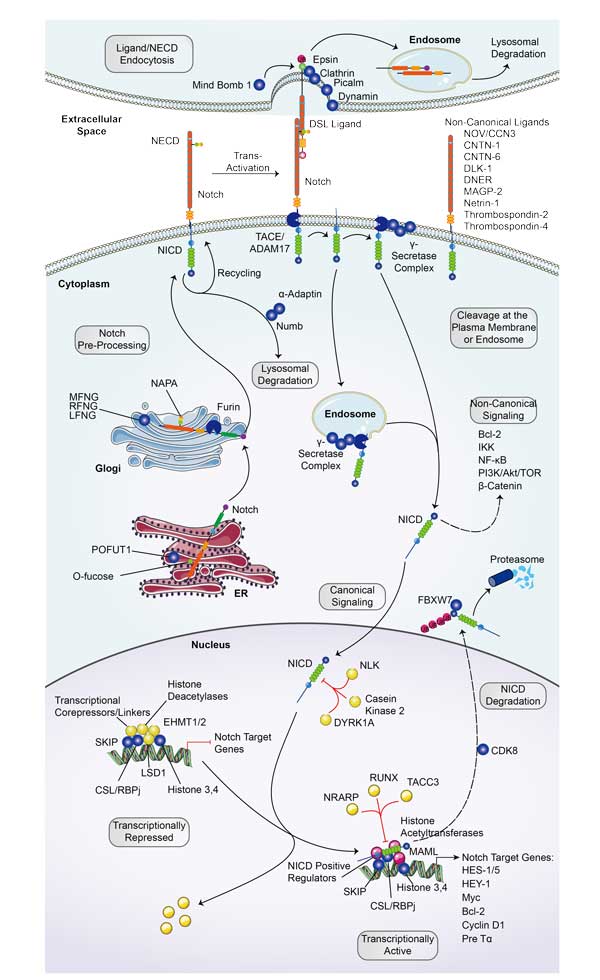
DNM2
-
Official Full Name
dynamin 2 -
Overview
Dynamins represent one of the subfamilies of GTP-binding proteins. These proteins share considerable sequence similarity over the N-terminal portion of the molecule, which contains the GTPase domain. Dynamins are associated with microtubules. They have been implicated in cell processes such as endocytosis and cell motility, and in alterations of the membrane that accompany certain activities such as bone resorption by osteoclasts. Dynamins bind many proteins that bind actin and other cytoskeletal proteins. Dynamins can also self-assemble, a process that stimulates GTPase activity. Five alternatively spliced transcripts encoding different proteins have been described. Additional alternatively spliced transcripts may exist, but their full-length nature has not been determined. [provided by RefSeq, Jun 2010] -
Synonyms
DNM2;dynamin 2;DYN2;CMT2M;DYNII;LCCS5;CMTDI1;CMTDIB;DI-CMTB;dynamin-2;dynamin II
Recombinant Proteins
- Human
- Rhesus macaque
- Rat
- Mouse
- E.coli
- Mammalian Cells
- HEK293
- Wheat Germ
- HeLa
- In Vitro Cell Free System
- GST
- His
- T7
- DDK
- Myc
- Non
- Avi
- Fc
- Flag
Background
What is DNM2 protein?
DNM2 gene (dynamin 2) is a protein coding gene which situated on the short arm of chromosome 19 at locus 19p13. Dynamins represent one of the subfamilies of GTP-binding proteins. These proteins share considerable sequence similarity over the N-terminal portion of the molecule, which contains the GTPase domain. Dynamins are associated with microtubules. They have been implicated in cell processes such as endocytosis and cell motility, and in alterations of the membrane that accompany certain activities such as bone resorption by osteoclasts. Dynamins bind many proteins that bind actin and other cytoskeletal proteins. Dynamins can also self-assemble, a process that stimulates GTPase activity. The DNM2 protein is consisted of 870 amino acids and DNM2 molecular weight is approximately 98.1 kDa.
What is the function of DNM2 protein?
The DNM2 protein is a protein that plays a variety of roles in cells. It is a member of the dynamin family, which is mainly involved in the regulation of cell membrane remodeling and endocytosis, and is crucial for the uptake of nutrients, signaling molecules and pathogens by cells. DNM2 facilitates endocytosis by helping endocytosis vesicles separate from cell membranes by forming helical structures. In addition, DNM2 is involved in regulating cytoplasmic division during cell division, as well as maintaining synaptic plasticity in nerve cells. Abnormal functioning of DNM2 has been linked to a variety of diseases, including neurodegenerative diseases and certain types of cancer.
DNM2 related signaling pathway
Dnm2-related signaling pathways are mainly involved in endocytosis and cytoplasmic division. DNM2 is a GTP enzyme that plays a key role in endocytosis, mediating the shear and release of endocytotic vesicles through its GTP enzyme activity. During cytoplasmic division, DNM2 interacts with a variety of proteins, including RhoA, Rab11, Coronin, etc., to jointly regulate the assembly and contraction of actin-myosin rings to ensure the normal progress of cell division. In addition, DNM2 is involved in biological processes such as cell migration, cell polarity establishment, and the development and maintenance of neural synapses.
DNM2 related diseases
DNM2 protein is associated with many diseases, especially myopathy. Mutations in the DNM2 gene can lead to autosomal dominant central nuclear myopathy (CNM), a congenital myopathy characterized by the presence of a large number of muscle nuclei in the center of muscle fibers. The clinical manifestations of DNM2-related CNM include eyelid ptosis, extraocular muscle paralysis, facial muscle weakness, limb weakness, Achilles tendon contracture and spinal deformity. In addition, mutations in the DNM2 gene are also associated with Charcot-Marie-Tooth (CMT) peripheral neuropathy. Studies have shown that DNM2 gene mutation may lead to phenotypic improvement of mytubulin 1 (MTM1) related diseases, and DNM2 knockdown may have a positive effect on the treatment of CNM.
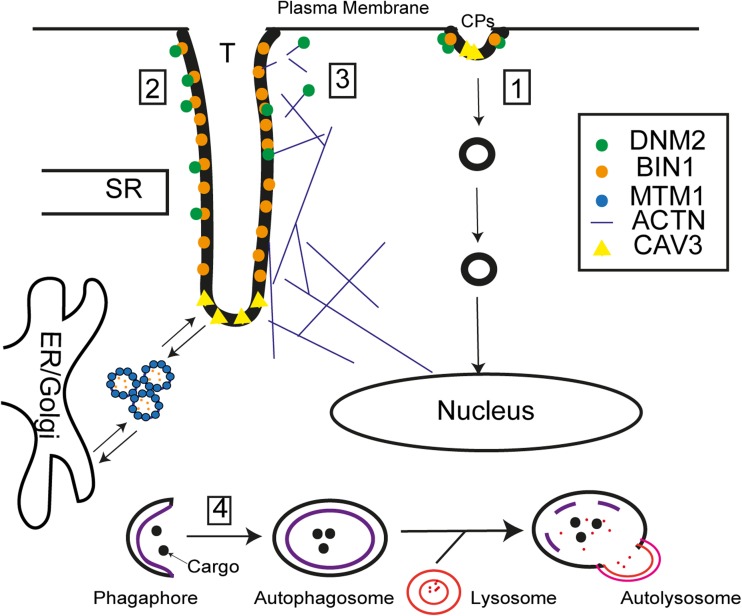
Fig1. Potential membrane trafficking events disrupted in DNM2 centronuclear myopathy. (Mo Zhao, 2018)
Bioapplications of DNM2
Recombinant human DNM2 protein (rhDNM2) is of great value in biomedical research and clinical application. Mutations in the DNM2 gene are associated with a variety of diseases, including central nuclear myopathy (CNM), Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease (CMT), and congenital contracture syndrome. By studying rhDNM2, scientists can gain a deeper understanding of the pathogenesis of these diseases and explore possible treatments. For example, for CNM caused by DNM2 gene mutations, researchers are exploring strategies for gene replacement or editing using viral vectors, as well as treatment by reducing DNM2 expression. In addition, rhDNM2 is also used in drug screening and disease modeling, providing an important tool for the development of new therapeutic drugs and methods.
Case Study
Case Study 1: Runzhao Guo, 2022
Microtubule stability, crucial for cellular processes like axonal transport, is influenced by dynamin-2, which is known for its role in membrane fission. Although dynamin-2's role in microtubule regulation is established, the mechanisms are not fully understood. This study explored dynamin-2's intrinsic effects on microtubules using HeLa cells with a heterozygous DNM2 mutation, which showed increased stabilized microtubules. Wild-type dynamin-2 reduced this stabilization, but self-assembly-defective mutants did not, indicating that dynamin-2's self-assembly is key to its regulatory function. Additionally, a GTPase-defective dynamin-2 mutant, K44A, mimicked the effect of wild-type, suggesting that its GTPase activity may not be essential for microtubule stability regulation.
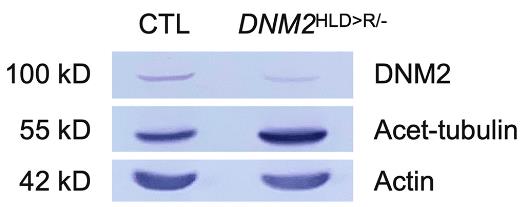
Fig1. Immunoblotting of cell lysates from control (CTL) or heterozygous DNM2 mutant cells.
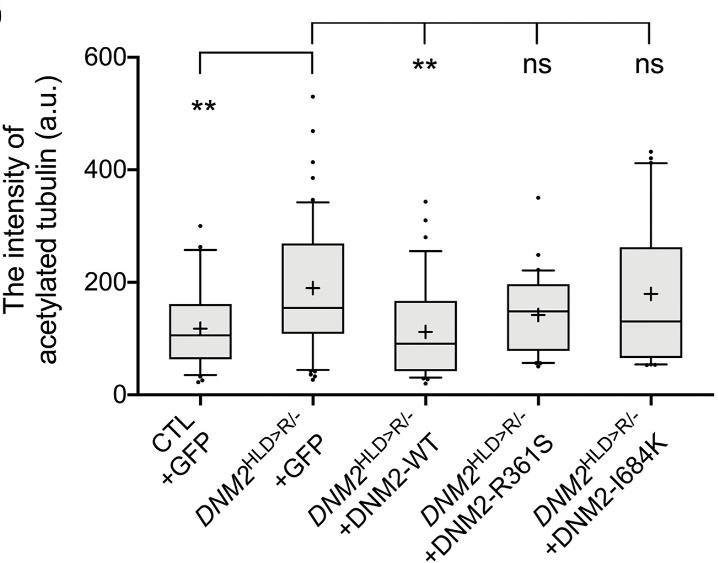
Fig2. Effect of GFP-dynamin-2-R361S and -I684K mutant expressions on microtubule stabilization.
Case Study 2: Sophia B Chernikova, 2018
Initially responsive triple-negative breast cancers often recur as chemo-resistant, linked to heightened homology-directed repair (HDR). HDR inhibitors could enhance chemo effects. Researchers screened for HDR inhibitors and found several affecting microtubule dynamics. Suppressing dynamin 2 (DNM2), key in cellular trafficking and microtubules, reduced HDR and increased chemosensitivity. High DNM2 levels in tumors correlated with poor chemo outcomes, particularly in TNBC. DNM2-related DNA repair trafficking is vital for HDR, predicting chemo success, and is a potential therapeutic target.
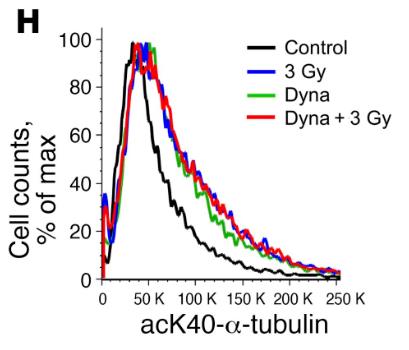
Fig3. FACS analysis of CHO AA8 cells irradiated with 3 Gy in the absence and presence of the dynamin 2 (DNM2) inhibitor dynasore.
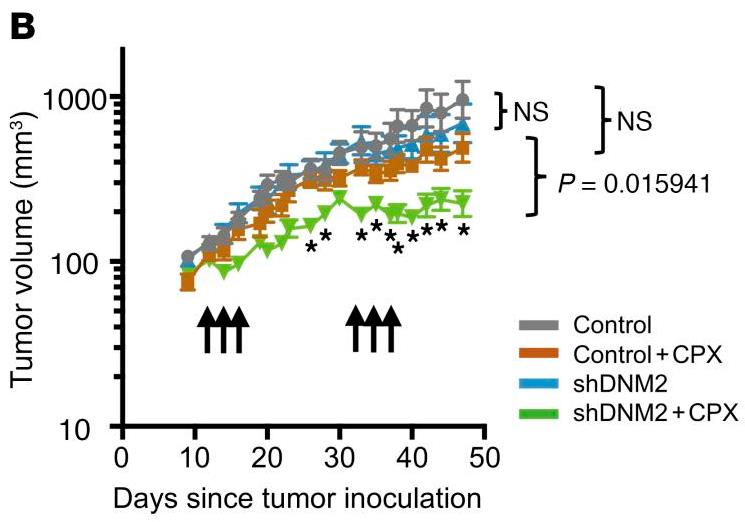
Fig4. DNM2 knockdown increases tumor sensitivity to cyclophosphamide (CPX) in an orthotopic model of TNBC.
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
.jpg)
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (DNM2-20H)
.
.jpg)
Fig2. SDS-PAGE (DNM2-2786H)
Involved Pathway
DNM2 involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways DNM2 participated on our site, such as Adaptive Immune System,Arf6 trafficking events,Axon guidance, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with DNM2 were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| Developmental Biology | FRS2B,MED26,EFNA5,ARPC2,MED23,EBF1,EFNA1B,AP2B1,NRP1A,CD24 |
| Endocytosis | RAB5B,CHMP4A,WWP1,FAM21C,PIP5K1A,MDM2,EPN3,CHMP2A,TGFBR1B,TSG101 |
| Bacterial invasion of epithelial cells | ACTB,CLTC,CAV2,CAV3,ITGB1,PIK3R5,SHC2,CAV1,CRK,GAB1 |
| Clathrin derived vesicle budding | HIP1RB,NAPAB,SNX9,PICALMA,APPB,BLOC1S4,BLOC1S1,GAK,CLTB,SNX9A |
| Endocrine and other factor-regulated calcium reabsorption | ATP1B4,CALB1,GNAS,KLK2,KLK1B8,KLK1B22,SLC8A1,ATP1A4,ESR1,KLK1B26 |
| Arf6 trafficking events | ADRB2,CLTC,SPAG9,CTNNA1,CHRM2,EXOC1,EXOC5,PTBP3,EXOC6,EDNRB |
| Axon guidance | NCAN,ABLIM3,DAB2IPB,RHOD,Ntng2,DLG4,SPRED2,EFNB2,UNC5D,RGMB |
| Adaptive Immune System | TRIM11,CYBB,STIM1B,RNF144B,DCTN6,PIK3AP1,RASGRP2,UBE2E3,KLRB1A,Siglece |
Protein Function
DNM2 has several biochemical functions, for example, D2 dopamine receptor binding,GTP binding,GTPase activity. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by DNM2 itself. We selected most functions DNM2 had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with DNM2. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| protein kinase binding | TRIM5,CDH2,GRIN2A,TUBB3,PARN,TICAM1,ADCY6,MAPKAP1,CCNE2,PTPRK |
| enzyme binding | ADORA2A,GSTM2,RAD9A,LDB2,UGT1A6B,AXIN2,LAMP1,TNKS2,UBE2I,ZFP346 |
| microtubule binding | TUBGCP5,KLC3,CCDC88A,MAP1LC3B,KIF3B,KIF22,CHD4A,GCAP14,REEP4,NPSNL |
| SH3 domain binding | PLSCR3,SH2D2A,MVB12A,TOM1L1,DOCK1,WIPF3,EPS15,CBL,OSTF1,REPS1 |
| GTP binding | GNA13A,GNAQ,TUBA1B,RAB1,GTPBP1L,RND1,ACSM1,SEPT9,GFM2,GNAO1 |
| phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase regulatory subunit binding | XBP1,PTPN13,PIK3AP1,FAM83B,PIK3R1,FAM83A |
| D2 dopamine receptor binding | CLIC6,PPP1R9B |
| protein binding | SYNGR1,GJD3,PITPNC1,COQ7,KIAA1958,MINK1,BMI1,CDC20,CYGB,CLEC4G |
| nitric-oxide synthase binding | SNTA1,SCN5A,DMD,CDH2,SLC14A2,ACTB,CALM1,CALM2,CALM3,CAV3 |
Interacting Protein
DNM2 has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with DNM2 here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of DNM2.
GRB2;SNX9;SH3GL2;AMPH;ITSN1
DNM2 Related Signal Pathway
Resources
Related Services
Related Products
References
- Jungbluth, H; Gautel, M; et al. Pathogenic mechanisms in centronuclear myopathies. FRONTIERS IN AGING NEUROSCIENCE 6:-(2014).
- Liu, XH; Fruhstorfer, C; et al. A New AHI-1-DNM2-BCR-ABL Complex Regulates Endocytosis Processes in Chronic Myeloid Leukemia. BLOOD 124:-(2014).