STAT3
-
Official Full Name
Signal Transducer And Activator Of Transcription 3 (Acute-Phase Response Factor) -
Overview
The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the STAT protein family. In response to cytokines and growth factors, STAT family members are phosphorylated by the receptor associated kinases, and then form homo- or heterodimers that translocate to the cell nucleus where they act as transcription activators. This protein is activated through phosphorylation in response to various cytokines and growth factors including IFNs, EGF, IL5, IL6, HGF, LIF and BMP2. This protein mediates the expression of a variety of genes in response to cell stimuli, and thus plays a key role in many cellular processes such as cell growth and apoptosis. -
Synonyms
STAT3;signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (acute-phase response factor);APRF;HIES;FLJ20882;MGC16063;OTTHUMP00000198123;OTTHUMP00000198128;DNA-binding protein APRF;acute-phase response factor
Recombinant Proteins
- Human
- Mouse
- Cattle
- Chicken
- Rat
- Zebrafish
- Human/Mouse/Rat/Bos/taurus/Cattle
- Sf9 Cells
- E.coli
- Insect Cells
- Mammalian Cells
- HEK293
- Wheat Germ
- Yeast
- Insect cells
- Human Cells
- HeLa
- In Vitro Cell Free System
- GST
- His
- Non
- DDK
- Myc
- MBP
- Flag
- SUMO
- Avi
- Fc
Background
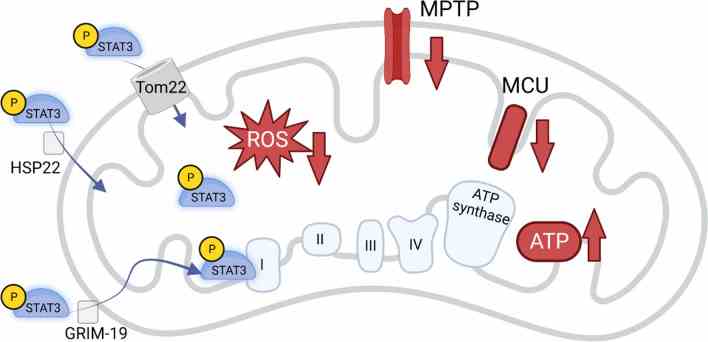
Fig1. Schematic overview of STAT3 import, localization, and function in mitochondria. (David Achudhan, 2024)
What is STAT3 protein?
STAT3 gene (signal transducer and activator of transcription 3) is a protein coding gene which situated on the long arm of chromosome 17 at locus 17q21. The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the STAT protein family. In response to cytokines and growth factors, STAT family members are phosphorylated by the receptor associated kinases, and then form homo- or heterodimers that translocate to the cell nucleus where they act as transcription activators. This protein is activated through phosphorylation in response to various cytokines and growth factors including IFNs, EGF, IL5, IL6, HGF, LIF and BMP2. This protein mediates the expression of a variety of genes in response to cell stimuli, and thus plays a key role in many cellular processes such as cell growth and apoptosis. This gene also plays a role in regulating host response to viral and bacterial infections. The STAT3 protein is consisted of 770 amino acids and STAT3 molecular weight is approximately 88.1 kDa.
What is the function of STAT3 protein?
Once activated, STAT3 translocates to the nucleus, where it binds to specific DNA sequences and regulates the transcription of target genes involved in cell growth, differentiation, and survival. STAT3 plays a role in controlling cell cycle progression and is involved in the expression of genes that are crucial for cell proliferation and differentiation. STAT3 can have anti-apoptotic effects under certain conditions, such as when activated by the leptin receptor, potentially through the transactivation of BIRC5. STAT3 is essential in the regulation of immune responses, including the development and function of various immune cells. STAT3 is involved in the regulation of inflammatory processes, and its activation is associated with the production of acute-phase proteins.
STAT3 Related Signaling Pathway
Central to STAT3 function is the JAK-STAT signaling pathway, where cytokines and growth factors trigger receptor-associated JAK kinases to phosphorylate STAT3, leading to its dimerization and nuclear translocation to regulate gene expression. STAT3 is a primary mediator of IL-6-type cytokine signaling, which is crucial for inflammatory responses and is implicated in various diseases when dysregulated. STAT3 promotes cell growth and survival by inducing the expression of genes involved in cell cycle progression and inhibiting apoptosis. STAT3 is essential in the development and function of immune cells, influencing processes such as T cell differentiation and natural killer cell activity.
STAT3 Related Diseases
Its abnormal activation is often observed in various cancers, where it can foster uncontrolled cell proliferation and resistance to cell death, playing a role in tumor progression and metastasis. Autoimmune diseases, such as systemic lupus erythematosus and rheumatoid arthritis, also involve STAT3 due to its impact on immune cell regulation and inflammation. Additionally, STAT3 contributes to inflammatory bowel disease through its role in intestinal inflammation and immune response modulation. The protein's involvement extends to cardiovascular diseases, including atherosclerosis, where it may affect vascular cell behavior and contribute to plaque formation. In the context of infectious diseases, STAT3's activation can modulate the host's response to pathogens. Furthermore, STAT3 has been implicated in neurodegenerative conditions like Alzheimer's and Parkinson's diseases, potentially influencing neuroinflammation and neuronal survival.
Bioapplications of STAT3
Bioapplications include the development of small molecule inhibitors and other modalities designed to modulate STAT3 activity, potentially leading to novel cancer treatments. The identification of STAT3 as a key player in various diseases has spurred the search for specific inhibitors and antagonists, which are being explored for their potential use in treating STAT3-related pathologies. STAT3's differential expression in disease states makes it a candidate for diagnostic biomarkers, aiding in the early detection and stratification of patients with STAT3-associated diseases. STAT3's involvement in multiple pathways makes it a subject of research for target validation in drug discovery, ensuring that interventions are effective and specific.
Case Study
Case Study 1: Sunanda Singh, 2022
STAT3 and KRAS regulate cell proliferation, survival, apoptosis, cell migration, and angiogenesis. Aberrant expression of STAT3 and mutant active forms of KRAS have been well-established in the induction and maintenance of multiple cancers. STAT3 and KRAS mutant proteins have been considered anti-cancer targets; however, they are also considered to be clinically "undruggable" intracellular molecules, except for KRAS(G12C). Here researchers report a first-in-class molecule, a novel, single domain camelid VHH antibody (15 kDa), SBT-100, that binds to both STAT3 and KRAS and can penetrate the tumor cell membrane, and significantly inhibit cancer cell growth. Additionally, SBT-100 inhibits KRAS GTPase activity and downstream phosphorylation of ERK in vitro. In addition, SBT-100 inhibits the growth of multiple human cancers in vitro and in vivo.
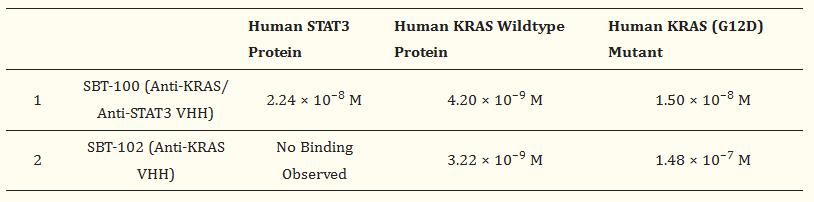
Fig1. Binding affinity of SBT-100 for human STAT3 and KRAS determined using Biacore 3000.
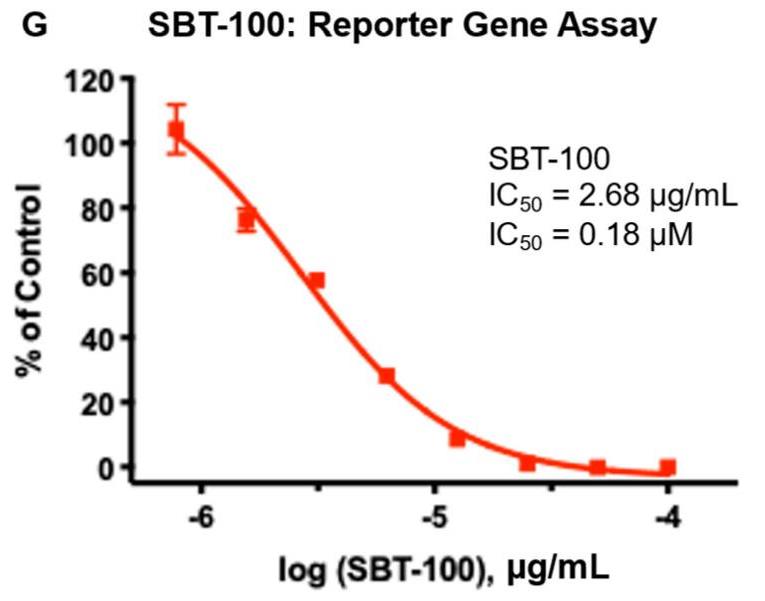
Fig2. STAT3 luciferase reporter assay in HEK 293T cells with SBT-100 treatment after IL-6 stimulation.
Case Study 2: Kunyan He, 2013
In this study, EGFR signaling was blocked by a small molecule (G5-7) that selectively inhibited Janus kinase 2 (JAK2)-mediated phosphorylation and activation of EGFR and STAT3 (signal transducer and activator of transcription 3) by binding to JAK2, thereby decreasing the activity of downstream signaling by mTOR (mammalian target of rapamycin) and inducing cell cycle arrest. G5-7 inhibited the proliferation of PTEN-deficient glioblastoma cell lines harboring a constitutively active variant of EGFR (U87MG/EGFRvIII) and human glioblastoma explant neurosphere cultures, but the drug only weakly inhibited the proliferation of either glioblastoma cell lines that were wild type for EGFR and stably transfected with PTEN (U87MG/PTEN) or normal neural progenitor cells and astrocytes. Additionally, G5-7 reduced vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) secretion and endothelial cell migration and induced apoptosis in glioblastoma xenografts, thereby suppressing glioblastoma growth in vivo.
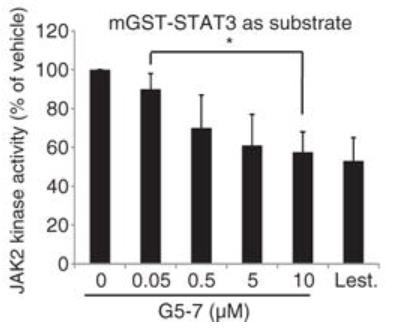
Fig3. Analysis of the in vitro kinase activity of JAK2 on STAT3.
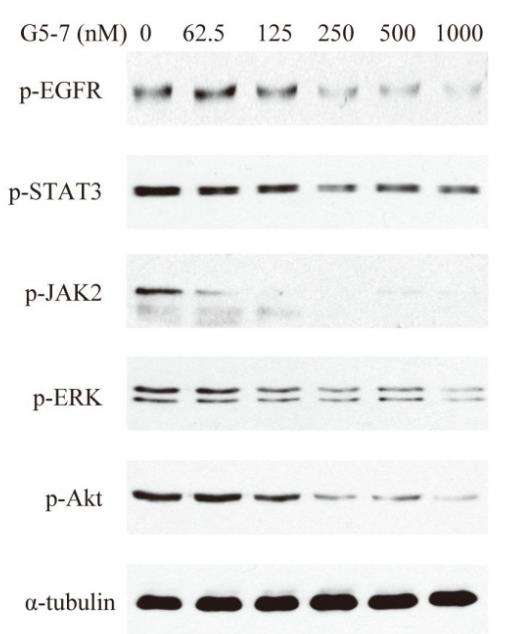
Fig4. G5-7 dose-dependently suppresses JAK2/EGFR/STAT3 signaling.
Quality Guarantee
Involved Pathway
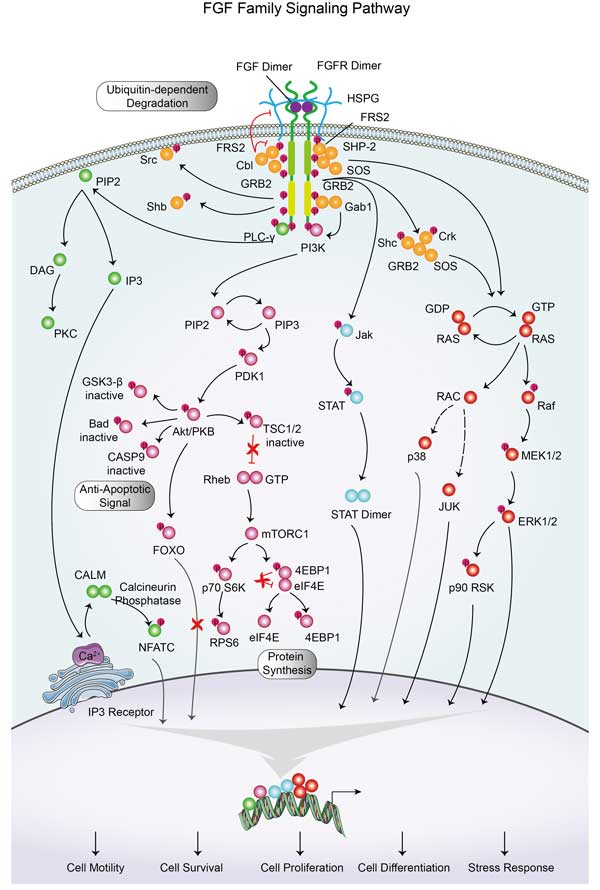
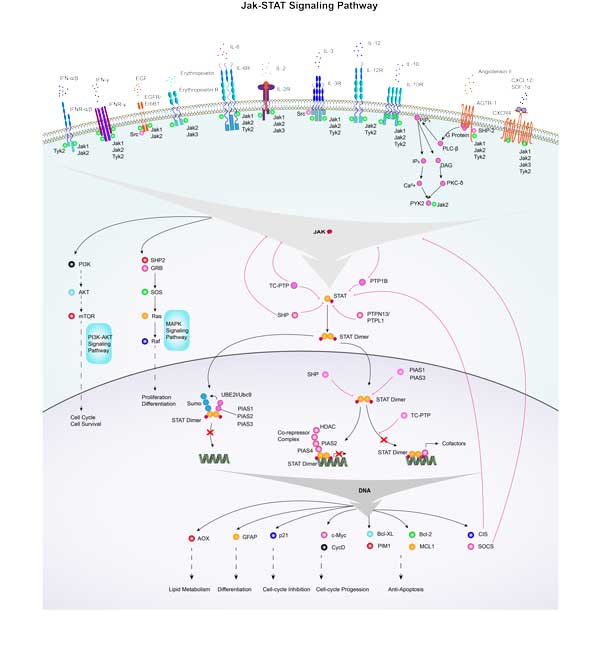
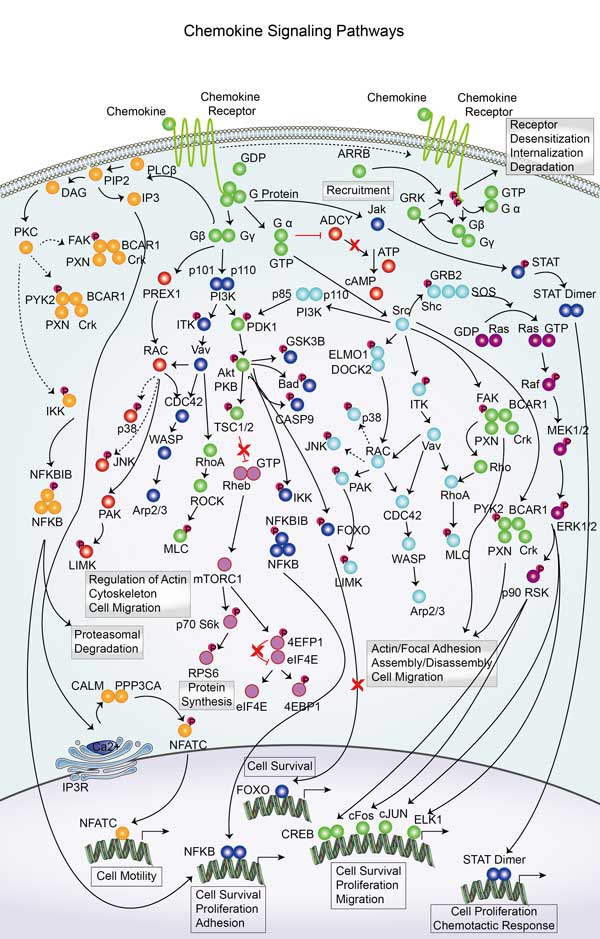
STAT3 involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways STAT3 participated on our site, such as Chemokine signaling pathway,HIF- signaling pathway,FoxO signaling pathway, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with STAT3 were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| Measles | FCGR2B,IL2RB,IFNGR1,BBC3,TRP53,AKT2,FAS,CCNE1,CD209A,DDX58 |
| Jak-STAT signaling pathway | SOCS1,EPO,TYK2,TP-1,PIAS1,AKT2,PIAS4A,Il23a,GRB2A,PIK3CD |
| Epstein-Barr virus infection | POLR2E,HSPA8,BCL2,PIK3R3,POLR3K,HLA-DRB5,TAB2,MAP3K7,HSPA2,EP300 |
| Chemokine signaling pathway | PLCB3,VAV3,CXCL8,CCR7,GNG7,NCF1,CRK,Cxcl15,NFKB1,PARD3 |
| Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) | STAT1,HLA-DMA,IL12B,TLR2,TGFB2,IL12A,IL5,IL22,STAT4,IL23 |
| Pancreatic cancer | SMAD2,PIK3R3,NFKB1,BAD,KRAS,AKT1,RAD51,RAC3,MAPK9,TGFB2 |
| HIF- signaling pathway | ANGPT1,PLCG1,PRKCG,ERBB2,INS,MKNK2,GM5506,PRKCB,ANGPT4,PDHA1 |
| Insulin resistance | PIK3R3,PIK3R5,PIK3CD,RPS6KA3A,PTPN1,TRIB3,PRKAG2,TNF,PPARAB,PDPK1B |
| Hepatitis B | STAT6,IFNA17,IFIH1,MAPK3,TLR3,KRAS,FAS,TGFBR1,MAPK8,TGFB2 |
Protein Function
STAT3 has several biochemical functions, for example, CCR5 chemokine receptor binding,DNA binding,RNA polymerase II core promoter proximal region sequence-specific DNA binding. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by STAT3 itself. We selected most functions STAT3 had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with STAT3. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| protein phosphatase binding | ANAPC5,ITPR1,CTNNB1,VCAN,MAPK14,MET,KAT2A,CSF1R,MAP3K5,CSK |
| transcriptional activator activity, RNA polymerase II transcription regulatory region sequence-specific binding | MAFB,GATA4,NHLH1,SOHLH2,FEZF2,MYOD1,LMO2,MAFF,MYF6,ONECUT3 |
| protein dimerization activity | HNF1A,NEUROD4,EBF2,NPAS4,USF1L,DERL3,HES2.1,PIP4K2AA,MESPAB,MYCH |
| DNA binding | IRF1B,ZFP382,HER7,HER5,MYCA,HIST1H2AI,ZNF444,FLYWCH1,OTPA,NKX2.3 |
| RNA polymerase II core promoter proximal region sequence-specific DNA binding | NKX3-2,SP1,NKX2,PER1,MYPOP,POU2F3,MEOX1,NFE2L3,GMEB2,TFAP2E |
| transcription factor activity, sequence-specific DNA binding | LBX1,HIVEP2,TP73,CREMB,WT1A,NEUROG1,MNX2A,DMRT2,TBX21,NR2F6A |
| signal transducer activity | GPR34A,PROKR1A,SLC35B2,PTK2,TACR1A,OLFR149,OLFR50,TOLLIP,GNAO1A,CXCR7B |
| RNA polymerase II transcription factor activity, ligand-activated sequence-specific DNA binding | NR5A1B,NR5A2,NR2F1,RORAB,NR1I3,NR2F1B,RORA,NR1D2,ESRRB,NR4A2A |
| transcriptional activator activity, RNA polymerase II core promoter proximal region sequence-specific binding | KLF13,FOS,NR4A1,TRP53,FOSB,ONECUT1,CEBPG,ATOH1,FOXI1,TFE3A |
Interacting Protein
STAT3 has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with STAT3 here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of STAT3.
EGFR;ERBB2
STAT3 Related Signal Pathway
Resources
Gene Families
Research Area
- Cancer Drug Targets
- Apoptosis Transcription Factors and Regulators
- Gamete Markers
- Transcription Factors in the Akt Pathway
- Negative Regulators of the Jak/STAT Pathway
- STAT
- Cancer Stem Cell Transcription Factors
- Epithelial Stem Cell Transcription Factors
- Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transcription Factors and Regulators
- Mesenchymal Stem Cell Transcription Factors
- Neural Stem Cell Transcription Factors
- Embryonic and Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell Markers
- Intracellular Signaling Molecules in Angiogenesis
- Pluripotent Stem Cell Transcription Factors
- T Follicular Helper (Tfh) Cells
- Th17 Cells
- Th22 Cells
- IL-10 Signaling Related Molecules
- IL-12 Signaling Related Molecules
- IL-6 Signaling Related Molecules
- Dendritic Cell Development
- MDSC Intracellular Signaling Factors
Related Services
Related Products
References
- Ye, F; Tang, CL; et al. MDM2-dependent positive-feedback loop is involved in inhibition of miR-375 and miR-106b induced by Helicobacter pylori lipopolysaccharide. INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF CANCER 136:2120-2131(2015).
- Lu, K; Fang, XS; et al. The STAT3 inhibitor WP1066 reverses the resistance of chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells to histone deacetylase inhibitors induced by interleukin-6. CANCER LETTERS 359:250-258(2015).



.jpg)
.jpg)