STAT1
-
Official Full Name
signal transducer and activator of transcription 1, 91kDa -
Overview
The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the STAT protein family. In response to cytokines and growth factors,;STAT family members are phosphorylated by the receptor associated kinases, and then form homo- or heterodimers that;translocate to the cell nucleus where they act as transcription activators. This protein can be activated by various;ligands including interferon-alpha, interferon-gamma, EGF, PDGF and IL6. This protein mediates the expression of a;variety of genes, which is thought to be important for cell viability in response to different cell stimuli and;pathogens. Two alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding distinct isoforms have been described. -
Synonyms
STAT1;signal transducer and activator of transcription 1, 91kDa;signal transducer and activator of transcription 1, 91kD;signal transducer and activator of transcription 1-alpha/beta;ISGF 3;STAT91;transcription factor ISGF 3 components p91/p84;transcription factor ISGF-3 components p91/p84;signal transducer and activator of transcription-1;CANDF7;ISGF-3;DKFZp686B04100
Recombinant Proteins
- Human
- Mouse
- Chicken
- Rhesus macaque
- E.coli
- Insect Cells
- Sf9 Cells
- Sf21 Cells
- Mammalian Cells
- HEK293
- HeLa
- His
- GST
- Non
- T7
- MBP
- Avi
- Fc
- Flag
- DDK
- Myc
Background
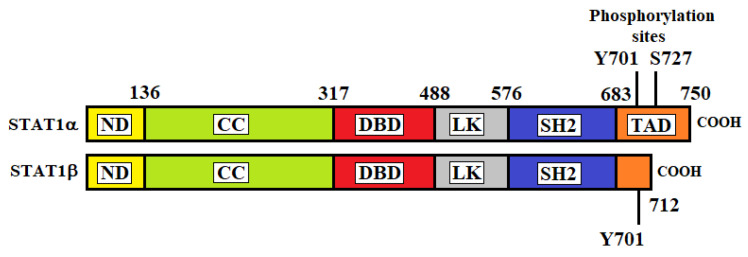
Fig1. Structures of STAT1α and STAT1β. (Manlio Tolomeo, 2022)
What is STAT1 Protein?
STAT1 gene (signal transducer and activator of transcription 1) is a protein coding gene which situated on the long arm of chromosome 2 at locus 2q32. The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the STAT protein family. In response to cytokines and growth factors, STAT family members are phosphorylated by the receptor associated kinases, and then form homo- or heterodimers that translocate to the cell nucleus where they act as transcription activators. The protein encoded by this gene can be activated by various ligands including interferon-alpha, interferon-gamma, EGF, PDGF and IL6. This protein mediates the expression of a variety of genes, which is thought to be important for cell viability in response to different cell stimuli and pathogens. The protein plays an important role in immune responses to viral, fungal and mycobacterial pathogens. The STAT1 protein is consisted of 750 amino acids and STAT1 molecular weight is approximately 87.3 kDa.
What is the Function of STAT1 Protein?
STAT1 protein is a member of the signal transduction and transcriptional activator family, which plays a key role in the signal response of cytokines and growth factors. STAT1 is activated mainly by phosphorylation of its C-terminal tyrosine and serine residues, forming dimers and translocating into the nucleus to regulate the expression of target genes. The signaling pathway of STAT1 depends on interferon (IFN) signaling, which is involved in the regulation of cell anti-proliferation, apoptosis, cell proliferation, negative regulation of cell cycle, inhibition of tumor angiogenesis, and weakening of tumor migration and invasion. In addition, STAT1 also plays a role in the mechanism of the formation of CD8 T cell responses in vivo, influencing the proliferation of CD8 T cells by regulating STAT1-dependent signaling pathways. The function of STAT1 is not limited to tumor suppression; its overactivation may promote the proliferation and drug resistance of tumor cells in some cases.
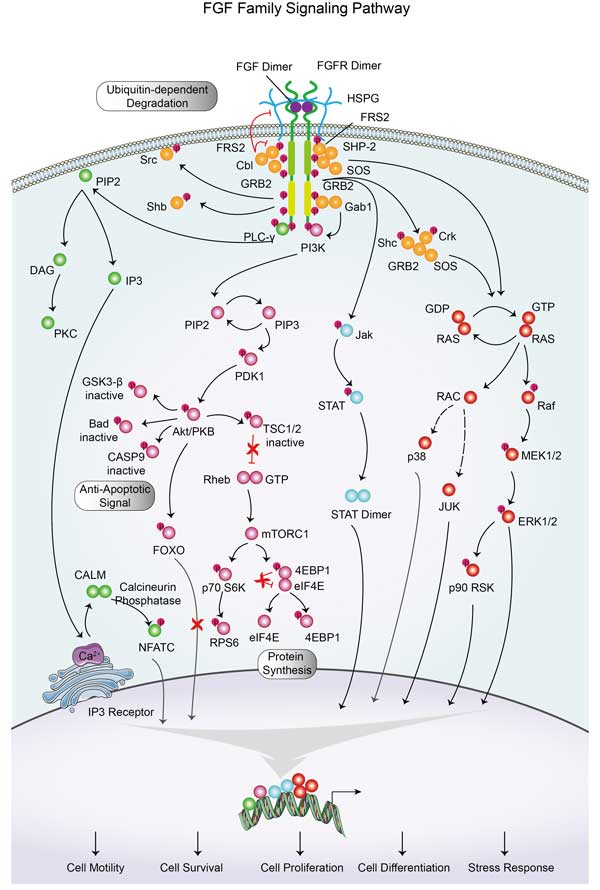
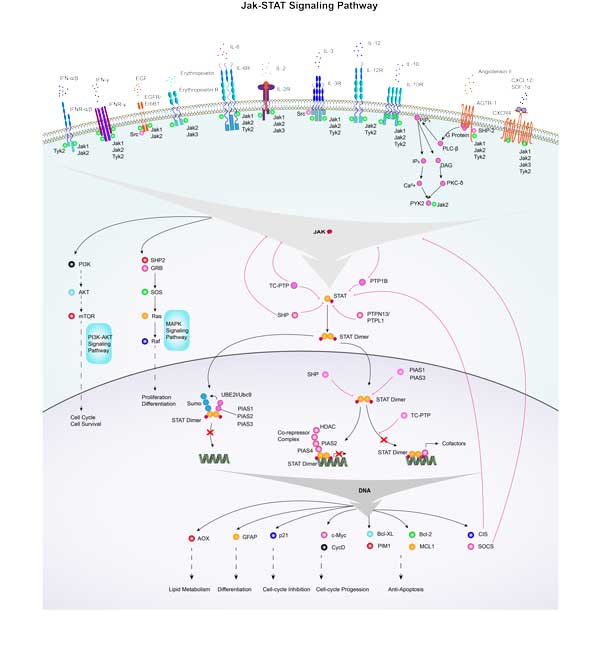
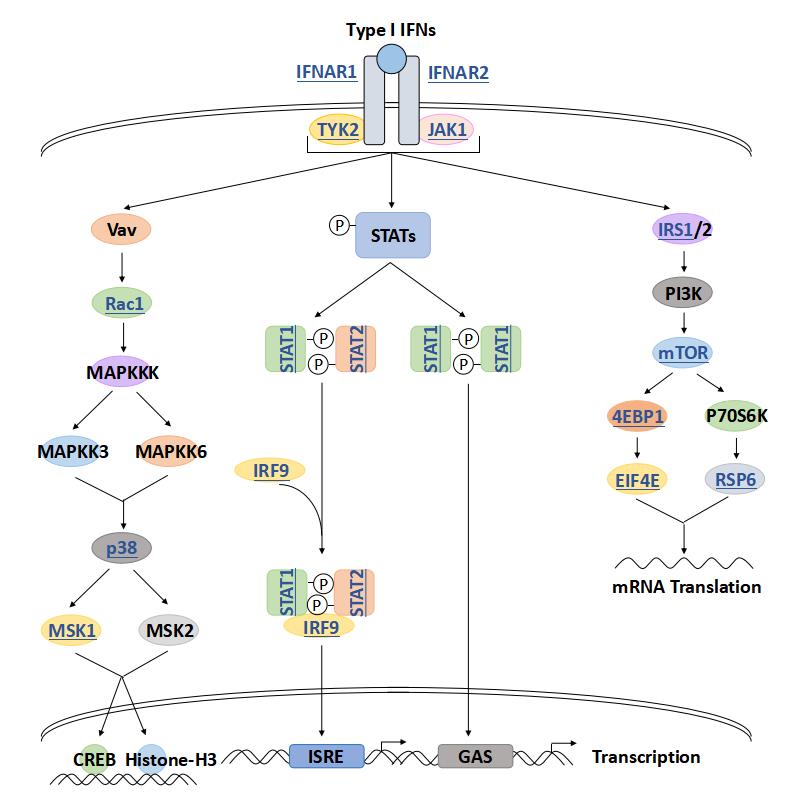
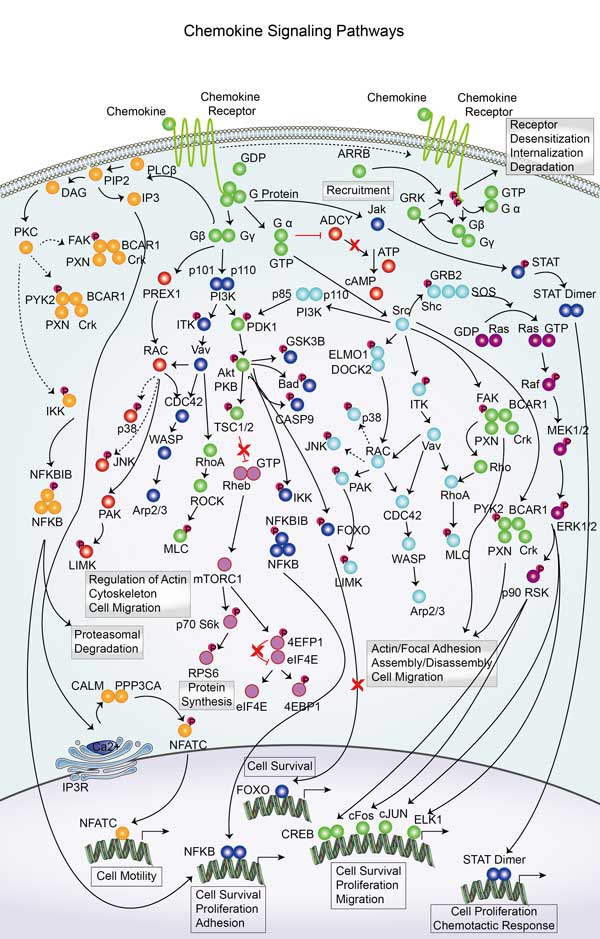
STAT1 Related Signaling Pathway
STAT1 is a major effector molecule in interferon signaling pathways, specifically type I and Type II interferon (IFN-α/β and IFN-γ) signaling pathways. STAT1 is involved in the signaling of various cytokines, such as IL-6, IL-10, etc. These cytokines activate JAKs through specific receptor binding, thereby activating STAT1 and regulating the proliferation, differentiation and function of immune cells. STAT1 can form heterodimers with other STAT family members or homologous dimers with itself to participate in complex signal regulation networks. STAT1 activity is regulated by negative regulators including the SOCS protein family, PIAS proteins, and tyrosine phosphatase, which inhibit the overactivation of the JAK-STAT signaling pathway through different mechanisms.
STAT1 Related Diseases
Abnormal activity of the STAT1 protein has been associated with a variety of diseases, especially viral infections and immunodeficiency diseases associated with interferon signaling pathways, such as chronic viral infections, certain types of cancer (due to its role in cell proliferation and anti-tumor immunity), autoimmune diseases (such as systemic lupus erythematosus, due to its role in immune regulation), and autoimmune diseases (such as systemic lupus erythematosus). And certain primary immunodeficiency diseases (such as inherited STAT1 deficiency due to mutations in the STAT1 gene), in which dysfunction of STAT1 may lead to increased susceptibility to pathogens, abnormal immune system function, or impairment of tumor surveillance mechanisms.
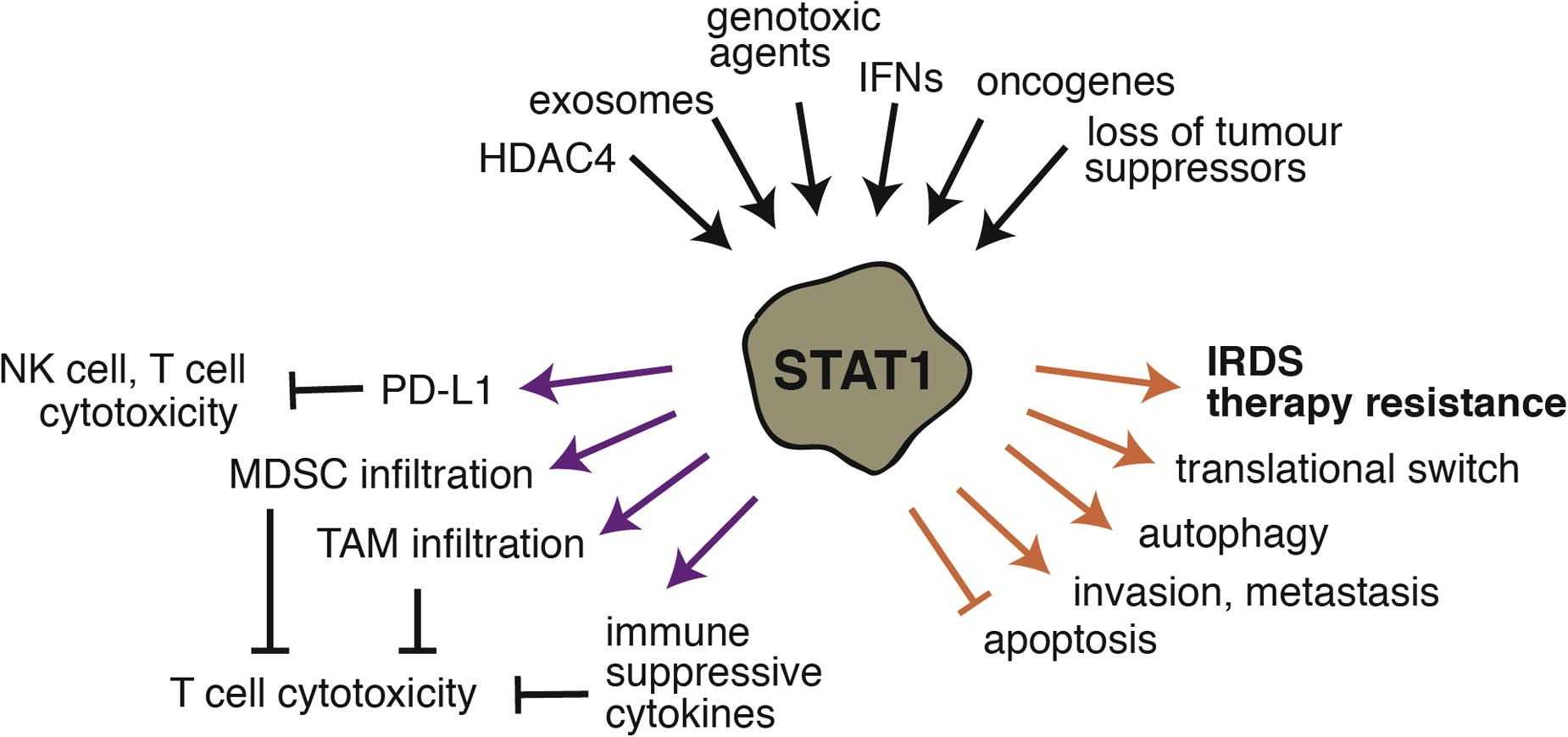
Fig2. Tumour promoting functions of STAT1. (Katrin Meissl, 2017)
Bioapplications of STAT1
Due to its central role in the interferon signaling pathway, STAT1 protein's relevant off-the-shelf applications are mainly concentrated in the field of antiviral and anti-tumor therapy. For example, interferon therapy uses STAT1-mediated signaling to enhance the body's antiviral response and immune surveillance, and is widely used in the treatment of chronic viral infections such as hepatitis B and C. In addition, the activation status of STAT1 has also been used as a biomarker to assess treatment response and prognosis in certain cancers. In immunomodulatory therapy, the function of STAT1 is indirectly affected by drugs that target the JAK-STAT pathway for the treatment of autoimmune diseases and certain types of cancer. However, due to the broad role of STAT1 in multiple biological processes, these treatments need to carefully balance their efficacy against possible side effects.
Case Study
Case Study 1: Cunyang Gu, 2023
Tubulointerstitial fibrosis (TIF) is an important pathological change that occurs during the development of diabetic kidney disease. The epithelial‑mesenchymal transition (EMT) of renal tubular epithelial cells is a manifestation of TIF. STAT1, a member of the STAT family of transcription factors, can be modified by the small ubiquitin‑related modifier (SUMO), thus affecting the activity of STAT1. The present study investigated the role of STAT1 SUMOylation in high glucose‑induced tubular EMT by western blotting, immunocytochemistry, immunofluorescence, co‑immunoprecipitation and dual luciferase reporter analysis. The results indicated that in the process of high glucose‑induced EMT, STAT1 activation protected the cells from EMT. However, high glucose also increased the SUMOylation of STAT1, which prevented STAT1 from exerting an effective protective role by inhibiting its activity.
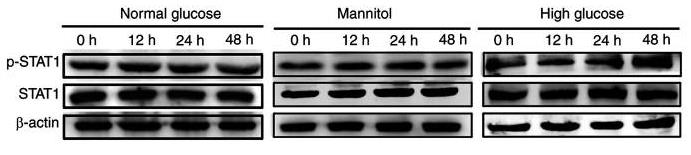
Fig1. The activation of STAT1 was detected using western blotting.
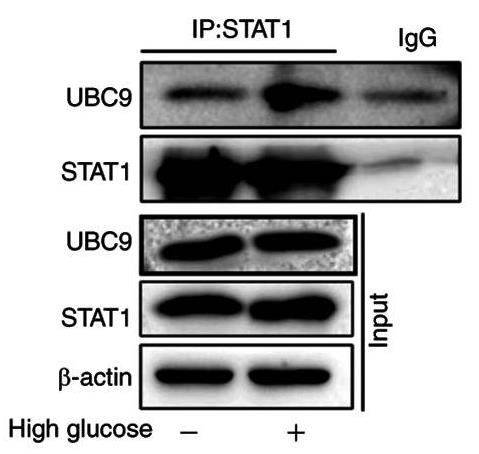
Fig2. Co-IP suggested that the binding of STAT1 and UBC9 was upregulated under high-glucose conditions.
Case Study 2: Fanchen Wang, 2020
Signal transducer and activator of transcription-1 (STAT1) is an important factor in various cellular processes. The cancer stem cell (CSC) is considered as a tumor-initiating cell that drives the inner hierarchy in many cancers including epithelial ovarian cancer (EOC). Here, this study explored for the first time the regulation of STAT1 on stemness properties in chemoresistant EOC cells. The paclitaxel (PTX)-resistant EOC cell line (OV3R-PTX) was derived from PTX-sensitive OVCAR-3 cells treated by the PTX regimen. A single cell clone OV3R-PTX-B4 was selected by fluorescence-activated cell sorting. PTX-resistant cells grew slowly in conventional 2D and 3D cultures, but tumor xenograft with PTX-resistant cells grew fast in nude mice. Interestingly, OV3R-PTX-B4 cells shared the characteristics of CSCs and stemness properties were found to be increased in the non-adherent spheroid culture system. The PTX-resistant cells had a high expression of CSC-related markers and low expression of STAT1 that had a high methylation level of CpG in its promoter region. Overexpressed STAT1 suppressed stemness properties, cell proliferation, and colony formation and favored the overall survival of patients with EOC.
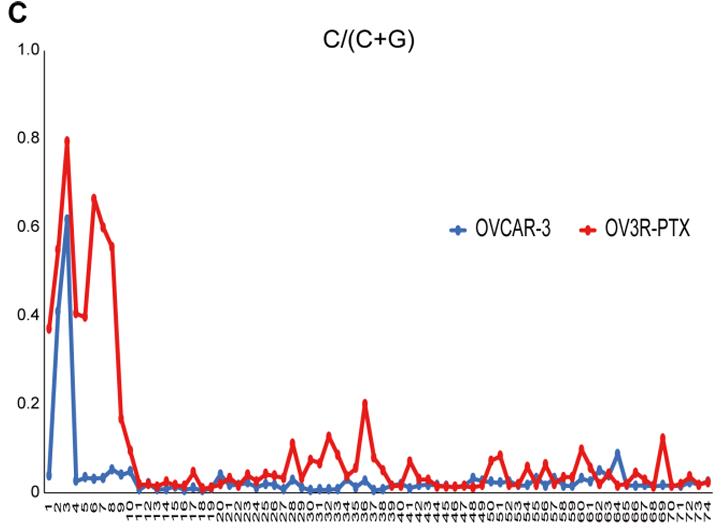
Fig3. Methylation level in a STAT1 promoter region detected by bisulfite sequencing.
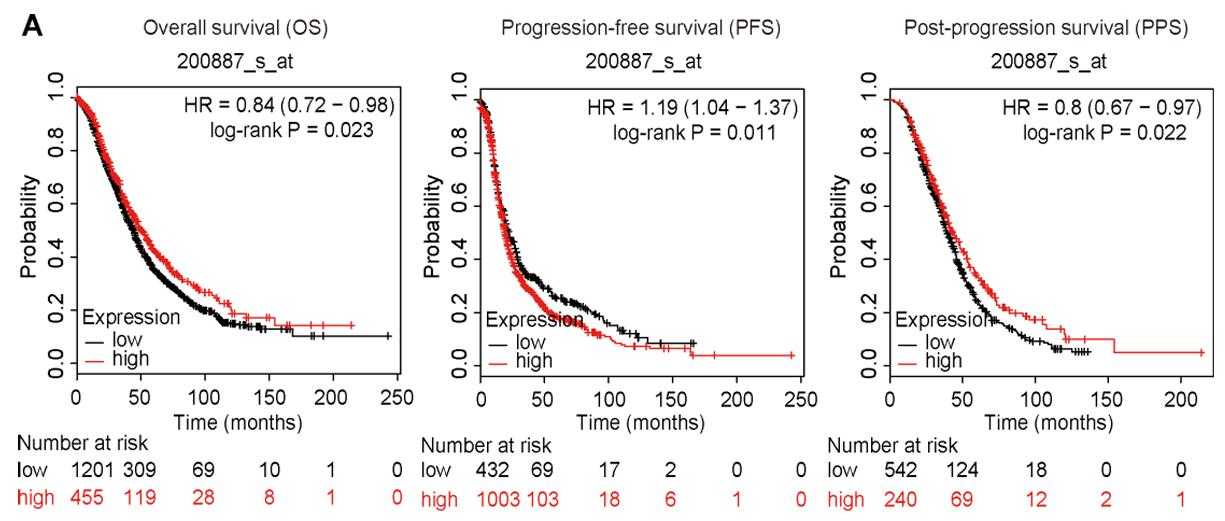
Fig4. Kaplan-Meier curves of the OS, PFS, and PPS of all patients with OC are presented.
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
.jpg)
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (STAT1-4597H)
.
.jpg)
Fig2. SDS-PAGE (STAT1-5249H)
Involved Pathway
STAT1 involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways STAT1 participated on our site, such as Chemokine signaling pathway,Osteoclast differentiation,Toll-like receptor signaling pathway, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with STAT1 were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| Jak-STAT signaling pathway | STAT5A,AOX3L1,IL28A,SOCS9,IL13RA1,CCND2A,IFNA14,IL13,PTPN11B,PTPN2B |
| Pathways in cancer | WNT3A,CCNA1,FGF18,XIAP,GLI3,FGF3,SFPI1,FGF14,SKP2,KRAS |
| Hepatitis B | IFNB1,ELK1,IFNA13,IFN-a,PIK3R3,BIRC5,IRF7,IFNA2,CCNE1,IKBKB |
| Toxoplasmosis | HSPA1A,IL10RB,PIK3R2,TRAF6,IRGM,LAMC1,MAPK12,ITGB1,HLA-DMA,TGFB1 |
| Osteoclast differentiation | ACP5,MAP2K6,LILRB4,PPARG,MAPK11,IFNG,FCGR2C,LILRB1,TNFRSF11A,TNFRSF11B |
| Leishmaniasis | H2-AA,FCGR2C,IRAK1,ITGB2,TLR4,HLA-DQA1,HLA-DOA,TRAF6,TGFB2,RELA |
| Pancreatic cancer | SMAD3,RAC2,MAPK9,BAD,RALGDS,TGFBR2,SMAD4,TP53,AKT2,MAPK10 |
| Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) | NFKB1,IL23,HLA-DRB5,IL21,HLA-DRA,MAF,IL12RB2,Il4ra,IL18R1,RORA |
| Chemokine signaling pathway | CCL20,IKBKB,LYN,CCL28,CXCL8,BRAF,GNG11,Ccl12,CCL11,PLCB1 |
Protein Function
STAT1 has several biochemical functions, for example, . Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by STAT1 itself. We selected most functions STAT1 had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with STAT1. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|
Interacting Protein
STAT1 has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with STAT1 here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of STAT1.
STAT2;IFNGR1;EGFR
STAT1 Related Signal Pathway
Resources
Gene Families
Research Area
- Apoptosis Transcription Factors and Regulators
- Transcription Factors in the Akt Pathway
- Negative Regulators of the Jak/STAT Pathway
- STAT
- Mesenchymal Stem Cell Transcription Factors
- Intracellular Signaling Molecules in Angiogenesis
- Reperfusion Injury Therapeutic Targets
- Th1 Cells
- IL-10 Signaling Related Molecules
- IL-12 Signaling Related Molecules
- IL-6 Signaling Related Molecules
- MDSC Intracellular Signaling Factors
Related Services
Related Products
References
- Li, J; Jie, HB; et al. PD-1/SHP-2 Inhibits Tc1/Th1 Phenotypic Responses and the Activation of T Cells in the Tumor Microenvironment. CANCER RESEARCH 75:508-518(2015).
- Matsushita, H; Hosoi, A; et al. Cytotoxic T Lymphocytes Block Tumor Growth Both by Lytic Activity and IFN gamma-Dependent Cell-Cycle Arrest. CANCER IMMUNOLOGY RESEARCH 3:26-36(2015).