LGALS3
-
Official Full Name
lectin, galactoside-binding, soluble, 3 -
Overview
This gene encodes a member of the galectin family of carbohydrate binding proteins. Members of this protein family have an affinity for beta-galactosides. The encoded protein is characterized by an N-terminal proline-rich tandem repeat domain and a single C-terminal carbohydrate recognition domain. This protein can self-associate through the N-terminal domain allowing it to bind to multivalent saccharide ligands. This protein localizes to the extracellular matrix, the cytoplasm and the nucleus. This protein plays a role in numerous cellular functions including apoptosis, innate immunity, cell adhesion and T-cell regulation. Alternate splicing results in multiple transcript variants -
Synonyms
L31;GAL3;MAC2;CBP35;GALBP;GALIG;LGALS3;Galactose specific lectin 3;L34;L-31;L-34;Laminin binding protein;Lectin L 29;MGC105387;Galectin-3;LGALS3;CBP35;GAL3;GALBP;GALIG;L31;LGALS2;MAC2;35 kDa lectin;IgE-binding protein;MAC-2 antigen;carbohydrate-binding protein 35;galactose-specific lectin 3;laminin-binding protein;lectin L-29
Recombinant Proteins
- Human
- Mouse
- Cynomolgus
- Rhesus macaque
- Rat
- Rabbit
- Chicken
- E.coli
- E. coli
- N-His
- Mammalian Cells
- HEK293
- HeLa
- GST
- His
- Non
- Avi
- Fc
- DDK
- Myc
- Flag
Background
What is LGALS3 protein?
LGALS3 (galectin 3) gene is a protein coding gene which situated on the long arm of chromosome 14 at locus 14q22. This gene encodes a member of the galectin family of carbohydrate binding proteins. Members of this protein family have an affinity for beta-galactosides. The encoded protein is characterized by an N-terminal proline-rich tandem repeat domain and a single C-terminal carbohydrate recognition domain. This protein can self-associate through the N-terminal domain allowing it to bind to multivalent saccharide ligands. The LGALS3 protein is consisted of 454 amino acids and its molecular mass is approximately 51.7 kDa.
What is the function of LGALS3 protein?
This protein localizes to the extracellular matrix, the cytoplasm and the nucleus. This protein plays a role in numerous cellular functions including apoptosis, innate immunity, cell adhesion and T-cell regulation. Galectin-3 mediates with the alpha-3, beta-1 integrin the stimulation by cspg4 of endothelial cells migration. Galectin-3 plays an necessary part during the acquisition of vasculogenic mimicry and angiogenic properties associated with melanoma progression. LGALS3 overexpression is highly expressed in early stages of papillary carcinoma, and its expression intensity declines during tumor progression.
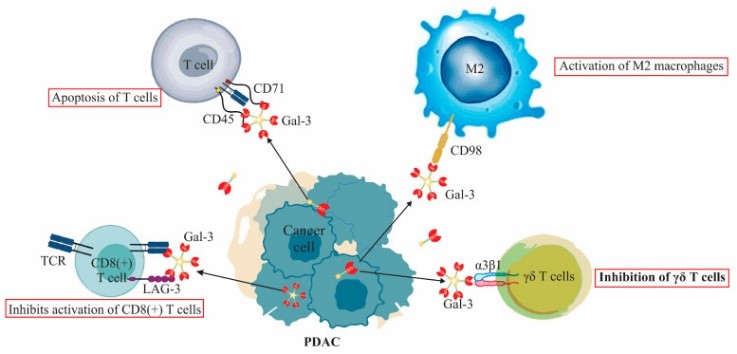
Fig1. Extracellular functions of Galectin-3 (Gal-3) in PDAC immune modulation. (Milica Dimitrijevic Stojanovic, 2023)
LGALS3 Related Signaling Pathway
LGALS3 can participate in biological processes such as cell proliferation, differentiation and apoptosis by activating MAPK (including ERK, JNK and p38) signaling pathways. LGALS3 can affect the activity of Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway and PI3K/AKT signaling pathway to regulate cell proliferation and migration. LGALS3 activates the NF-κB signaling pathway, which promotes inflammation and immune responses. LGALS3 is also associated with several other signaling pathways and biological processes, such as TGF-β signaling pathway, JAK/STAT signaling pathway, and autophagy.
LGALS3 Related Diseases
LGALS3 is abnormally expressed in a variety of cancers, including lung, breast, and colorectal cancers. It can promote the proliferation, invasion and metastasis of tumor cells by activating PI3K/AKT, Wnt/β-catenin and NF-κB signaling pathways. The study found that mutations in the LGALS3 gene are associated with the development of diabetes. LGALS3 can promote the proliferation and migration of vascular smooth muscle cells by activating MAPK/ERK signaling pathway, thus participating in the occurrence and development of atherosclerosis, which may be related to the occurrence and development of obesity.
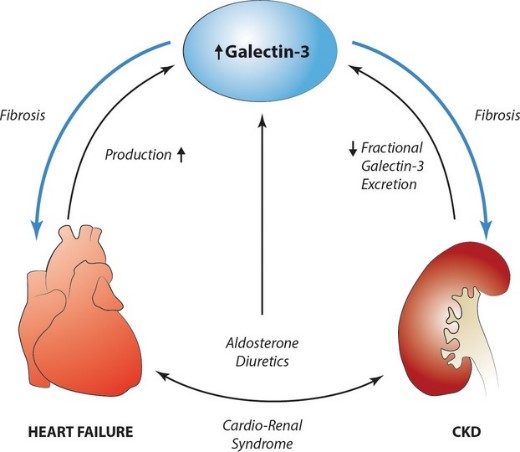
Fig2. The role of galectin-3 in the cardiorenal syndrome. (Wouter C Meijers, 2014)
Bioapplications of LGALS3
LGALS3 is abnormally expressed in a variety of tumors and therefore can be used as a potential tumor marker. By detecting the level of LGALS3 in serum or tissue, it can help diagnose certain types of cancer, such as breast cancer, prostate cancer, etc. LGALS3 can accelerate wound healing by promoting cell proliferation, migration, and angiogenesis, and may have potential applications in wound repair, fracture healing, and nerve regeneration. LGALS3 is an important biomarker that can be used for drug screening and evaluation.
Case Study
Case study 1: Sebastian Bänfer, 2018
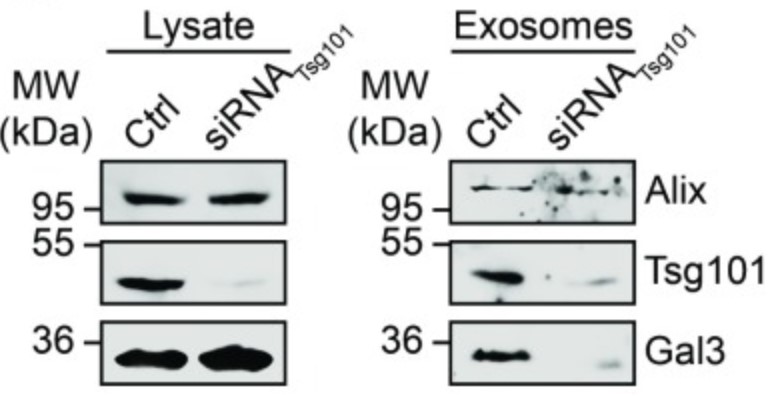
The beta-galactoside binding lectin galectin-3 (Gal3) is found intracellularly and in the extracellular space. Secretion of this lectin is mediated independently of the secretory pathway by a not yet defined nonclassical mechanism. Superresolution and electron microscopy studies visualized Gal3 recruitment and sorting into intraluminal vesicles and the team found Gal3 in the lumen of exosomes in this study. Exosomal Gal3 release depends on the endosomal sorting complex required for transport I (ESCRT-I) component Tsg101 and functional Vps4a. In addition, the researchers identified a highly conserved tetrapeptide P(S/T)AP motif in the amino terminus of Gal3 that mediates a direct interaction with Tsg101. Here the team conclude that Gal3 is a member of endogenous non-ESCRT proteins which are P(S/T)AP tagged for exosomal release.
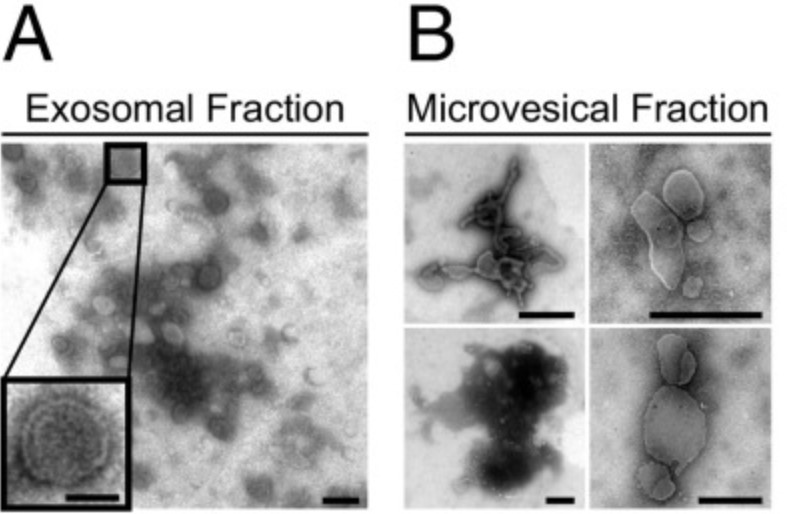
Fig1. Gal3 is contained in exosomes. (A and B) The 100,000 × g pellets (exosomes) (A) or the 10,000 × g pellets (microvesicles) (B) were subjected to negative staining for electron microscopy. Inset shows the typical appearance of an exosome.
Case study 2: Annett Koch, 2010
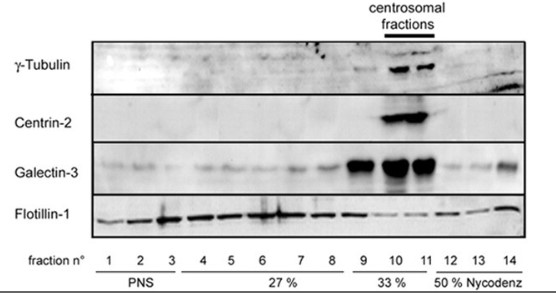
Galectin-3 is a beta-galactoside-binding protein widely expressed in all epithelia where it is involved in tissue homeostasis and cancer progression. The researchers investigated the potential role of galectin-3 on early events in polarization of epithelial renal cells, using three-dimensional cultures of MDCK cells and also galectin-3 null mutant mouse kidneys. The results show that depletion in galectin-3 systematically leads to severe perturbations of microtubular network associated with defects in membrane compartimentation, both in vitro and in vivo. Moreover, the absence of galectin-3 impinges on the morphology of the primary cilium, which is three times longer and unusually shaped. Collectively, these data establish galectin-3 as a key determinant in epithelial morphogenesis via its effect on centrosome biology.
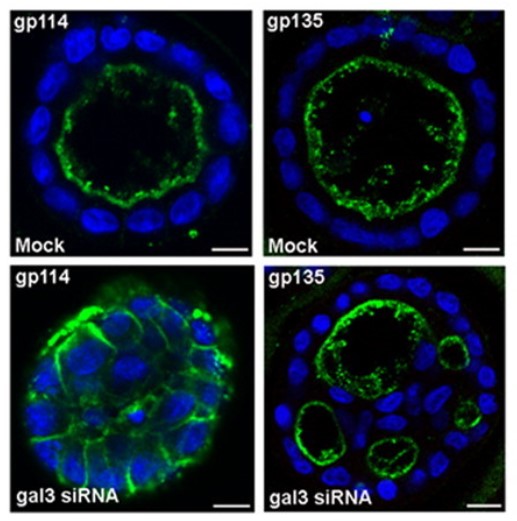
Fig3. Depletion of galectin-3 leads to abnormal cystogenesis in MDCK cells. MDCK cells were cultured in Matrigel 3D matrix for 5 d.
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
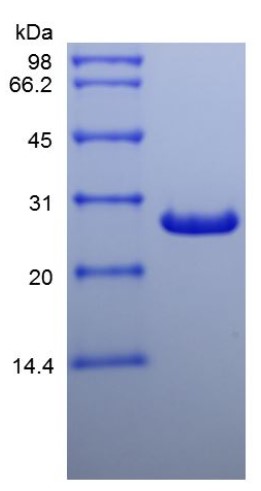
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (LGALS3-4952H) (PROTOCOL for western blot)
.
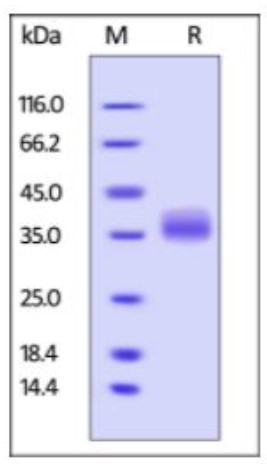
Fig2. SDS-PAGE (LGALS3-276H) (PROTOCOL for western blot)
Involved Pathway
LGALS3 involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways LGALS3 participated on our site, such as AGE/RAGE pathway,Advanced glycosylation endproduct receptor signaling,Hedgehog signaling events mediated by Gli proteins, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with LGALS3 were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| Spinal Cord Injury | PTPRZ1,GAP43,LILRB3,MBP,OMG,RTN4,GDNF,TNFSF13B,KLK8,NOX4 |
| Immune System | BTR16,ASB14,TRIM38,GBP1,CTSE,DEFA6,POLR3GLA,KIF5B,PPAPDC1B,PVRL2L |
| AGE/RAGE pathway | EGFR,JAK2,MMP13,TIRAP,ATF2,CHUK,DDOST,MAPK14,JUN,AGER |
| Hedgehog signaling events mediated by Gli proteins | SAP30,IFT88,SAP18,CSNK1G3,SIN3B,MTSS1,KIF3A,CSNK1G2,SPOP |
| Advanced glycosylation endproduct receptor signaling | AGER,S100A12,S100B,ALCAMB,DDOST,SAA1,APPB,APPA |
| Innate Immune System | DEFB4A,CD180,CFHL4,DEFB119,PELI1,CHST13,DHX9,KIR3DS1,RCA2.1,DEFA5 |
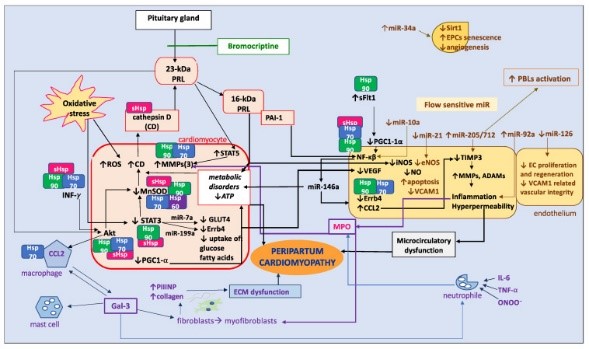
Fig1. Pathophysiology of peripartum cardiomyopathy (PPCM), changed based on the results of the paper by Hilfiker-Kleiner et al. (Karolina E Kryczka, 2024)
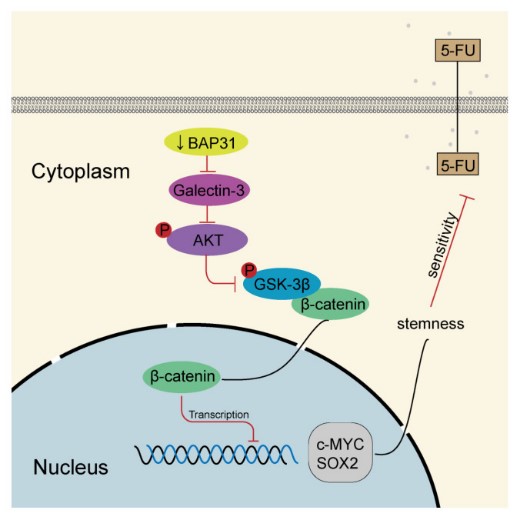
Fig2. Schematic model of knockdown of BAP31 downregulating galectin-3 to inhibit Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway to modulate 5-FU chemosensitivity and cancer stemness in colorectal cancer. (Jingjing Liu, 2023)
Protein Function
LGALS3 has several biochemical functions, for example, IgE binding,carbohydrate binding,chemoattractant activity. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by LGALS3 itself. We selected most functions LGALS3 had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with LGALS3. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| carbohydrate binding | SELL,Il2,GALNT1,CANX,REG3G,CLEC4A2,LGALS7B,ATRN,KLRB1,SIGLEC7 |
| poly(A) RNA binding | SAMD4,CLNS1A,RAVER1,SMG1,ALDOA,RPP25L,EIF5B,FASN,NOM1,RPL14 |
| protein binding | DPYSL5,GZMA,GNGT1,DDC,DERL1,GM5506,RNF111,CCDC85B,HESX1,CEP57L1 |
| chemoattractant activity | CCL3,VHL,FGF7,FGF10,VEGFC,CCL15,CXCL12A,HMGB2,SAA4,CXCL12 |
| IgE binding | CD247L,MS4A2,FCER2,FCER1A,FCER1G,Fcer2a |
| laminin binding | NID1,LRRC15,ECM1,LGALS2A,LGALS1,BCAM,THBS1,TINAGL1,RPSA,ITGB1 |
Interacting Protein
LGALS3 has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with LGALS3 here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of LGALS3.
SS18L1;CD6;GOLGA2;PPIG;ALCAM;PRR13;AHSG;MICA
Resources
Research Area
Related Services
Related Products
References
- Nio-Kobayashi, J; Boswell, L; et al. The Loss of Luteal Progesterone Production in Women Is Associated With a Galectin Switch via alpha 2,6-Sialylation of Glycoconjugates. JOURNAL OF CLINICAL ENDOCRINOLOGY & METABOLISM 99:4616-4624(2014).
- Ma, J; Yao, YL; et al. MiR-152 functions as a tumor suppressor in glioblastoma stem cells by targeting Kruppel-like factor 4. CANCER LETTERS 355:85-95(2014).



