Kinin System
Related Symbol Search List
Immunology Background
Available Resources for Kinin System Research
Creative BioMart strives to be a leading force in the field of kinin system research. We are dedicated to continuously updating our product range and resources, providing cutting-edge tools and information to researchers to drive advancements in this vital area of knowledge.
- Our extensive portfolio includes essential items such as recombinant proteins, which play a crucial role in unraveling the functions and mechanisms of the kinin system.
- With a team of experienced experts who possess deep knowledge in kinin system research, we are committed to providing tailor-made solutions that meet the unique requirements of each researcher.
- Furthermore, we offer comprehensive resource support, including involved pathways, protein functions, interacting proteins, and other valuable information. Ultimately, our goal is to enhance the impact of their research efforts.
Our Featured Products
| Cat.# | Product name | Species | Source (Host) | Tag |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| KLK1-299H | Active Recombinant Human KLK1 protein, His-tagged | Human | HEK293 | His |
| F12-12617H | Recombinant Human F12 protein, His-tagged | Human | E.coli | His |
| Kng1-3300M | Active Recombinant Mouse Kng1 protein(Glu21-Ser480), His-tagged | Mouse | HEK293 | C-His |
About Kinin System
The kinin system, also known as the kallikrein-kinin system, is a complex biochemical pathway involved in regulating inflammation, blood pressure, and blood coagulation. It is named after its main component, kinins, which are small bioactive peptides that exert a variety of physiological effects. It consists of a cascade of proteins and peptides that interact with specific receptors to mediate their effects. The primary components of the kinin system are kininogens, kinins, and kinin receptors.
- Kininogens: Kininogens are large plasma proteins synthesized in the liver and found in the blood. They are inactive precursors that can be enzymatically cleaved to produce kinins. The two main types of kininogens are high-molecular-weight kininogen (HMWK) and low-molecular-weight kininogen (LMWK).
- Kinins: Kinins are small peptides that are generated through the proteolytic cleavage of kininogens by specific enzymes, mainly kallikreins. The most well-known and biologically active kinins are bradykinin and kallidin. Bradykinin is generated primarily from HMWK, while kallidin is generated from both HMWK and LMWK.
- Kinin Receptors: Kinins exert their effects by interacting with specific G protein-coupled receptors known as kinin receptors. There are two primary types of kinin receptors: B1 receptors and B2 receptors. B2 receptors are constitutively expressed and widely distributed in various tissues, while B1 receptors are induced during inflammation. Activation of kinin receptors leads to the initiation of intracellular signaling pathways that mediate the biological effects of kinins.
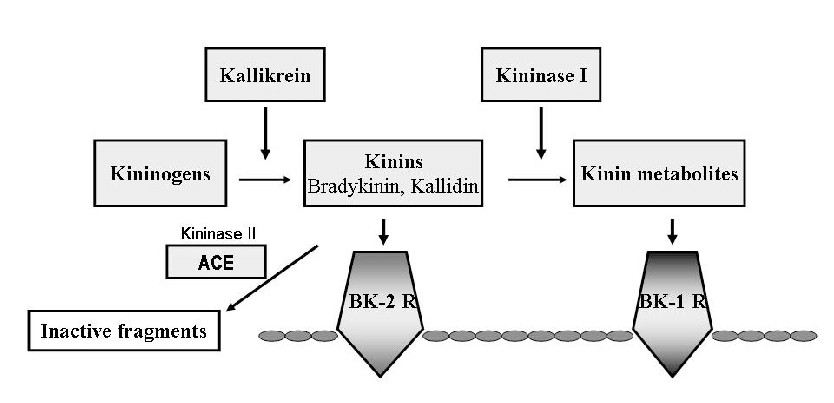 Fig.1 The human kininogen-kallikrein-kinin-system. (Liesmaa I, 2010)
Fig.1 The human kininogen-kallikrein-kinin-system. (Liesmaa I, 2010)
Functions of the Kinin System
The kinin system has diverse physiological functions, including:
- Inflammation: Kinins play a crucial role in the inflammatory response. They promote vasodilation (widening of blood vessels), increase vascular permeability, and attract immune cells to the site of inflammation. These effects contribute to the redness, swelling, and heat associated with inflammation.
- Blood Pressure Regulation: Kinins are potent vasodilators, meaning they relax blood vessels, leading to decreased peripheral resistance and increased blood flow. This vasodilation can help regulate blood pressure.
- Pain Modulation: Kinins can sensitize sensory nerve fibers, leading to the perception of pain. They can also interact with pain receptors, contributing to the hypersensitivity and pain associated with inflammation.
- Tissue Repair: Kinins promote tissue repair by stimulating the release of growth factors and cytokines, which facilitate the healing process.
Imbalances or dysregulation of the kinin system can contribute to various pathological conditions. For example, excessive kinin production or impaired breakdown can result in conditions such as hereditary angioedema, a rare genetic disorder characterized by recurrent episodes of severe swelling.
The kinin system has been a target for therapeutic interventions. Inhibitors of kinin receptors, such as angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors, are commonly used to treat hypertension by reducing the production of bradykinin. Additionally, drugs that target specific components of the kinin system are being investigated for potential therapeutic applications in conditions such as inflammation and pain management. Understanding the kinin system's role and its interactions provides insights into various physiological and pathological processes and potential therapeutic avenues.
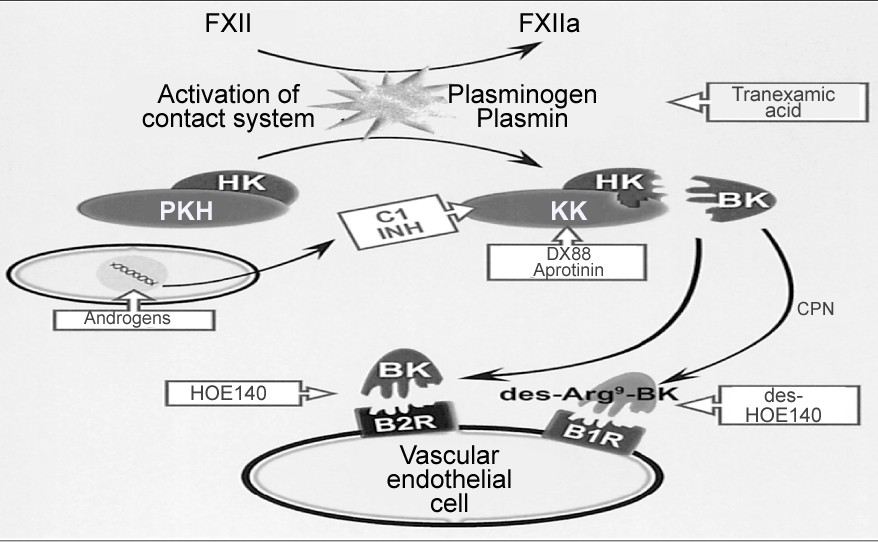 Fig.2 Pharmacological targets to modulate the kallikrein-kinin activity. (Sharma J N, 2012)
Fig.2 Pharmacological targets to modulate the kallikrein-kinin activity. (Sharma J N, 2012)
Tranexamic acid inhibits fibrinolysis and DX88 and C1INH inhibit the serine activity of plasma kallikrein, although androgens stimulate the synthesis of C1INH. B1 and B2 antagonists block the activation of their respective receptors.
We are committed to helping you achieve your scientific goals and make meaningful contributions to the field of kinin system research. Contact us today to learn more about our products and resources.
References:
- Liesmaa I. Regulation of Kinin receptor Expression in Heart Failure with a Focus on Vascular Endothelium[J]. Helsingin Yliopisto, 2010.
- Moreau ME, Garbacki N, Molinaro G, Brown NJ, Marceau F, Adam A. The kallikrein-kinin system: current and future pharmacological targets. J Pharmacol Sci. 2005;99(1):6-38. doi:10.1254/jphs.srj05001x
- Marceau F. Drugs of the Kallikrein–Kinin System. Encyclopedia. Available at: https://encyclopedia.pub/entry/46838. Accessed February 07, 2024.
- Sharma, Jagdish & AL-Sherif, G. The Kinin System: Present and Future Pharmacological Targets. Am. J. Biomed. Sci. (2011) 3. 156-169. 10.5099/aj110200156.
- Sharma J N. The Role of Inflammatory Mediator Bradykinin in Cardiovascular and Renal Diseases[J]. Journal of Autacoids, 2012, 01(S1). DOI:10.4172/scientificreports.142.

