Recombinant Human EHMT1 Protein, GST-tagged
| Cat.No. : | EHMT1-88H |
| Product Overview : | Recombinant Human EHMT1 protein, fused with N-terminal GST-tag, was expressed in E. coli. |
- Specification
- Gene Information
- Related Products
- Citation
- Download
| Species : | Human |
| Source : | E.coli |
| Tag : | GST |
| Protein Length : | 894-1298 |
| Description : | GLP, in complex with the highly homologous G9a, is the major histone H3 lysine-9 (H3K9) methyltransferase for euchromatin and can also dimethylate p53K373, a modification correlating with levels of inactive p53. This latter result, along with the fact tha |
| Form : | 25.4 mM Na2HPO4/NaH2PO4, pH 7.4, 137 mM NaCl, 2.7 mM KCl, 3 mM DTT, 30% (w/v) glycerol. |
| Molecular Mass : | 80.0 kDa |
| Purity : | >80% by SDS-PAGE |
| Storage : | Store at -80°C. Thaw quickly and store on ice before use. Avoid repeated freezing and thawing cycles. |
| Gene Name | EHMT1 euchromatic histone-lysine N-methyltransferase 1 [ Homo sapiens ] |
| Official Symbol | EHMT1 |
| Synonyms | EHMT1; euchromatic histone-lysine N-methyltransferase 1; euchromatic histone methyltransferase 1; histone-lysine N-methyltransferase EHMT1; bA188C12.1; Eu HMTase1; FLJ12879; KIAA1876; KMT1D; H3-K9-HMTase 5; G9a like protein; G9a-like protein 1; lysine N-methyltransferase 1D; histone H3-K9 methyltransferase 5; histone-lysine N-methyltransferase, H3 lysine-9 specific 5; GLP; GLP1; FP13812; EUHMTASE1; Eu-HMTase1; RP11-188C12.1; DKFZp667M072; |
| Gene ID | 79813 |
| mRNA Refseq | NM_001145527 |
| Protein Refseq | NP_001138999 |
| MIM | 607001 |
| UniProt ID | Q9H9B1 |
| Chromosome Location | 9 |
| Pathway | Lysine degradation, organism-specific biosystem; Lysine degradation, conserved biosystem; |
| Function | histone methyltransferase activity (H3-K27 specific); histone methyltransferase activity (H3-K9 specific); histone-lysine N-methyltransferase activity; metal ion binding; methyltransferase activity; p53 binding; protein binding; protein-lysine N-methyltra |
| ◆ Recombinant Proteins | ||
| EHMT1-5063M | Recombinant Mouse EHMT1 Protein | +Inquiry |
| EHMT1-006H | Recombinant Human EHMT1 Protein, GST-tagged | +Inquiry |
| EHMT1-88H | Recombinant Human EHMT1 Protein, GST-tagged | +Inquiry |
| EHMT1-4381HF | Recombinant Full Length Human EHMT1 Protein, GST-tagged | +Inquiry |
| EHMT1-181H | Active Recombinant Human EHMT1 protein, GST-tagged | +Inquiry |
| ◆ Cell & Tissue Lysates | ||
| EHMT1-6685HCL | Recombinant Human EHMT1 293 Cell Lysate | +Inquiry |
The SETD6 Methyltransferase Plays an Essential Role in Hippocampus-Dependent Memory Formation
Journal: Biological psychiatry PubMed ID: 31378303 Data: 2020/12/12
Authors: William M. Webb, Ashleigh B. Irwin, Farah D. Lubin
Article Snippet:To determine whether SETD6, RELA, or EHMT1 interact in the rat hippocampus in vivo , we used protein co-immunoprecipitation assays and found interactions between SETD6 and RELA in the nuclear, but not the cytoplasmic fractions, of CA1 ( ).. We next used a recombinant, GST-tagged EHMT1 peptide (Creative BioMart) to pull down EHMT1 in the same region and found an interaction between EHMT1 and SETD6 in the nuclear, but not the cytoplasmic, fractions ( ). fig ft0 fig mode=article f1 fig/graphic|fig/alternatives/graphic mode="anchored" m1 Open in a separate window Fig. 1. caption a7 caption a8 Learning triggers NF-κB -RELA methylation in the hippocampus, and RELA associates with SETD6 and EHMT1. (A) Schematic representing context fear conditioning followed by subdissection of CA1 and downstream tests. (B) Immunoblotting revealed no change in SETD6 protein expression following training (cytoplasmic protein fraction, n =4, p =0.5693, unpaired t-test), while RELA-K310me1 (cytoplasmic protein fraction, n =6, p =0.0460, unpaired t-test) expression and H3K9me2 (histones extracted from nuclear fraction, n =8, p =0.0210, unpaired t-test) levels both increased in area CA1. (C) Representative images from dorsal hippocampal slices show increased fluorescent signal when treated with anti-RELA-K310me1 antibody and developed with FITC-conjugated secondary antibody. (D) Protein co-immunoprecipitation and GST-glutathione assays revealed in vivo interactions between RELA and SETD6 as well as EHMT1 in the nuclear, but not the cytoplasmic, fractions of hippocampal (CA1) lysates.
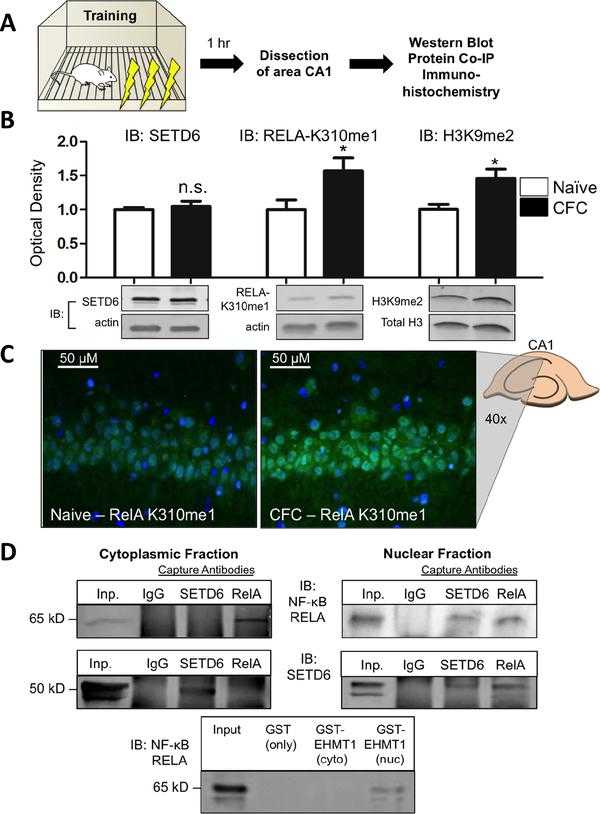
(A) Schematic representing context fear conditioning followed by subdissection of CA1 and downstream tests. (B) Immunoblotting revealed no change in SETD6 protein expression following training (cytoplasmic protein fraction, n=4, p=0.5693, unpaired t-test), while RELA-K310me1 (cytoplasmic protein fraction, n=6, p=0.0460, unpaired t-test) expression and H3K9me2 (histones extracted from nuclear fraction, n=8, p=0.0210, unpaired t-test) levels both increased in area CA1. (C) Representative images from dorsal hippocampal slices show increased fluorescent signal when treated with anti-RELA-K310me1 antibody and developed with FITC-conjugated secondary antibody. (D) Protein co-immunoprecipitation and GST-glutathione assays revealed in vivo interactions between RELA and SETD6 as well as
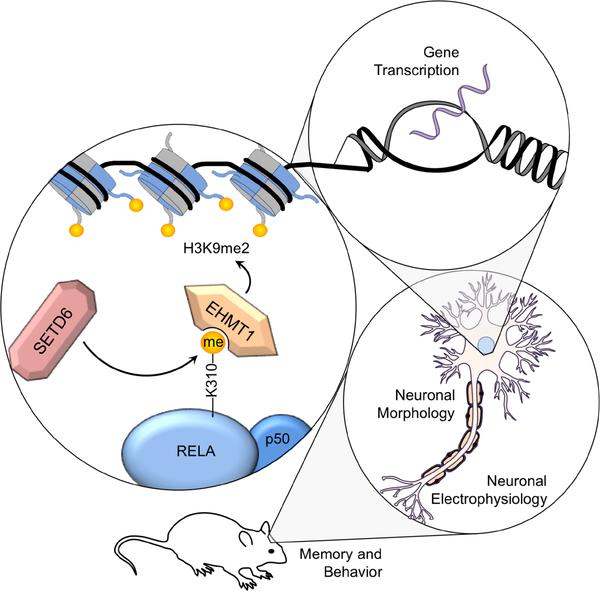
We hypothesize that SETD6 monomethylates NF-κB RELA at Lysine 310, promoting the recruitment of
Not For Human Consumption!
Inquiry
- Reviews (0)
- Q&As (0)
Ask a Question for All EHMT1 Products
Required fields are marked with *
My Review for All EHMT1 Products
Required fields are marked with *



