F12
-
Official Full Name
coagulation factor XII -
Overview
Coagulation factor XII also known as Hageman factor is a plasma protein. It is the zymogen form of factor XIIa, an enzyme (EC 3.4.21.38) of the serine protease (or serine endopeptidase) class. In humans, factor XII is encoded by the F12 gene. -
Synonyms
coagulation factor XII (Hageman factor);F12;HAF;HAE3;HAEX;coagulation factor XII;Hageman factor;OTTHUMP00000223845;beta-factor XIIa part 1;beta-factor XIIa part 2;coagulation factor XIIa heavy chain;coagulation factor XIIa light chain
Recombinant Proteins
- Human
- Rat
- Mouse
- Pig
- E.coli
- Human Plasma
- Insect Cells
- Mammalian Cells
- Wheat Germ
- HEK293
- Yeast
- In Vitro Cell Free System
- His
- Non
- GST
- T7
- Avi
- Fc
- SUMO
Background
What is F12 Protein?
Factor XII, also known as Hageman factor, is a plasma protein that plays a part in blood clotting. It's part of the coagulation cascade, activating factor XI and kallikrein when it encounters surfaces like glass. Interesting enough, despite its role in forming blood clots, deficiencies in Factor XII usually don't cause bleeding issues but are linked to prolonged clotting time in lab tests. Factor XII is being studied for its potential in developing new anticoagulant drugs, as it might help treat thrombosis without affecting normal hemostasis.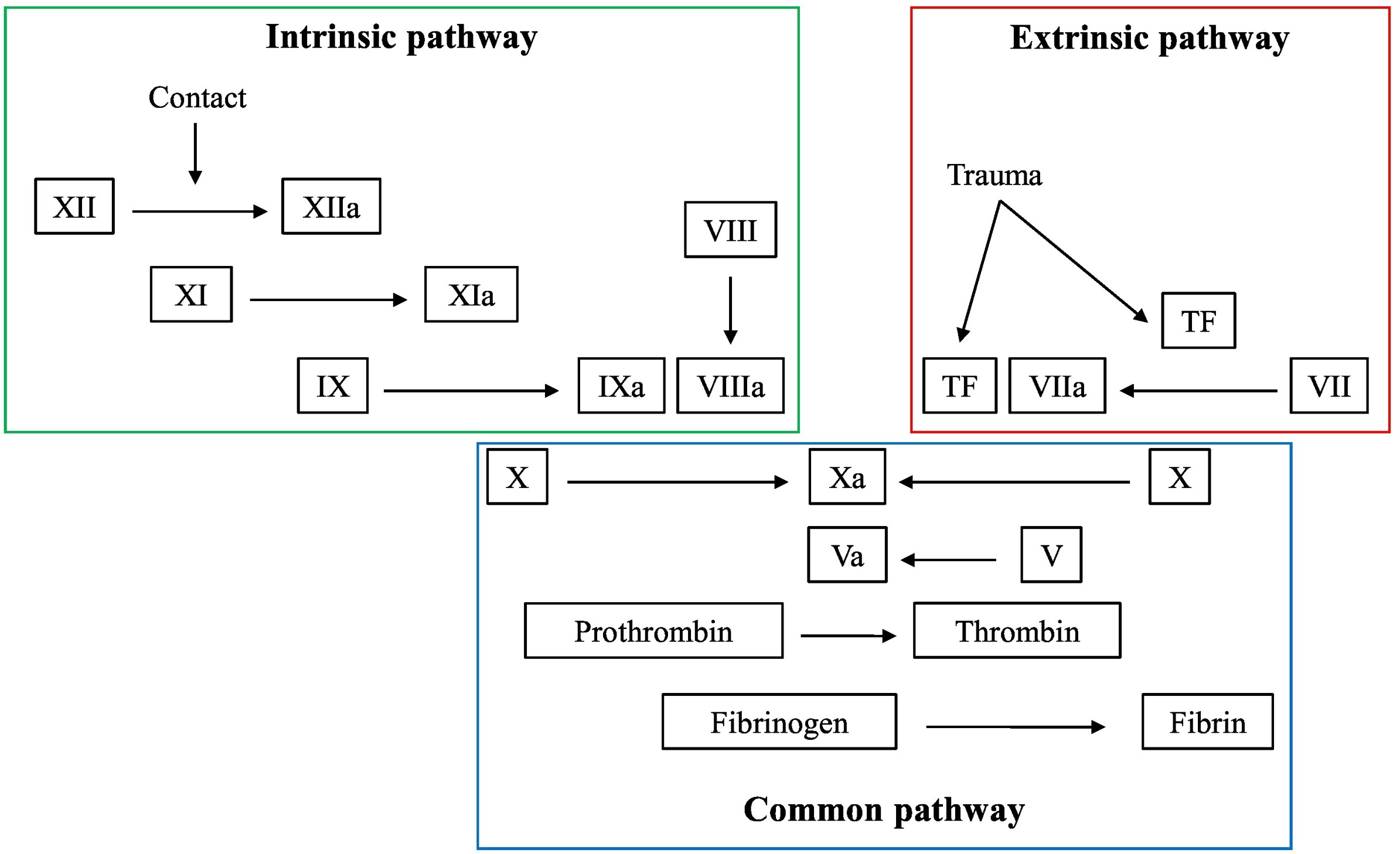
Fig1. Schematic overview of the coagulation system. (Karsten Engseth Kluge, 2022)
What is the Function of F12 Protein?
Factor XII, or Hageman factor, is a protein involved in blood clotting, part of the coagulation cascade, and helps activate factors XI and prekallikrein. It gets activated by negatively charged surfaces like glass, triggering the intrinsic pathway. Besides its role in lab tests, Factor XII is involved in clot formation through platelet-released polyphosphates. Although essential in vitro, deficiencies in Factor XII don't typically cause bleeding issues but can affect lab clotting times. It's a target for developing anticoagulant drugs since blocking it can reduce thrombosis risk without affecting normal bleeding control.F12 Related Signaling Pathway
Factor XII kicks off the intrinsic blood coagulation pathway by activating upon contact with negatively charged surfaces. It triggers a chain reaction involving factor XI and prekallikrein, leading to fibrin formation, which helps in clot development. While it doesn't typically cause bleeding issues when deficient, it plays a significant role in thrombosis, making it a target for new anticoagulant drugs, aiming to minimize clotting while preserving normal bleeding functions.F12 Related Diseases
F12-related diseases often involve genetic mutations affecting blood clotting. These conditions can lead to bleeding issues or sometimes excessive clotting, which are both dangerous in different ways. The most well-known is Factor XII deficiency, a rare disorder that, surprisingly, usually doesn’t cause symptoms or lead to excessive bleeding, unlike what you might expect from a clotting disorder. It can, however, be discovered accidentally during blood tests done for other reasons. Those with the deficiency might not need treatment if there aren’t any symptoms. Understanding these diseases requires a detailed look at one's genetic makeup, often necessitating specific blood tests and family history reviews.Bioapplications of F12
Bioapplications of F12 typically relate to its role in medical and scientific research, particularly focused on blood coagulation and immune response mechanisms. Factor XII, or Hageman Factor, is pivotal in the initiation of the intrinsic pathway of blood coagulation. It gets activated when blood comes into contact with foreign surfaces, and in clinical settings, its function can be analyzed to understand clotting disorders or used in developing anticoagulant therapies. Recent research also explores the potential of Factor XII inhibitors in reducing the risk of thrombosis without heightened bleeding risks, which is a promising development in cardiovascular treatments. Factor XII's interactions are tested using synthetic substances in labs, fostering advancements in how scientists tackle issues like stroke or thrombosis. Overall, F12's biological interactions offer vast potentials for new therapeutic pathways and innovations.Case Study
Case Study 1: Rezvani-Sharif A. et al. PLoS Comput Biol. 2024
The kallikrein-kinin system (KKS) controls inflammation and blood pressure but can cause problems like HAE if unbalanced. Researchers crafted a model detailing FXII activation, kallikrein feedback, and bradykinin production. It uses both surface and solution reactions, validated with data on dextran sulphate and inhibitors. The model shows minimal FXII activation triggers further activation, with a bell curve of KKS activity related to DXS sites. In HAE plasma, C1 esterase inhibitor shortage boosts bradykinin, with CSL312 effectively reducing its generation.-
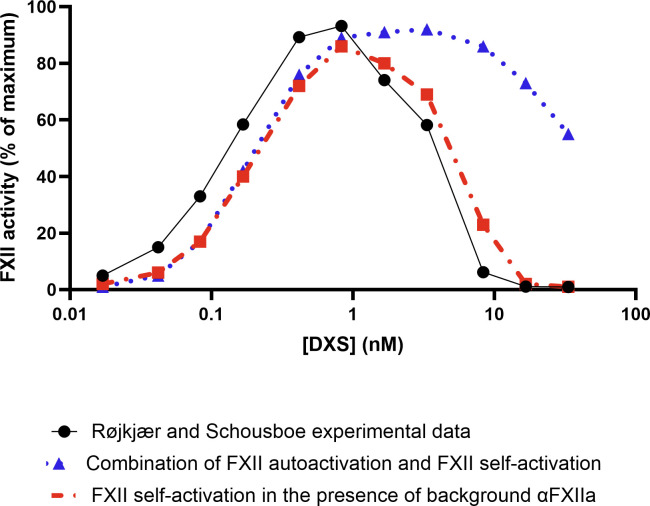 Fig1. FXII activation versus DXS concentration via two alternative FXII activation mechanisms.
Fig1. FXII activation versus DXS concentration via two alternative FXII activation mechanisms. -
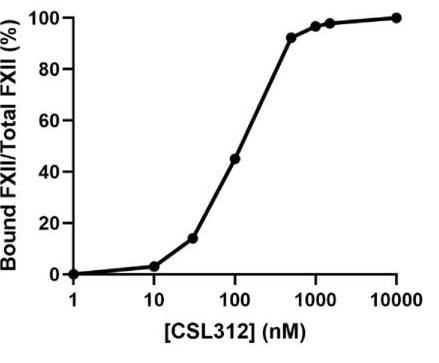 Fig2. Simulated data showing the proportion of CSL312-FXII complex to total FXII in plasma equilibrated with different concentrations of CSL312.
Fig2. Simulated data showing the proportion of CSL312-FXII complex to total FXII in plasma equilibrated with different concentrations of CSL312.
Case Study 2: Elwakiel A. et al. Nat Commun. 2024
Coagulation factor XII (FXII) acts as both a protease promoting thrombosis and as a zymogen via receptors like uPAR. While its levels rise in diabetes and DKD, its role in DKD wasn't known. FXII is expressed in kidney cells, and its presence in urine links to kidney issues in DKD. Mice lacking FXII are shielded from kidney damage caused by high blood sugar. FXII interacts with uPAR on kidney cells, triggering integrin β1 signaling, leading to oxidative stress and cell aging. Blocking uPAR or integrin β1 reduces cell damage. This reveals how FXII signaling drives aging in cells and suggests new diagnostic and treatment paths for DKD and related conditions.-
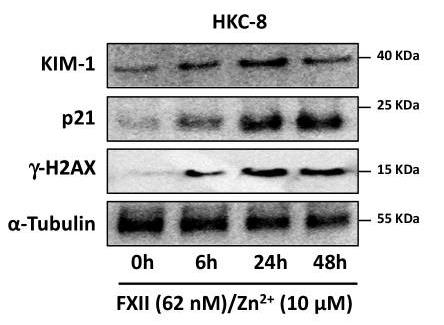 Fig3. Representative immunoblots for γ-H2AX, p21, and KIM-1 expression in HKC-8 cells exposed to purified human FXII.
Fig3. Representative immunoblots for γ-H2AX, p21, and KIM-1 expression in HKC-8 cells exposed to purified human FXII. -
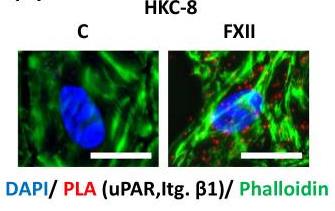 Fig4. Representative images of proximity ligation assay.
Fig4. Representative images of proximity ligation assay.
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
-
.jpg) Fig1. SDS-PAGE (F12-3606H)
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (F12-3606H) -
.jpg) Fig2. SDS-PAGE (F12-773H)
Fig2. SDS-PAGE (F12-773H)
Involved Pathway
F12 involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways F12 participated on our site, such as Complement and coagulation cascades, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with F12 were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| Complement and coagulation cascades | FGG,CR2,PLAT,MASP1,C8A,PLAU,CFB,CFH,F10,F8 |
-
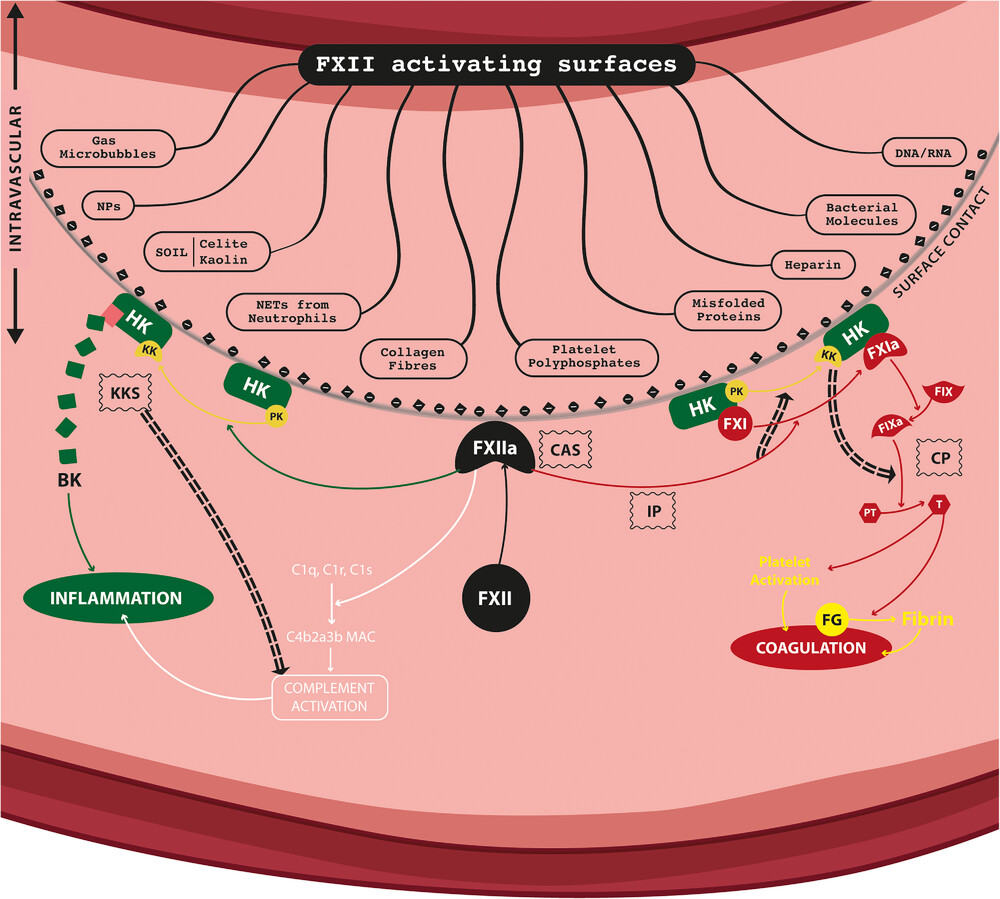 Fig1. Overview of the contact activation (CAS) and kallikrein/kinin (KKS) systems, with the known mechanisms of FXII activation and its physiological consequences. (Sabino Padilla, 2023)
Fig1. Overview of the contact activation (CAS) and kallikrein/kinin (KKS) systems, with the known mechanisms of FXII activation and its physiological consequences. (Sabino Padilla, 2023) -
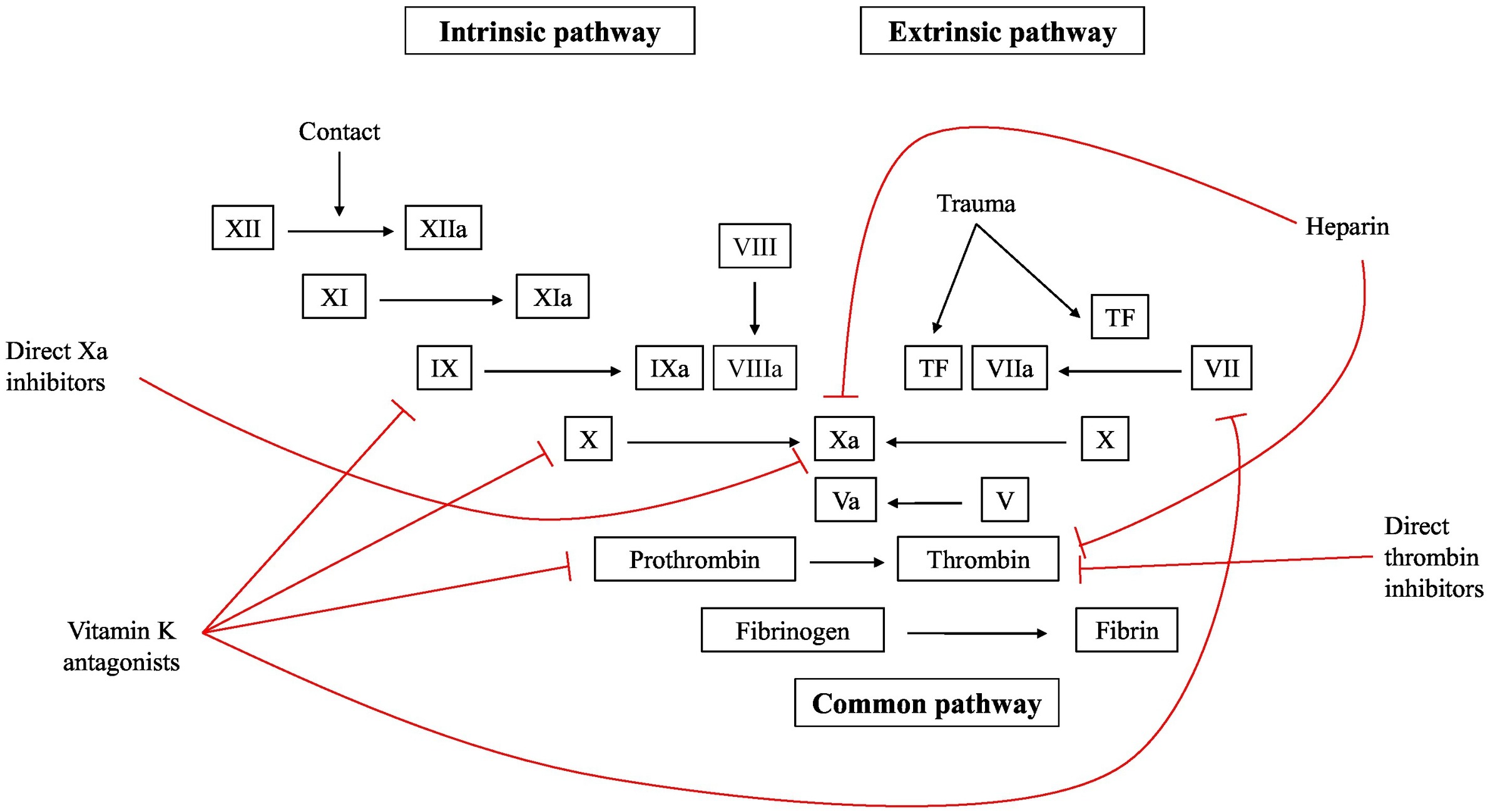 Fig2. Targets for anticoagulant therapies in use today. (Karsten Engseth Kluge, 2022)
Fig2. Targets for anticoagulant therapies in use today. (Karsten Engseth Kluge, 2022)
Protein Function
F12 has several biochemical functions, for example, misfolded protein binding,protein binding,serine-type aminopeptidase activity. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by F12 itself. We selected most functions F12 had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with F12. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| serine-type endopeptidase activity | KLK1B11,PREP,KLK1B1,KLK7,PRSS48,CTRB1,Acr,PRSS22,GZMM,TMPRSS5 |
| protein binding | ATXN1,SH2B1,CD97,GOLPH3,HIST1H3A,GTF2IRD2,ZNF83,TBC1D17,BTN2A2,SART3 |
| misfolded protein binding | DNAJC10,EDEM1,HDAC6,CLU,HSPA5,DNAJB9,DNAJC3,HSPD1,BAG6,SDF2L1 |
Interacting Protein
F12 has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with F12 here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of F12.
KNG1;C1QBP;GP1BA
Resources
Research Area
Related Services
Related Products
References
- Karton, A; Goerigk, L; et al. Accurate Reaction Barrier Heights of Pericyclic Reactions: Surprisingly Large Deviations for the CBS-QB3 Composite Method and Their Consequences in DFT Benchmark Studies. JOURNAL OF COMPUTATIONAL CHEMISTRY 36:622-632(2015).
- Ohnishi, Y; Ishimura, K; et al. Massively Parallel MP2-F12 Calculations on the K Computer. INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF QUANTUM CHEMISTRY 115:333-341(2015).



