IL-6 Signaling Related Molecules
Related Symbol Search List
Immunology Background
Available Resources for IL-6 Signaling Related Molecules Research
Creative BioMart offers researchers a wide range of products related to IL-6 signaling molecules. The product portfolio includes recombinant proteins, protein pre-coupled magnetic beads, cell and tissue lysates, and more. All of these are designed to meet the specific needs of researchers conducting comprehensive studies in a variety of areas.
Alongside our extensive product offering, we also strive to offer a wealth of information on IL-6 signaling molecules. Our resources cover a wide range of topics, including pathways, protein functions, interacting proteins, related articles, and research areas, serving as valuable references for researchers looking to deepen their understanding of these molecules and their crucial roles in physiological processes.
Our Featured Products
| Cat.# | Product name | Species | Source (Host) | Tag |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| STAT1-2996H | Recombinant Human STAT1 protein, GST-tagged | Human | E.coli | GST |
| STAT2-2997H | Recombinant Human STAT2, GST-tagged | Human | E.coli | GST |
| STAT3-1496H | Recombinant Human STAT3, GST-tagged | Human | Sf9 Insect Cell | GST |
| JAK1-2667H | Recombinant Human JAK1 protein, His-tagged | Human | E.coli | His |
| JAK2-254H | Recombinant Human JAK2 Protein, His-tagged | Human | E.coli | His |
About IL-6 Signaling Related Molecules
The IL-6 family of cytokines activates several signaling molecules that mediate their diverse biological effects. These signaling molecules are involved in intracellular signal transduction pathways and regulate gene expression, cell survival, proliferation, differentiation, and immune responses.
Janus Kinases (JAKs)
Janus kinases are a family of cytoplasmic tyrosine kinases that play a crucial role in IL-6 family signaling. JAKs are associated with the intracellular domains of IL-6 family receptors and become activated upon ligand binding. There are four members of the JAK family: JAK1, JAK2, JAK3, and Tyrosine kinase 2 (Tyk2). Activated JAKs phosphorylate specific tyrosine residues on the receptor, allowing subsequent recruitment and phosphorylation of signal transducer and activator of transcription (STAT) proteins.
Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription (STAT) Proteins
STAT proteins are a family of transcription factors that are activated downstream of IL-6 family receptors. Upon phosphorylation by JAKs, STAT proteins form dimers and translocate to the nucleus, where they regulate gene expression. Different IL-6 family cytokines can activate different STAT proteins. For example, IL-6 primarily activates STAT3, while IL-11 activates STAT1, STAT3, and STAT5.
Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinases (MAPKs)
MAPKs are a family of serine/threonine kinases that are involved in IL-6 family signaling. The three major MAPK pathways activated by IL-6 family cytokines are the extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK), p38, and c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) pathways. These pathways regulate various cellular processes, including proliferation, differentiation, and inflammation.
Phosphoinositide 3-Kinase (PI3K)
PI3K is a lipid kinase that is activated by IL-6 family cytokines. It plays a role in cell survival, growth, and metabolism. Activation of PI3K leads to the production of phosphatidylinositol-3,4,5-trisphosphate (PIP3), which recruits and activates downstream effector molecules, such as Akt (protein kinase B), regulating various cellular responses.
Suppressor of Cytokine Signaling (SOCS) Proteins
SOCS proteins are negative regulators of IL-6 family signaling. They act as feedback inhibitors to control the intensity and duration of cytokine signaling. SOCS proteins, including SOCS1 and SOCS3, are induced upon cytokine stimulation and inhibit JAK-STAT signaling by binding to phosphorylated receptors or JAKs, thereby preventing further signal transduction.
Nuclear Factor-κB (NF-κB)
NF-κB is a transcription factor that plays a critical role in inflammation and immune responses. IL-6 family cytokines can activate NF-κB signaling, which regulates the expression of genes involved in inflammation and cell survival.
These signaling molecules form intricate networks and crosstalk with each other to mediate the effects of IL-6 family cytokines. The activation of these molecules leads to the transcriptional regulation of target genes, resulting in diverse cellular responses and the modulation of immune and inflammatory processes. Understanding the signaling pathways and interactions of these molecules provides insights into the mechanisms underlying IL-6 family-related diseases and potential therapeutic targets for intervention.
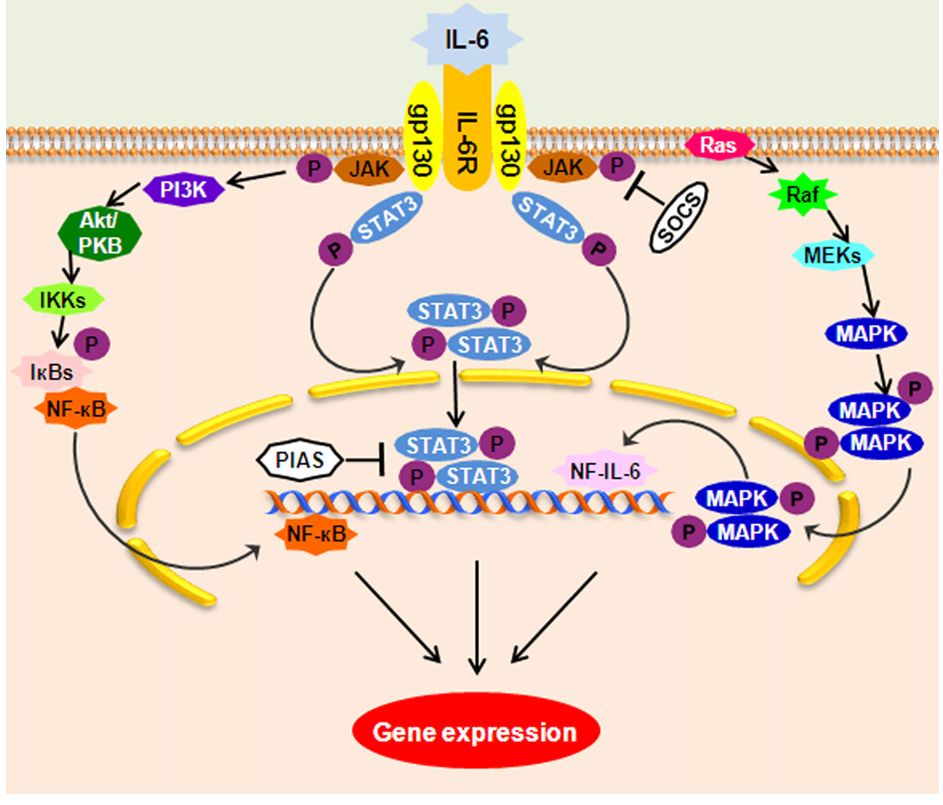 Fig.1 IL-6 signaling pathways. (Ataie-Kachoie, P., et al., 2013)
Fig.1 IL-6 signaling pathways. (Ataie-Kachoie, P., et al., 2013)
IL-6 binds to IL-6R to initiate cellular events including activation of JAK kinases, Ras and PI3k-mediated signaling which lead to activation of several transcription factors. SOCS and PIAS proteins negatively regulate IL-6 activity.
Mechanisms of IL-6 Signaling Pathway Regulation
The IL-6 signaling pathway is tightly regulated by various mechanisms, and its dysregulation has been implicated in several diseases. To modulate IL-6 signaling, different approaches have been explored, including small molecule compounds, antibodies, and other strategies. Here are some examples of the regulation of the IL-6 signaling pathway and its therapeutic applications:
Small Molecule Compounds
Small molecule compounds have been developed to target components of the IL-6 signaling pathway. For example:
- JAK Inhibitors: Small molecule inhibitors targeting Janus kinases (JAKs), such as tofacitinib and baricitinib, have been developed and approved for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis and other autoimmune conditions. These inhibitors interfere with JAK-mediated phosphorylation of the IL-6 receptor complex, thus inhibiting downstream signaling.
- STAT3 Inhibitors: Several small molecule compounds have been identified as inhibitors of STAT3, a key transcription factor in the IL-6 pathway. These compounds, such as Stattic and Cucurbitacin I, disrupt STAT3 dimerization or DNA binding, leading to the inhibition of IL-6-induced gene expression.
Antibodies
Monoclonal antibodies have been developed to target IL-6 itself or its receptors, offering a specific and potent way to modulate IL-6 signaling. Some examples include:
- IL-6 Antibodies: Antibodies directly targeting IL-6, such as tocilizumab and sarilumab, have been approved for the treatment of inflammatory conditions like rheumatoid arthritis and cytokine release syndrome associated with CAR-T cell therapy. These antibodies block IL-6 from binding to its receptors, preventing downstream signaling.
- IL-6 Receptor Antibodies: Antibodies targeting the IL-6 receptor (IL-6R) have also been developed. For instance, siltuximab, an anti-IL-6R antibody, has been approved for the treatment of Castleman disease, a lymphoproliferative disorder. By binding to IL-6R, these antibodies inhibit IL-6 trans-signaling.
Other Methods
In addition to small molecules and antibodies, other approaches have been employed to regulate IL-6 signaling:
- Gene Silencing: Small interfering RNA (siRNA) or short hairpin RNA (shRNA) techniques have been used to silence specific genes involved in the IL-6 signaling pathway. Targeting genes like IL-6, IL-6R, or STAT3 using RNA interference can effectively inhibit IL-6 signaling.
- MicroRNAs: MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are small RNA molecules that can regulate gene expression. Certain miRNAs can target components of the IL-6 signaling pathway, providing another means to modulate IL-6 signaling. For example, miR-124 and miR-27b have been shown to negatively regulate IL-6 or IL-6R expression.
- Combination Therapies: Combinations of different approaches, such as using JAK inhibitors in combination with IL-6 antibodies or other targeted therapies, have been explored to achieve synergistic effects and enhance therapeutic outcomes.
Studies have demonstrated the efficacy of these regulatory approaches inpreclinical and clinical settings. For example, clinical trials have shown the effectiveness of JAK inhibitors and IL-6 antibodies in reducing disease activity and improving clinical outcomes in rheumatoid arthritis, systemic juvenile idiopathic arthritis, and cytokine release syndrome. Moreover, these approaches are being investigated in other conditions associated with dysregulated IL-6 signaling, including Castleman disease, multiple myeloma, and certain cancers.
Overall, the regulation of the IL-6 signaling pathway through small molecule compounds, antibodies, and other methods provides promising therapeutic strategies for controlling inflammation and treating various diseases. Ongoing research continues to explore these approaches and identify novel targets and interventions to further refine the modulation of IL-6 signaling for improved clinical outcomes.
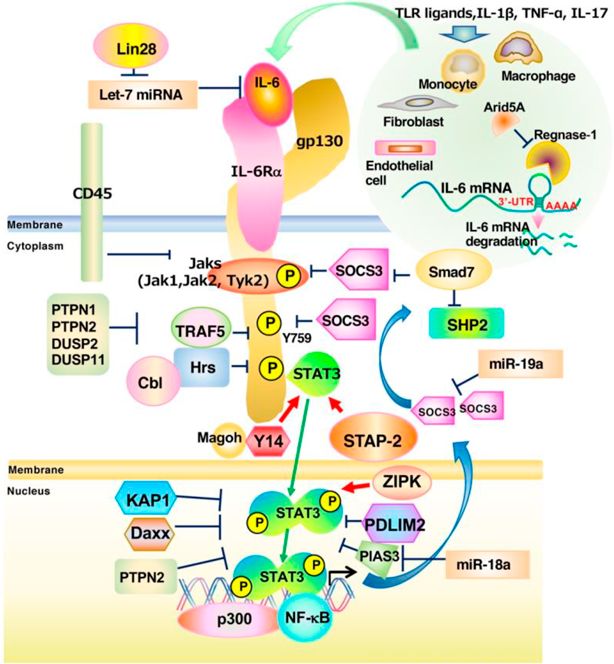 Fig.2 Positive and negative regulators of IL-6/STAT3-mediated signaling. (Matsuda T, 2023)
Fig.2 Positive and negative regulators of IL-6/STAT3-mediated signaling. (Matsuda T, 2023)
If you have any questions, requirements, or cooperation intentions, please feel free to contact us. We very much look forward to working with you and helping you achieve research and commercial success.
Related References:
- Ataie-Kachoie, P., Pourgholami, M.H., & Morris, D.L. (2013). Inhibition of the IL-6 signaling pathway: a strategy to combat chronic inflammatory diseases and cancer. Cytokine & growth factor reviews, 24 2, 163-73.
- Matsuda T. The Physiological and Pathophysiological role of IL-6/STAT3-mediated signal transduction and STAT3 binding partners in therapeutic applications. Biol Pharm Bull. 2023;46(3):364-378. doi:10.1248/bpb.b22-00887

