Human Platelet Factor 4
| Cat.No. : | PF4-52H |
| Product Overview : | Human PF |
- Specification
- Gene Information
- Related Products
- Citation
- Download
| Species : | Human |
| Source : | Human Platelets |
| Tag : | Non |
| Description : | Platelet factor-4 is a 70-amino acid protein that is released from the alpha-granules of activated platelets and binds with high affinity to heparin. Its major physiologic role appears to be neutralization of heparin-like molecules on the endothelial surface of blood vessels, thereby inhibiting local antithrombin III activity and promoting coagulation. As a strong chemoattractant for neutrophils and fibroblasts, PF4 probably has a role in inflammation and wound repair. Oncostatin-A is a member of the CXC chemokine family. Human PF4 is used for the proof of heparin-induced thrombocytopenia. Furthermore it is used as an inhibitor in the angiogenesis during tumor therapy. |
| Amino Acid Sequence : | The sequence of the first four N-terminal amino acids was determined and was found to be Glu-Ala-Glu-Glu. |
| Physical Appearance : | Sterile Filtered white lyophilized powder. |
| Purity : | Greater than 95.0% as determined by: (a) Analysis by RP-HPLC. (b) Analysis by SDS-PAGE. |
| Formulation : | The protein was lyophilized in PBS buffer. |
| Solubility : | It is recommended to reconstitute the lyophilized CXCL4 in sterile 18 MΩ-cm H2O not less than 100 µg/ml, which can then be further diluted to other aqueous solutions. |
| Activity Control : | Binding of HIT-antibodies. |
| Stability : | Human CXCL4 although stable at 25℃ 1 week, should be stored desiccated below -18℃. Please prevent freeze-thaw cycles. |
| Publications : |
| Gene Name | PF4 platelet factor 4 [ Homo sapiens ] |
| Synonyms | PF4; platelet factor 4; CXCL4; SCYB4; MGC138298; Iroplact; Oncostatin-A; C-X-C motif chemokine 4; chemokine (C-X-C motif) ligand 4 |
| Gene ID | 5196 |
| mRNA Refseq | NM_002619 |
| Protein Refseq | NP_002610 |
| MIM | 173460 |
| UniProt ID | P02776 |
| Chromosome Location | 4q12-q21 |
| Pathway | Chemokine signaling pathway; Cytokine-cytokine receptor interaction; Hemostasis; Signaling by GPCR |
| Function | chemokine activity; heparin binding |
| ◆ Recombinant Proteins | ||
| PF4-150H | Active Recombinant Human PF4 protein, His-tagged | +Inquiry |
| Pf4-4804M | Recombinant Mouse Pf4 Protein, Myc/DDK-tagged | +Inquiry |
| Pf4-31M | Recombinant Mouse Pf4 Protein | +Inquiry |
| PF4-267H | Recombinant Human PF4 Protein, MYC/DDK-tagged, C13 and N15-labeled | +Inquiry |
| Pf4-6743M | Recombinant Mouse Pf4 protein, hFc-tagged | +Inquiry |
| ◆ Native Proteins | ||
| PF4-253H | Native Human Platelet Factor 4 | +Inquiry |
| ◆ Cell & Tissue Lysates | ||
| PF4-3283HCL | Recombinant Human PF4 293 Cell Lysate | +Inquiry |
Interactions of Spike-RBD of SARS-CoV-2 and Platelet Factor 4: New Insights in the Etiopathogenesis of Thrombosis
Journal: International Journal of Molecular Sciences PubMed ID: 34445266 Data: 2021/8/9
Authors: Margherita Passariello, Cinzia Vetrei, Malgorzata Kloc
Article Snippet:The following human recombinant proteins and antibodies were used: human SARS-CoV-2 (2019-nCoV) chimeric Spike RBD-Fc protein (Sino Biological, 10108-H08H, Eschborn, Germany); human recombinant IgG1 Fc protein (R & D Systems, 110-HG, Minneapolis, MN, USA); human Platelet Factor 4 (Creative BioMart, PF4-52H, Shirley, NY, USA).. HRP conjugated anti-human Fc antibody (Sigma, AP113P, St. Louis, MO, USA); anti-human IgG (Fab’)2 goat monoclonal antibody (Abcam, ab98535, Cambridge, UK); rabbit polyclonal anti-PF4 antibody (Prodotti Gianni, ab9561, Milano, Italy).HRP conjugated anti-human Fc antibody (Sigma, AP113P, St. Louis, MO, USA); anti-human IgG (Fab’)2 goat monoclonal antibody (Abcam, ab98535, Cambridge, UK); rabbit polyclonal anti-PF4 antibody (Prodotti Gianni, ab9561, Milano, Italy).
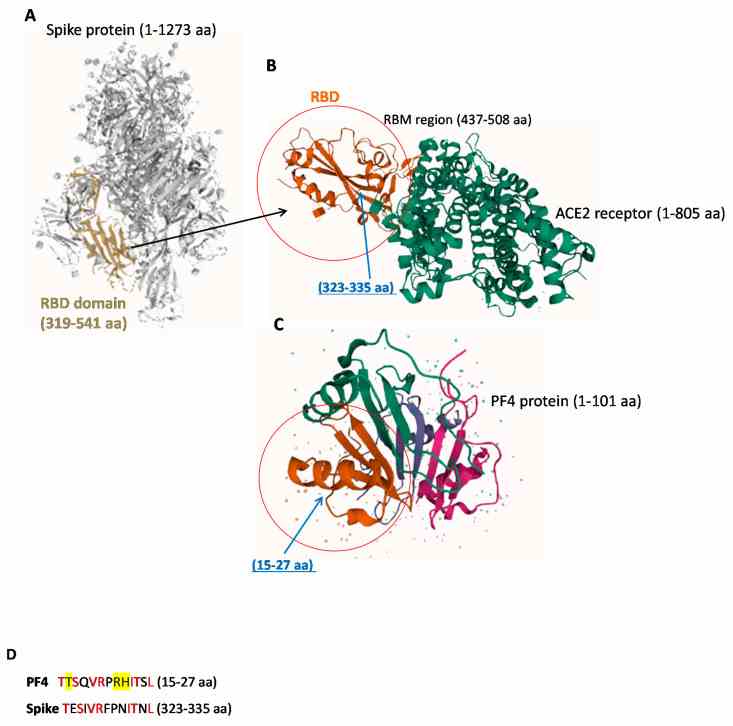
Representative images of 3D structures of SARS-CoV-2 RBD, ACE-2 and
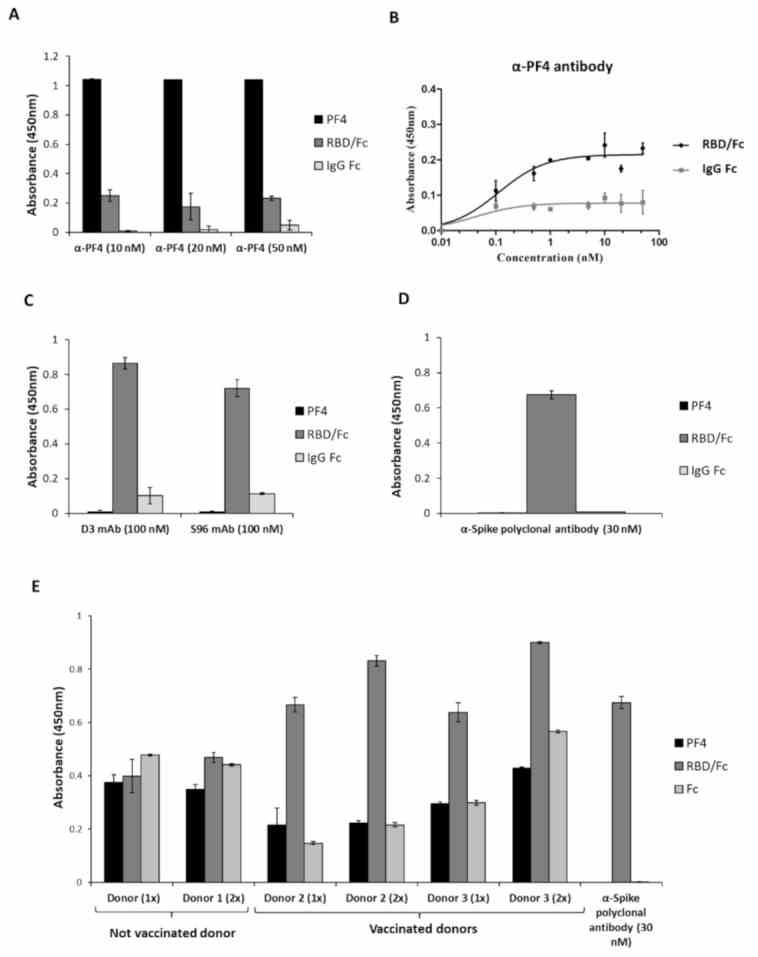
Cross-reactivity of the
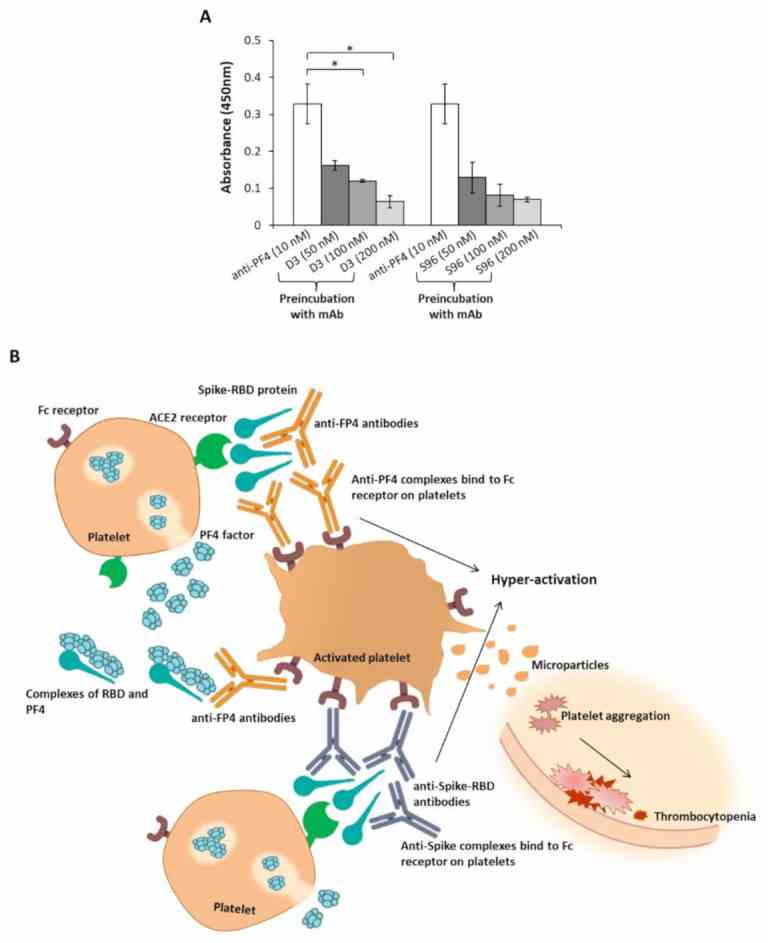
Interference of the novel anti-Spike mAbs in the interaction of the
Not For Human Consumption!
Inquiry
- Reviews (0)
- Q&As (0)
Ask a Question for All PF4 Products
Required fields are marked with *
My Review for All PF4 Products
Required fields are marked with *



