STAT6
-
Official Full Name
signal transducer and activator of transcription 6, interleukin-4 induced -
Overview
The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the STAT family of transcription factors. In response to cytokines and growth factors, STAT family members are phosphorylated by the receptor associated kinases, and then form homo- or heterodimers that translocate to the cell nucleus where they act as transcription activators. This protein plays a central role in exerting IL4 mediated biological responses. It is found to induce the expression of BCL2L1/BCL-X(L), which is responsible for the anti-apoptotic activity of IL4. Knockout studies in mice suggested the roles of this gene in differentiation of T helper 2 (Th2) cells, expression of cell surface markers, and class switch of immunoglobulins. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants.[provided by RefSeq, May 2010] -
Synonyms
STAT6;signal transducer and activator of transcription 6, interleukin-4 induced;STAT6B;STAT6C;D12S1644;IL-4-STAT;signal transducer and activator of transcription 6;STAT, interleukin4-induced;transcription factor IL-4 STAT
Recombinant Proteins
- Human
- Mouse
- Rat
- Rhesus macaque
- Zebrafish
- Insect Cells
- E.coli
- Mammalian Cells
- Sf9 Cells
- Human Cells
- HEK293
- HeLa
- His
- T7
- MBP
- GST
- Non
- Avi
- Fc
- DDK
- Myc
- Flag
Background
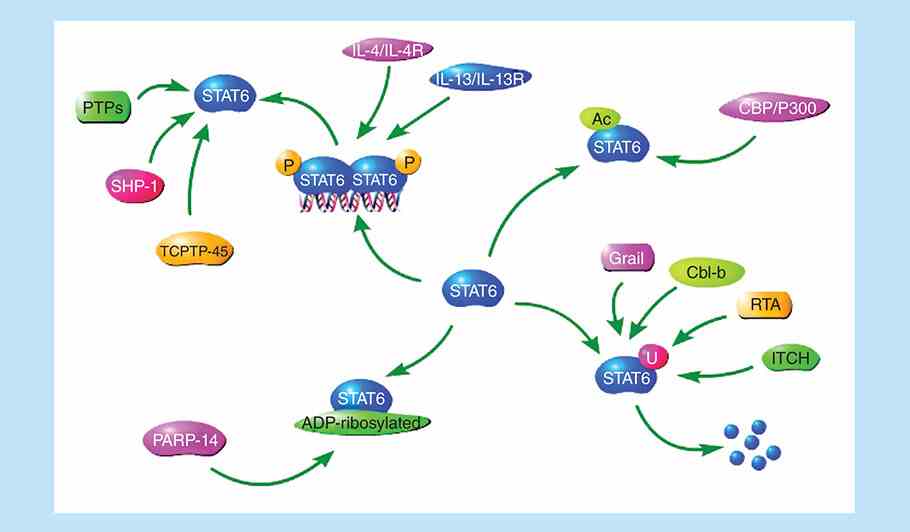
Fig1. The post-translational modification of STAT6. (Hao Huang, 2020)
What is STAT6 protein?
STAT6 gene (signal transducer and activator of transcription 6) is a protein coding gene which situated on the long arm of chromosome 12 at locus 12q13. The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the STAT family of transcription factors. In response to cytokines and growth factors, STAT family members are phosphorylated by the receptor associated kinases, and then form homo- or heterodimers that translocate to the cell nucleus where they act as transcription activators. This protein plays a central role in exerting IL4 mediated biological responses. It is found to induce the expression of BCL2L1/BCL-X(L), which is responsible for the anti-apoptotic activity of IL4. The STAT6 protein is consisted of 847 amino acids and STAT6 molecular weight is approximately 94.1 kDa.
What is the function of STAT6 protein?
STAT6 is a protein that plays a pivotal role in regulating immune responses, particularly in the development of allergic conditions and the differentiation of T helper 2 (Th2) cells. When activated, STAT6 dimerizes and translocates to the nucleus, where it acts as a transcription factor to regulate the expression of genes involved in immune responses, cell growth, and differentiation. It is activated by various cytokines, including interleukin-4 (IL-4) and IL-13, which are crucial for Th2 cell-mediated immune responses. The activation of STAT6 is a critical step in the signaling pathways that lead to the production of Th2-associated cytokines and the manifestation of allergic reactions.
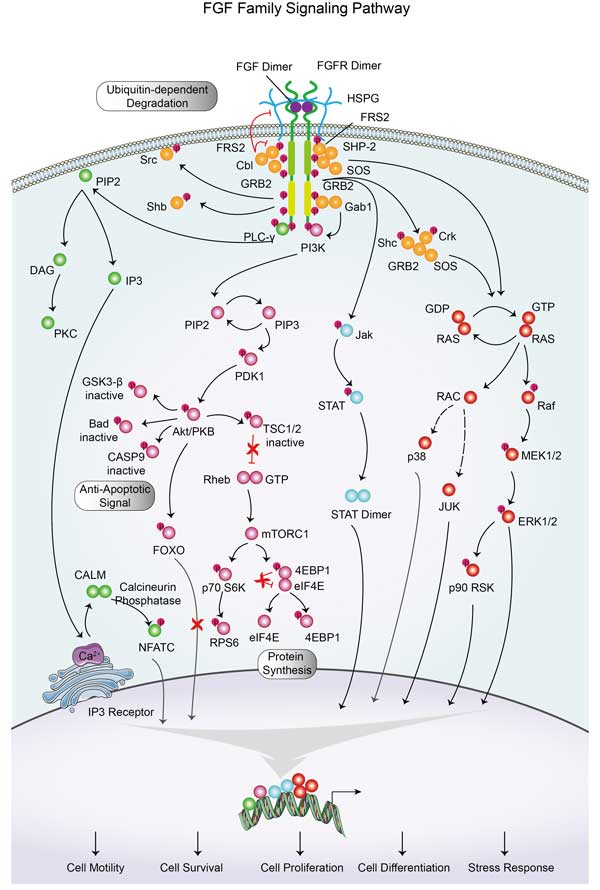
STAT6 Related Signaling Pathway
The JAK/STAT pathway is tightly regulated by negative feedback mechanisms, including the activation of suppressors of cytokine signaling (SOCS) proteins and protein tyrosine phosphatases (PTPs), which can dephosphorylate and inactivate STAT6. The binding of these cytokines leads to receptor dimerization, which brings the associated Janus kinases (JAKs) into proximity, activating them. Activated JAKs phosphorylate STAT6 on a specific tyrosine residue. This phosphorylation is essential for STAT6 activation. Once phosphorylated, STAT6 monomers dimerize through reciprocal phosphotyrosine-SH2 domain interactions and translocate to the nucleus.
STAT6 Related Diseases
Its dysregulation has been implicated in a spectrum of diseases, predominantly in the realm of allergic conditions and malignancies. Allergic diseases such as asthma, atopic dermatitis, eosinophilic esophagitis, and food allergies are often Th2-mediated, and STAT6 plays a crucial role in their pathophysiology by promoting Th2 differentiation and IgE production. Furthermore, STAT6's influence extends to the development and progression of certain types of cancer, including lymphomas and solitary fibrous tumors, where it contributes to tumor growth and the modulation of the tumor microenvironment. In pulmonary diseases, STAT6 is a key player in asthma pathogenesis and is also involved in acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS), pulmonary fibrosis, and the pulmonary antiviral response.
Bioapplications of STAT6
STAT6, with its pivotal role in immune responses and cell signaling, offers a rich landscape for bioapplications, particularly in the fields of immunology and oncology. In immunology, STAT6's ability to regulate Th2 cell differentiation and IgE production positions it as a potential target for therapeutic intervention in allergic diseases. Additionally, its involvement in the immune response to helminthic parasites suggests applications in combating parasitic infections. In oncology, the connection between STAT6 and tumor development, especially in lymphomas and fibrous tumors, makes it a candidate for targeted cancer therapies. Moreover, STAT6's role in the polarization of tumor-associated macrophages highlights its potential in modulating the immunosuppressive tumor milieu.
Case Study
Case Study 1: Luigi Russo, 2017
Crucial for immune and anti-inflammatory cellular responses, signal transducer and activator of transcription 6 (STAT6) regulates transcriptional activation in response to interleukin-4 and -13 -induced tyrosine phosphorylation by direct interaction with coactivators. The interaction of STAT6 with nuclear coactivator 1 (NCoA1) is mediated by a short region of the STAT6 transactivation domain that includes the motif LXXLL and interacts with the PAS-B domain of NCoA1. Despite the availability of an X-ray structure of the PAS-B domain/ Leu794-Gly814-STAT6 complex, the mechanistic details of this interaction are still poorly understood. Here, researchers determine the structure of the NCoA1257-385/STAT6783-814 complex using Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) and X-ray crystallography. The STAT6783-814 peptide binds with additional N-terminal amino acids to NCoA1257-385, compared to the STAT6794-814 peptide, explaining its higher affinity.
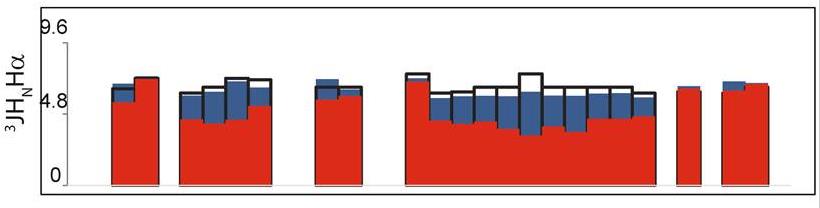
Fig1. 3JHNHα coupling constants for the STAT6783–814 peptide in the free (blue) and bound (red) state.
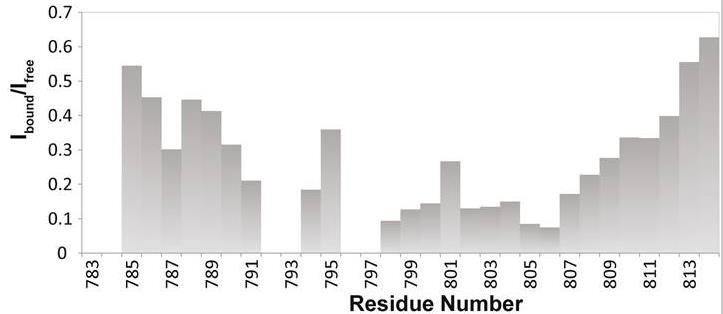
Fig2. Signal intensity ratios of STAT6783–814 bound to NCoA1 PAS-B domain (Ibound) and free (Ifree).
Case Study 2: James S Farrelly, 2019
In this study, researchers show that insulin receptor substrate (IRS)-1, IRS-2, and signal transducer and activator of transcription 6 (STAT6) are phosphorylated following IL-4 treatment in MCF-7 breast cancer cells. STAT6 DNA binding is enhanced by IL-4 treatment. To examine the role of STAT6 in IL-4-mediated growth inhibition and apoptosis, a full-length STAT6 cDNA was transfected into MCF-7 cells. Transient overexpression of STAT6 resulted in both cytoplasmic and nuclear expression of the protein, increased DNA binding in response to IL-4, and increased transactivation of an IL-4 responsive promoter. In STAT6-transfected cells, basal proliferation was reduced whereas apoptosis was increased. Finally, stable expression of STAT6 resulted in reduced foci formation compared to vector-transfected cells alone. These results suggest STAT6 is required for IL-4-mediated growth inhibition and induction of apoptosis in human breast cancer cells.
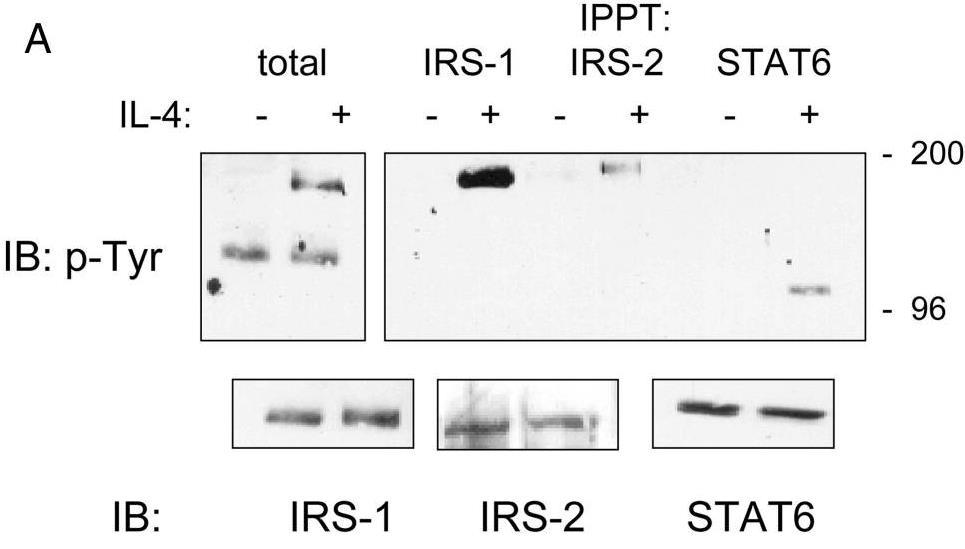
Fig3. WB of MCF-7 cells untreated or treated with IL-4.
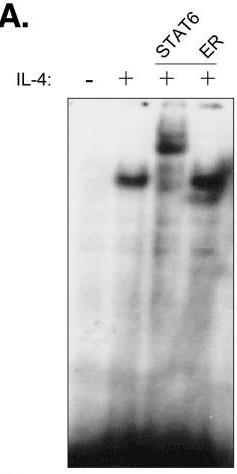
Fig4. MCF-7 cell nuclear extracts were incubated with labeled probe corresponding to the STAT6 binding site in the Fcγ1 gene promoter.
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
.jpg)
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (STAT6-6368H)
.
.jpg)
Fig2. SDS-PAGE (STAT6-2916H)
Involved Pathway
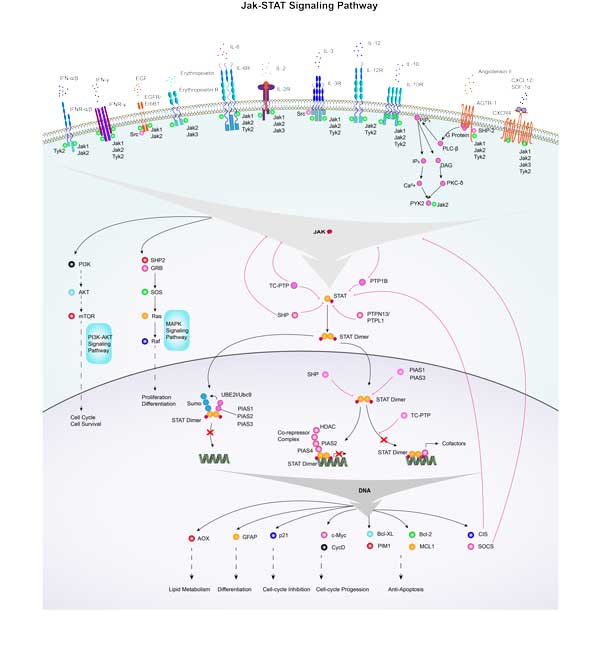
STAT6 involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways STAT6 participated on our site, such as Jak-STAT signaling pathway,Hepatitis B,Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with STAT6 were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| Hepatitis B | TGFBR1,NFKB1,EGR3,HRAS,MAVS,PRKCB,TGFB2,TRP53,PRKCG,Casp3 |
| Jak-STAT signaling pathway | IL-15RA,CRFB4,IL13RA1,IL6ST,PIK3R3A,LIF,IL9R,SOCS6,SOCS3B,IL6 |
| Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) | TGFB1,TGFB2,RORA,IFNG,HLA-DRB5,IFNGR2,HLA-DRA,IL17F,TLR5,HLA-DMB |
Protein Function
STAT6 has several biochemical functions, for example, RNA polymerase II core promoter sequence-specific DNA binding,identical protein binding,protein binding. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by STAT6 itself. We selected most functions STAT6 had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with STAT6. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| protein binding | CRLF3,PRDM7,ASAP3,BMF,DAPK2,NCAPD2,PIK3CD,TMEM106B,CFI,ILK |
| protein phosphatase binding | ANAPC7,AP3B1,JAK1,MVP,ANAPC5,IRS2,TP53,VCP,PPP6R1,ITPR1 |
| identical protein binding | ALAD,SIAH1,SCAND1,POU3F2,MPST,BRAP,SP100,DRG1,CLDN9,FUS |
| transcription factor activity, sequence-specific DNA binding | HOXC8A,ZNF584,ESR1,DMRT2A,BLF,HMG20A,CTCF,UBN1,SIN3A,RUNX3 |
| signal transducer activity | TMED4,OLFR78,GPR124,OLFCG1,TMTOPS3A,TSPAN6,TAAR12J,EMR4,COPS2,MTNR1C |
| RNA polymerase II core promoter sequence-specific DNA binding | TBR1,GBX2,GATA3,HEYL,SMAD5,RUVBL2,ZFPM1,NLRC5,SMYD3,YAP1 |
Interacting Protein
STAT6 has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with STAT6 here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of STAT6.
IL4R;TMEM173;TBK1
STAT6 Related Signal Pathway
Resources
Gene Families
Research Area
Related Services
Related Products
References
- van Slambrouck, C; Huh, J; et al. Nuclear Staining for Stat6 With the YE361 Monoclonal Antibody Is Restricted To Classical Hodgkin Lymphoma. MODERN PATHOLOGY 28:382A-383A(2015).
- van Slambrouck, C; Huh, J; et al. Nuclear Staining for Stat6 With the YE361 Monoclonal Antibody Is Restricted To Classical Hodgkin Lymphoma. LABORATORY INVESTIGATION 95:382A-383A(2015).