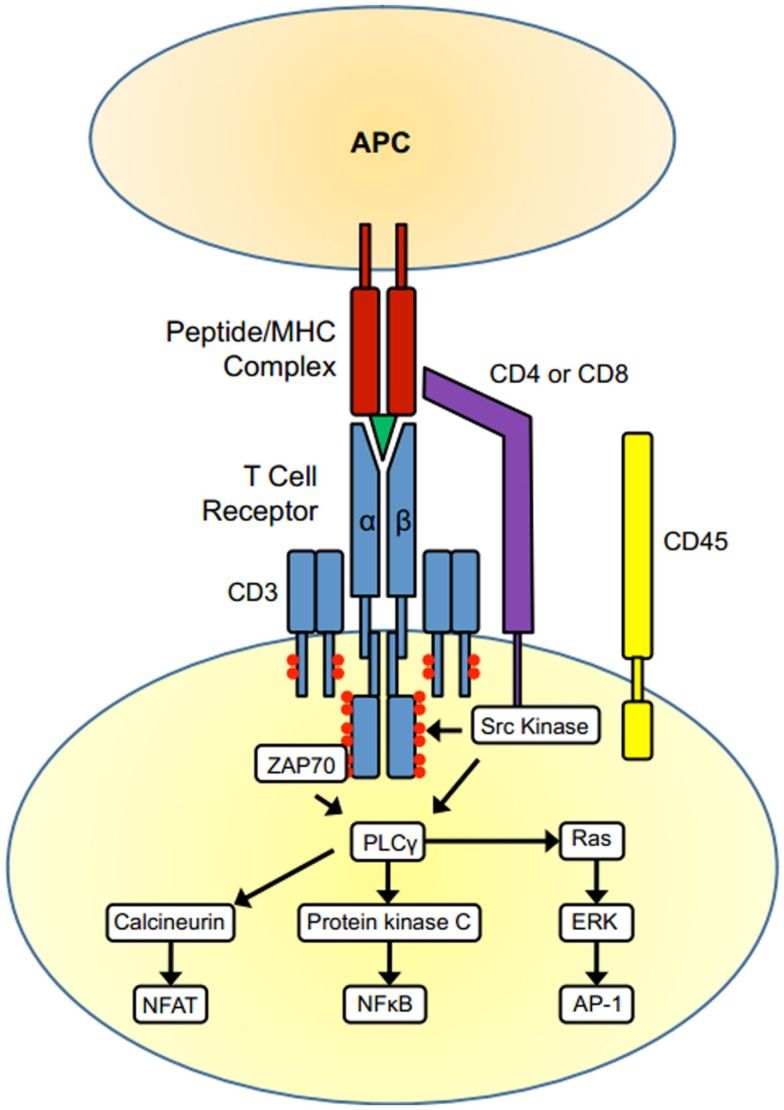 Fig.2 T cell activation. (Whitacre JM, et al., 2012)
Fig.2 T cell activation. (Whitacre JM, et al., 2012)
Importance of T Cell Antigen Recognition-Associated CD Antigens in the Immune Response
These CD antigens (CD3 complex, CD4 and CD8, CD28 and CTLA-4, CD45, CD40 ligand, and others, ) associated with T cell antigen recognition contribute to the specificity, regulation, and coordination of immune responses. They ensure proper T cell activation, enhance immune cell communication, modulate immune tolerance, and facilitate the generation of effective immune responses against pathogens, cancer cells, and other antigens. Understanding the functions and interactions of these CD antigens is essential for designing immunotherapies, vaccines, and treatments for immune-related diseases.
Choose Creative BioMart as your trusted partner, and embark on a journey of scientific exploration with confidence and precision. If you have any questions, requirements, or cooperation intentions, please feel free to contact us. We very much look forward to working with you and helping you achieve research and commercial success.
Related References
- Bosselut R. T cell antigen recognition: Evolution-driven affinities. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2019;116(44):21969-21971.
- Whitacre JM, Lin J, Harding A. T Cell Adaptive Immunity Proceeds through Environment-Induced Adaptation from the Exposure of Cryptic Genetic Variation. Front Genet. 2012;3:5.
- Majumdar, S., Pathak, S., & Nandi, D. (2018). Thymus: The Site for Development of Cellular Immunity. Resonance, 23, 197-217.

