Recombinant Human Serum/Glucocorticoid Regulated Kinase 1, His-tagged
| Cat.No. : | SGK1-1346H |
| Product Overview : | Recombinant human SGK1 protein was expressed with N-terminal His-tag in High-Five cells using baculovirus expression system and purified by using conventional chromatography techniques. MW: 44.5 kDa. |
- Specification
- Gene Information
- Related Products
- Citation
- Download
| Species : | Human |
| Source : | Hi-5 Insect Cells |
| Tag : | His |
| Protein Length : | 60-431aa |
| Description : | SGK1 is a serine/threonine protein kinase and a member of the AGC subfamily, which includes protein kinases A, G, and C. This protein plays an important role in activating certain potassium, sodium and chloride channels, suggesting an involvement in the regulation of processes such as cell survival, neuronal excitability, and renal sodium excretion. |
| Form : | Liquid. 20mM Tris-HCl buffer (pH8.0) containing 30% glycerol 0.2M NaCl,2mM DTT,0.1mM PMSF. |
| Molecular Mass : | 44.5 kDa (393aa) |
| AA Sequence : | MGSSHHHHHH SSGLVPRGSH MISQPQEPEL MNANPSPPPS PSQQINLGPS SNPHAKPSDF HFLKVIGKGS FGKVLLARHK AEEVFYAVKV LQKKAILKKK EEKHIMSERN VLLKNVKHPF LVGLHFSFQT ADKLYFVLDY INGGELFYHL QRERCFLEPR ARFYAAEIAS ALGYLHSLNI VYRDLKPENI LLDSQGHIVL TDFGLCKENI EHNSTTSTFC GTPEYLAPEV LHKQPYDRTV DWWCLGAVLY EMLYGLPPFY SRNTAEMYDN ILNKPLQLKP NITNSARHLL EGLLQKDRTK RLGAKDDFME IKSHVFFSLI NWDDLINKKI TPPFNPNVSG PNDLRHFDPE FTEEPVPNSI GKSPDSVLVT ASVKEAAEAF LGFSYAPPTD SFL |
| Purity : | >90% by SDS - PAGE |
| Applications : | SDS-PAGE |
| Storage : | Can be stored at 4°C short term (1-2 weeks). For long term storage, aliquot and store at -20°C or -70°C. Avoid repeated freezing and thawing cycles. |
| Concentration : | 0.25 mg/ml (determined by Bradford assay) |
| Gene Name | SGK1 serum/glucocorticoid regulated kinase 1 [ Homo sapiens ] |
| Official Symbol | SGK1 |
| Synonyms | SGK1; serum/glucocorticoid regulated kinase 1; serum/glucocorticoid regulated kinase , SGK; serine/threonine-protein kinase Sgk1; serine/threonine protein kinase SGK; serum/glucocorticoid-regulated kinase 1; SGK; |
| Gene ID | 6446 |
| mRNA Refseq | NM_001143676 |
| Protein Refseq | NP_001137148 |
| MIM | 602958 |
| UniProt ID | O00141 |
| Chromosome Location | 6q23 |
| Pathway | Aldosterone-regulated sodium reabsorption, organism-specific biosystem; Aldosterone-regulated sodium reabsorption, conserved biosystem; Class I PI3K signaling events, organism-specific biosystem; FoxO family signaling, organism-specific biosystem; Glucocorticoid receptor regulatory network, organism-specific biosystem; IL-6 Signaling Pathway, organism-specific biosystem; Insulin Pathway, organism-specific biosystem; |
| Function | ATP binding; calcium channel regulator activity; chloride channel regulator activity; nucleotide binding; potassium channel regulator activity; protein serine/threonine kinase activity; sodium channel regulator activity; |
| ◆ Recombinant Proteins | ||
| SGK1-4993H | Active Recombinant Human SGK1 protein, GST-tagged | +Inquiry |
| SGK1-2811H | Recombinant Human SGK1 Protein, Myc/DDK-tagged, C13 and N15-labeled | +Inquiry |
| SGK1-6046C | Recombinant Chicken SGK1 | +Inquiry |
| SGK1-30970TH | Recombinant Human SGK1 | +Inquiry |
| SGK1-6273H | Recombinant Human SGK1 Protein (Met1-Leu431), N-His tagged | +Inquiry |
The Bromodomain Protein 4 Contributes to the Regulation of Alternative Splicing
Journal: Cell reports PubMed ID: 31747612 Data: 2019/12/5
Authors: Sheetal Uppal, Anne Gegonne, Dinah S. Singer
Article Snippet:(+)- JQ1 , BPS Bioscience , 27400.(+)- JQ1 , BPS Bioscience , 27400.. Recombinant Human HNRNPM protein, His-tagged , Creative BioMart , 5432H.. Glutathione Agarose beads , Thermo Scientific , 16100.Glutathione Agarose beads , Thermo Scientific , 16100.
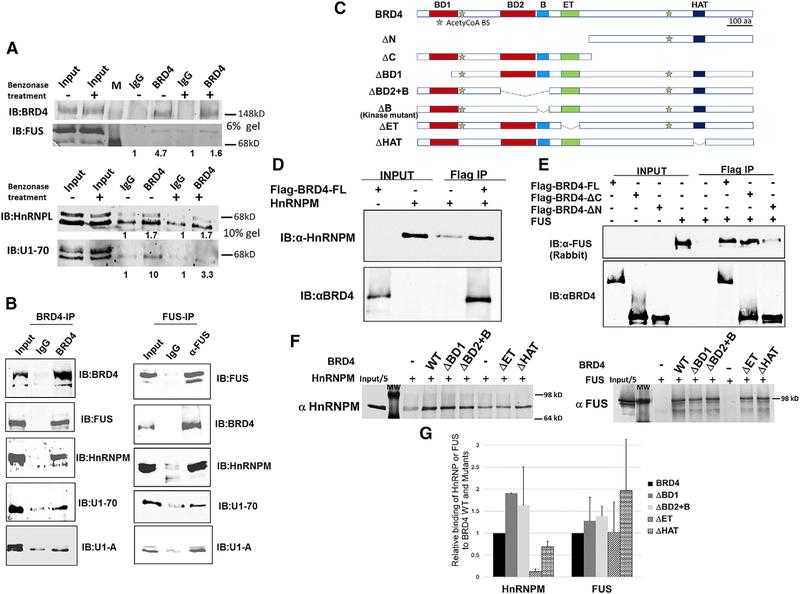
(A) Immunoblot of BRD4 immunoprecipitates from thymocyte nuclear extracts (with and without benzonase treatment) with indicated antibodies to splicing factors FUS, HnRNPL, and U1–70. The immunoprecipitates from a single extract were run on either a 6% gel to visualize BRD4 and Fus or on a 10% gel to visualize HnRNPL and U1–70. The values under the IP lanes indicate the enrichment of anti-BRD4 co-IP, relative to the IgG control. (B, left) Immunoblot of BRD4 immunoprecipitates from HeLa nuclear extracts with indicated antibodies to splicing factors FUS,
KEY RESOURCES TABLE
Not For Human Consumption!
Inquiry
- Reviews (0)
- Q&As (0)
Ask a Question for All SGK1 Products
Required fields are marked with *
My Review for All SGK1 Products
Required fields are marked with *



