MMP8
-
Official Full Name
matrix metallopeptidase 8 (neutrophil collagenase) -
Overview
Proteins of the matrix metalloproteinase (MMP) family are involved in the breakdown of extracellular matrix in normal physiological processes, such as embryonic development, reproduction, and tissue remodeling, as well as in disease processes, such as arthritis and metastasis. Most MMPs are secreted as inactive proproteins which are activated when cleaved by extracellular proteinases. However, the enzyme encoded by this gene is stored in secondary granules within neutrophils and is activated by autolytic cleavage. Its function is degradation of type I, II and III collagens. The gene is part of a cluster of MMP genes which localize to chromosome 11q22.3. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008] -
Synonyms
MMP8;matrix metallopeptidase 8 (neutrophil collagenase);HNC;CLG1;MMP-8;PMNL-CL;neutrophil collagenase;PMNL collagenase;matrix metalloproteinase-8;matrix metalloproteinase 8 (neutrophil collagenase);BB138268
Recombinant Proteins
- Human
- Mouse
- Rat
- Cynomolgus
- HEK293
- E.coli
- Mammalian Cells
- Human Cells
- CHO
- C-His
- Neutrophil granulocytes
- Wheat Germ
- In Vitro Cell Free System
- Human Neutrophil
- His
- Non
- Avi
- Fc
- T7
- Flag
- SUMO
- Myc
- GST
Background
What is MMP8 Protein?
MMP8 gene (matrix metallopeptidase 8) is a protein coding gene which situated on the long arm of chromosome 11 at locus 11q22. This gene encodes a member of the matrix metalloproteinase (MMP) family of proteins. These proteins are involved in the breakdown of extracellular matrix in embryonic development, reproduction, and tissue remodeling, as well as in disease processes, such as arthritis and metastasis. Proteolysis at different sites on this protein results in multiple active forms of the enzyme with distinct N-termini. This protein functions in the degradation of type I, II and III collagens. The MMP8 protein is consisted of 467 amino acids and MMP8 molecular weight is approximately 53.4 kDa.
What is the Function of MMP8 Protein?
The MMP8 protein is a member of the Matrix Metalloproteinases (MMPs) family. It plays a role in a variety of physiological and pathological processes, including embryonic development, tissue remodeling, and disease processes such as arthritis and metastasis. The main function of MMP8 protein is to degrade type I, II and III collagen. In addition, MMP8 plays an important role in inflammatory diseases and cancer progression. However, the role of MMP8 in cancer progression may be twofold, and it may have tumorigenic and anti-tumor properties, depending on the type of tumor and its stage of development and progression.
MMP8 Related Signaling Pathway
The study found that MMP8 is associated with alterations in neurobehavior, particularly regulating the behavior of mice under social stress, which involves signaling pathways that affect the extracellular matrix (ECM) and neural activity. MMP-8 inhibitors have demonstrated anti-inflammatory and antioxidant mechanisms involving NF-κB, Nrf2, and PPAR-γ signaling pathways, suggesting that MMP8 may play a role in neuroinflammation through these pathways. In our study, MMP8 is a newly discovered pathogenic factor in cerebral ischemia, suggesting that it may play a role by affecting the extracellular matrix and cell signaling pathways.
MMP8 Related Diseases
As a neutrophil collagenase, MMP8 is closely associated with the development of a variety of inflammatory diseases, autoimmune diseases, and cancers. It is involved in the regulation of cell migration, tissue remodeling and inflammatory response by degrading extracellular matrix components, and its abnormal expression or increased activity has been associated with pathological processes such as rheumatoid arthritis, multiple sclerosis, tumor invasion and metastasis, and depression. Therefore, MMP8 is considered a potential therapeutic target for these diseases.
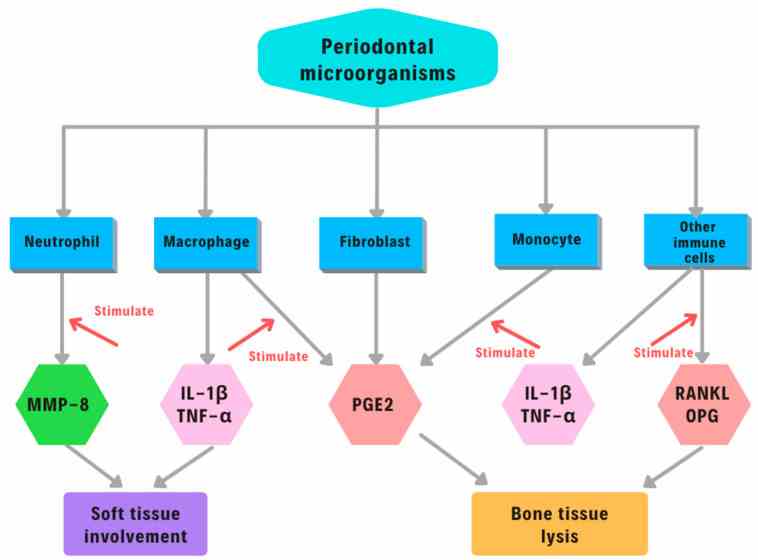
Fig1. Biomarkers in periodontal disease. (Ionut Luchian, 2022)
Bioapplications of MMP8
Due to its critical role in multiple pathological processes, MMP8 has emerged as a promising target in drug development and disease treatment, particularly in the areas of inflammation, autoimmune diseases, and certain cancer treatments. By inhibiting MMP8 activity or modulating its expression, it could potentially slow disease progression, improve clinical symptoms, and provide patients with new treatment options. In addition, the expression level of MMP8 is also being studied as a biomarker for certain disease states, contributing to disease surveillance and evaluation of therapeutic response.
Case Study
Case Study 1: K Juurikka, 2021
Researchers mapped the substrates of MMP8 to elucidate its previously shown tumour-protective role in oral tongue squamous cell carcinoma (OTSCC). MMP8 overexpressing (+) HSC-3 cells, previously demonstrated to have reduced migration and invasion, showed enhanced cell-cell adhesion. By analysing the secretomes of MMP8 + and control cells with terminal amine isotopic labelling of substrates (TAILS) coupled with liquid chromatography and tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS), researchers identified 36 potential substrates of MMP8, including FXYD domain-containing ion transport regulator 5 (FXYD5). Cleavage of FXYD5 by MMP8 was confirmed using recombinant proteins. Furthermore, they detected a loss of FXYD5 levels on cell membrane of MMP8 + cells, which was rescued by inhibition of the proteolytic activity of MMP8. Silencing (si) FXYD5 increased the cell-cell adhesion of control but not that of MMP8 + cells. FXYD5 is a novel substrate of MMP8 and reducing FXYD5 levels either with siRNA or cleavage by MMP8 increases cell adhesion leading to reduced motility.
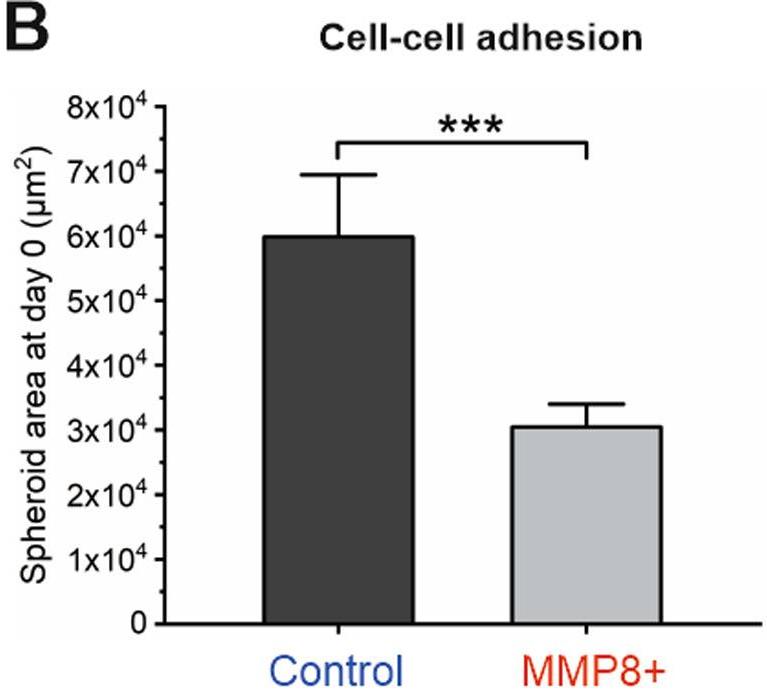
Fig1. The spheroid area of control and MMP8 + cells embedded in Myogel–Fibrin matrix at day 0.
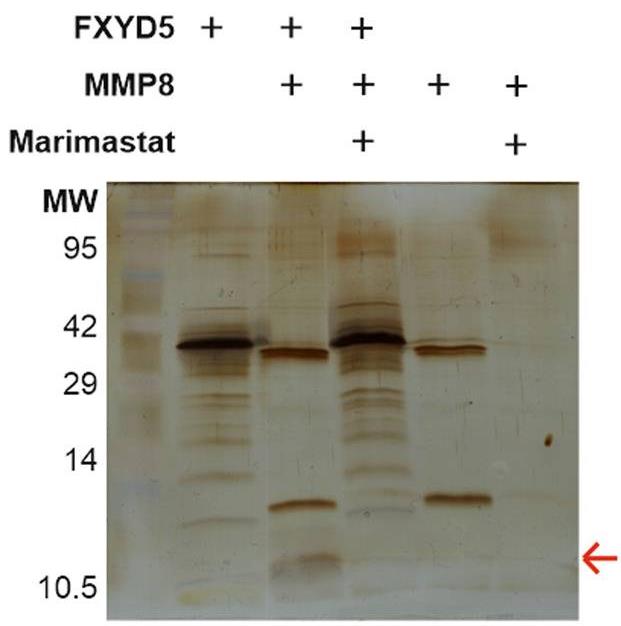
Fig2. Cleavage assay of recombinant FXYD5 with and without APMA-activated recombinant MMP8 using silver staining.
Case Study 2: An Fang, 2022
In this study, the effect of the matrix metallopeptidase (MMP) family on the permeability of the BBB during RABV infection was evaluated. The expression level of MMP8 was upregulated in mice infected with lab-attenuated RABV but not with wt RABV. Lab-attenuated RABV rather than wt RABV activates inflammatory signaling pathways mediated by the nuclear factor κB (NF-κB) and mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathways. Activated NF-κB (p65) and AP-1 (c-Fos) bind to the MMP8 promoter, resulting in upregulation of its transcription. Analysis of mouse brains infected with the recombinant RABV expressing MMP8 indicated that MMP8 enhanced BBB permeability, leading to infiltration of inflammatory cells into the central nervous system (CNS). In brain-derived endothelial cells, treatment with MMP8 recombinant protein caused the degradation of tight junction (TJ) proteins, and the application of an MMP8 inhibitor inhibited the degradation of TJ proteins after RABV infection.
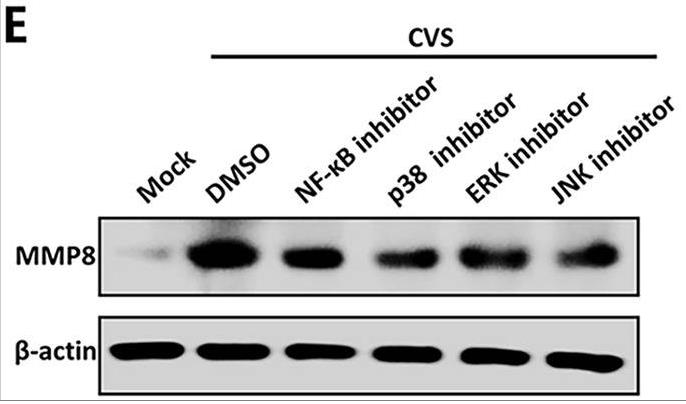
Fig3. MMP8 protein levels were assessed using Western blotting.
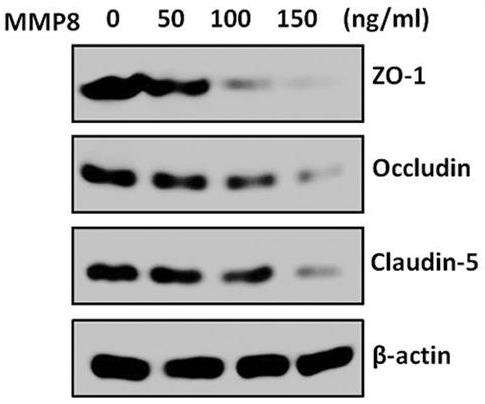
Fig4. The occludin, claudin-5, and ZO-1 expression levels in bEnd.3 cells were determined by Western blotting after treatment with MMP8 recombinant protein.
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
.jpg)
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (MMP8-2529H)
.
.jpg)
Fig2. SDS-PAGE (MMP8-5437H)
Involved Pathway
MMP8 involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways MMP8 participated on our site, such as Activation of Matrix Metalloproteinases,Collagen degradation,Degradation of the extracellular matrix, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with MMP8 were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| Activation of Matrix Metalloproteinases | CTSLL,TIMP2,CTSK,TPSAB1,MMP15,FURINB,FURINA,CTSG,MGC174152,ELANE |
| Collagen degradation | COL13A1,CTSD,CTSB,EMID2,MMP20,ELANE,MMP11,CTS7,COL23A1,MMP13 |
| Matrix Metalloproteinases | MMP26,MMP20,MMP11,MMP28,BSG,MMP19,MMP25,MMP17,TIMP2,MMP10 |
| Degradation of the extracellular matrix | ADAM9,CTRB1,COL19A1,CTSK,TLDC2,COL15A1B,ADAM8,ADAMTS18,MGC174152,COL23A1 |
| Extracellular matrix organization | COL10A1A,COL9A3,ASPN,TPSAB1,FN1B,LOXL1,BGNB,COL28A1D,MGC174857,SERPINH1 |
Protein Function
MMP8 has several biochemical functions, for example, calcium ion binding,metalloendopeptidase activity,serine-type endopeptidase activity. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by MMP8 itself. We selected most functions MMP8 had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with MMP8. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| calcium ion binding | NECAB2,ATP2C1,SYT17,OTOF,MATN3A,PCDH7,MYL12B,CABP1B,PCDH1G9,AIF1L |
| zinc ion binding | BAZ1A,THAP11,PNMA3,CNBPA,ZKSCAN5,HERC2,ZNF34,CA3,ZSWIM1,MICAL2 |
| metalloendopeptidase activity | UQCRC1,ADAMTS8,ADAMTS1,MMP3,ADAMTS18,UQCRC2B,ADAM33,IDE,ADAM19,MMP19 |
| serine-type endopeptidase activity | KLK15,LONP1,MCPT1,KLK1B3,TMPRSS2,PRSS33,Acr,PREP,F12,PRSS50 |
Interacting Protein
MMP8 has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with MMP8 here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of MMP8.
Resources
Gene Families
Related Services
Related Products
References
- Oberkofler, CE; Limani, P; et al. Systemic Protection Through Remote Ischemic Preconditioning Is Spread by Platelet-Dependent Signaling in Mice. HEPATOLOGY 60:1409-1417(2014).
- Yeo, ASL; Azhar, NA; et al. Lack of Clinical Manifestations in Asymptomatic Dengue Infection Is Attributed to Broad Down-Regulation and Selective Up-Regulation of Host Defence Response Genes. PLOS ONE 9:-(2014).