FURIN
-
Official Full Name
furin (paired basic amino acid cleaving enzyme) -
Overview
Proteins are normally synthesized in an inactive form and later require proteolytic processing to become active. Proprotein convertases make up a family of serine proteases capable of activating substrates that will subsequently intervene in extracellular -
Synonyms
FURIN;furin (paired basic amino acid cleaving enzyme);FUR, PACE, paired basic amino acid cleaving enzyme (furin, membrane associated receptor protein) , PCSK3;SPC1;FES upstream region;dibasic processing enzyme;dibasic-processing enzyme;furi
Recombinant Proteins
- Human
- Mouse
- Rhesus macaque
- Rat
- Chicken
- Xenopus laevis
- Bovine
- E.coli
- HEK293
- Mammalian Cells
- CHO
- S2 Cells
- Hi-5 Insect Cells
- Sf9 Cells
- BSC40
- Insect Cells
- In Vitro Cell Free System
- His
- Avi
- Fc
- Non
- GST
- GFP
- DDK
- Myc
- Flag
Background
What is FURIN protein?
FURIN gene (furin, paired basic amino acid cleaving enzyme) is a protein coding gene which situated on the long arm of chromosome 15 at locus 15q26. This gene encodes a member of the subtilisin-like proprotein convertase family, which includes proteases that process protein and peptide precursors trafficking through regulated or constitutive branches of the secretory pathway. It encodes a type 1 membrane bound protease that is expressed in many tissues, including neuroendocrine, liver, gut, and brain. The encoded protein undergoes an initial autocatalytic processing event in the ER and then sorts to the trans-Golgi network through endosomes where a second autocatalytic event takes place and the catalytic activity is acquired. The FURIN protein is consisted of 794 amino acids and FURIN molecular weight is approximately 86.7 kDa.
What is the function of FURIN protein?
FURIN protein is a widespread endoprotease in eukaryotic cells, also known as a member of the precursor protein convertase family. FURIN recognizes and cuts the specific amino acid sequences of a variety of precursor proteins, thereby activating these proteins to perform their biological functions. FURIN's substrates include neuropeptides, peptide hormones, growth factors, receptors, plasma proteases, matrix metalloproteinases and bacterial exotoxins, which play important roles in many biological processes. FURIN is involved in the regulation of various physiological processes through its protease activity, including cell signaling, cell proliferation, differentiation, and immune response.
FURIN related signaling pathway
Furin-related signaling pathways are mainly involved in the processing and maturation of proteins within cells. FURIN is a precursor protein convertase belonging to the Subtilis protease family that cleaves peptides inside the Golgi apparatus to activate a variety of proteins, including growth factors, receptors, adhesion molecules, and enzymes. FURIN's activity influences many biological processes, such as embryonic development, cell migration, wound healing, and disease processes (such as cancer invasion and metastasis).
FURIN related diseases
FURIN is associated with a variety of diseases, especially those involving abnormal processing of protein precursors. It is overexpressed in some cancers, such as liver and bowel cancer, and upregulation of FURIN is associated with tumor development, aggressiveness, and poor prognosis. In addition, FURIN is involved in viral infections, such as coronaviruses, including SARS-CoV-2 (the virus that causes COVID-19), which rely on FURIN to lyse spike proteins, thereby facilitating the entry of the virus into host cells. In addition, the activity of FURIN has been associated with cardiovascular diseases, fibrotic disorders and certain genetic diseases.
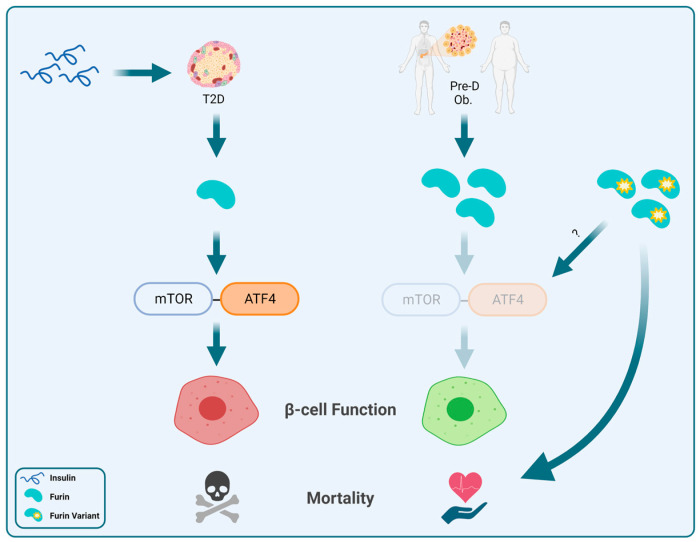
Fig1. Proposed model of the potential roles of furin and its variants in β-cell function and overall health. (Sulaiman K Marafie, 2023)
Bioapplications of FURIN
As an important precursor protein convertase, rhFURIN is involved in the maturation of many biologically active molecules, including growth factors, hormones, receptors, and extracellular matrix proteins. It plays a key role in the localization of cells, the processing of proteins in secretory pathways, and the occurrence and development of diseases. rhFURIN's activity can be determined by specific fluorescent substrates, which makes it useful in drug screening, disease modeling, and biochemical studies. In addition, inhibitors of rhFURIN are being investigated for the treatment of cancer and other diseases caused by FURIN's abnormal activity, making it an important target for drug development and biomarker research.
Case Study
Case Study 1: Thomas P. Peacock, 2021
SARS-CoV-2 enters cells by cleaving its spike protein at two sites, with a furin-cleavable sequence at S1/S2. This sequence boosts SARS-CoV-2 infection in lung and human airway cells, likely via TMPRSS2, which helps the virus avoid antiviral proteins. A SARS-CoV-2 variant lacking this cleavage site had reduced shedding in ferrets and didn't transmit to contacts. Most SARS-CoV-2 sequences from patients lack deletions at this site, suggesting it's important for the virus.
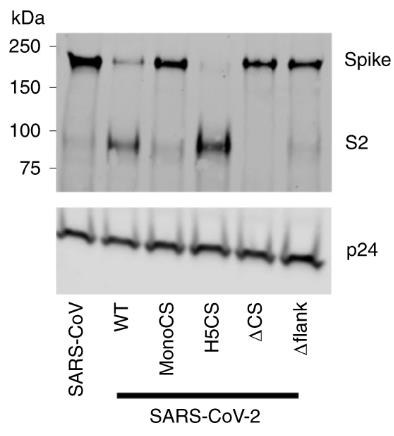
Fig1. Western blot analysis of concentrated lentiviral PVs with different coronavirus spike proteins.
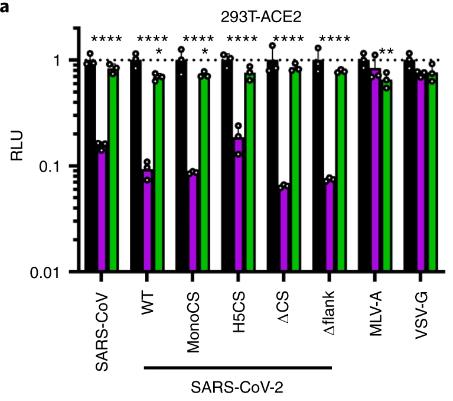
Fig2. Inhibition of entry of lentiviral PVs into 293T-ACE2.
Case Study 2: S M Cork, 2012
BAI1, a G protein-coupled receptor found in the brain, has been linked to suppressed tumor growth in various cancers. Its N-terminal cleavage by extracellular proteases, such as furin and MMP-14, generates a 40-kDa fragment called Vasculostatin-40, which can inhibit angiogenesis. This discovery of a proteolytic mechanism regulating BAI1 activity reveals new insights into its role as a tumor suppressor and suggests potential therapeutic strategies for cancer and vascular diseases.
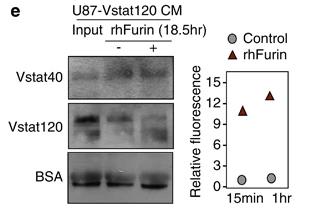
Fig3. In vitro cleavage assay of Vstat120 with rhFurin.
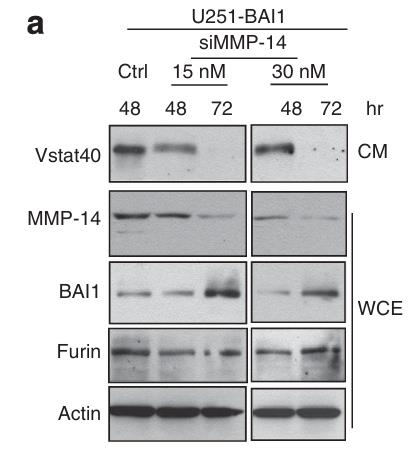
Fig4. SiRNA-mediated knockdown of MMP-14 expression yielded virtually complete abrogation of Vstat40 in the presence of furin.
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
.jpg)
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (FURIN-7820H)
.
.jpg)
Fig2. SDS-PAGE (FURIN-6584H)
Involved Pathway
FURIN involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways FURIN participated on our site, such as Influenza A, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with FURIN were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| Influenza A | HSPA2,TNFRSF10A,IL8L1,TYK2,CYCS,HSPA6,PIK3R5,IFNB1,IFNA16,HLA-DOA |
Protein Function
FURIN has several biochemical functions, for example, endopeptidase activity,metal ion binding,nerve growth factor binding. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by FURIN itself. We selected most functions FURIN had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with FURIN. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| peptidase activity | ADAM25,CASP8,PLAUA,UCHL3,CTSM,CAPN8,MMP25,TRY,AGA,AGBL4 |
| metal ion binding | ZDHHC16A,GM12824,CYP4A10,ZXDB,ALDH1A2,ZFPM2,IKBKG,TOPAZ1,PPARDB,PHLPP2 |
| peptide binding | CRIP1,RNPEP,AVPR2,GNRHR4,ERAP2,LTA4H,LNPEP,CTSB,CLTA,TPP1 |
| endopeptidase activity | SENP3,PSMA5,PSMB2,PARL,P4HB,KLK1B11,MMP1A,PSMA4,ECE1,SENP3B |
| protease binding | TIMP3,TP53,NFRKB,FLOT1,FN1,SRI,KIT,BCL2,FLOT2,BDKRB2 |
| protein binding | PPP3CC,MYO7B,TRIM31,HDAC5,POP7,PLGRKT,USP5,SPON2,NLRP3,ZNF434 |
| serine-type endopeptidase activity | HTRA1A,KLK5,PROZ,CTRL,PREPL,KLK4,FAP,PRSS54,MASP2,TMPRSS11G |
| nerve growth factor binding | NGFRB,PCSK6,SORT1,NTRK1,NGFR |
| serine-type endopeptidase inhibitor activity | SPINT2,ITIH5,SPINT1A,SERPINH1B,APPA,APLP2,SERPINA6,SPINT4,SERPINA11,TFPI2 |
Interacting Protein
FURIN has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with FURIN here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of FURIN.
MSTN;MST1R;DDX56;ABCC6;Gorasp2;BAG6;MMP14;HUWE1;Dennd6a;SGTB;TGOLN2;GORASP2;Spn42Da
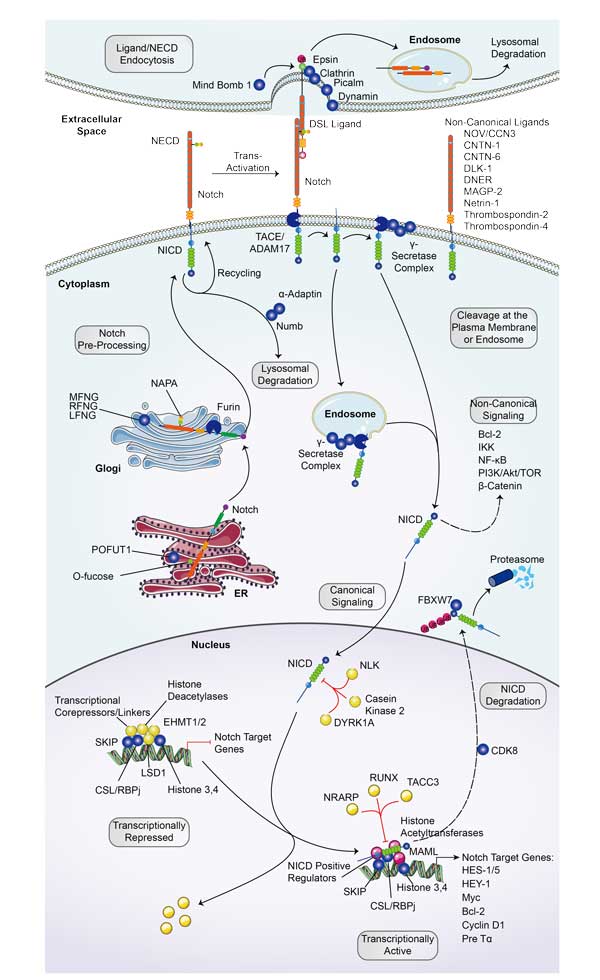
FURIN Related Signal Pathway
Resources
Related Services
Related Products
References
- Gierer, S; Muller, MA; et al. Inhibition of Proprotein Convertases Abrogates Processing of the Middle Eastern Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus Spike Protein in Infected Cells but Does Not Reduce Viral Infectivity. JOURNAL OF INFECTIOUS DISEASES 211:889-897(2015).
- Pasetto, M; Antignani, A; et al. Whole-genome RNAi screen highlights components of the endoplasmic reticulum/Golgi as a source of resistance to immunotoxin-mediated cytotoxicity. PROCEEDINGS OF THE NATIONAL ACADEMY OF SCIENCES OF THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA 112:E1135-E1142(2015).