Neurotrophin
Related Symbol Search List
Immunology Background
Available Resources for Neurotrophin Research
At Creative BioMart, we take pride in our wide selection of products related to neurotrophins. Our extensive range includes recombinant proteins, protein pre-coupled magnetic beads, cell and tissue lysates, chromatography reagents, and other essential items. These products have been carefully selected to cater to a variety of research needs. Moreover, our customized services are designed to meet your specific requirements, ensuring that you receive the exact product needed for your experiments.
In addition to our diverse product offerings and tailored services, we also provide a wealth of resources for your reference. These resources cover all aspects of neurotrophins, including involved pathways, protein function, interacting proteins, related articles, research areas, and other pertinent topics. Serving as invaluable references, these resources enable researchers to enhance their knowledge of neurotrophins and their vital role in physiological processes.
Our Featured Products
| Cat.# | Product name | Species | Source (Host) | Tag |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BDNF-243H | Recombinant Human BDNF protein, His-tagged | Human | E.coli | His |
| BDNF-491H | Recombinant Human BDNF protein, His-tagged | Human | HEK293 | His |
| CDNF-484H | Recombinant Human CDNF Protein, His/GST-tagged | Human | E.coli | His/GST |
| Cdnf-486R | Recombinant Rat Cdnf Protein, His-tagged | Rat | E.coli | His |
| MANF-536H | Recombinant Human MANF protein | Human | E.coli | N/A |
| MANF-3205H | Recombinant Human MANF, His tagged | Human | Human Cell | His |
| NGF-573H | Active Recombinant Human Nerve Growth Factor (beta polypeptide) | Human | E.coli | N/A |
| NGF-05H | Active Recombinant Human NGF protein | Human | HO | N/A |
| Ngf-477M | Recombinant Mouse Ngf, None tagged | Mouse | CHO | N/A |
| NTF4-1385H | Recombinant Human NTF4, GST-tagged | Human | E.coli | GST |
About Neurotrophin
Neurotrophins are a family of proteins that play a crucial role in the development, survival, and function of neurons in the nervous system. They are signaling molecules that regulate various cellular processes, including neuronal growth, differentiation, synaptic plasticity, and cell survival. The neurotrophin family consists of four main members: nerve growth factor (NGF), brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), neurotrophin-3 (NT-3), and neurotrophin-4/5 (NT-4/5).
- Nerve Growth Factor (NGF): NGF was the first neurotrophin to be discovered and characterized. It is primarily involved in the survival and maintenance of sympathetic and sensory neurons. NGF has also been implicated in the regulation of immune responses, pain perception, and neuroplasticity.
- Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor (BDNF): BDNF is widely expressed in the central nervous system (CNS) and is involved in the survival, growth, and differentiation of various neuronal populations. It plays a critical role in synaptic plasticity, learning, and memory. BDNF has been implicated in the pathophysiology of several neurological and psychiatric disorders, such as Alzheimer's disease, depression, and schizophrenia.
- Neurotrophin-3 (NT-3): NT-3 is involved in the development and survival of different types of neurons in the CNS and peripheral nervous system (PNS). It promotes the growth and differentiation of sensory neurons, motor neurons, and certain interneurons. NT-3 is crucial for the development of proprioceptive sensory neurons and has been studied for its potential therapeutic applications in nerve regeneration.
- Neurotrophin-4/5 (NT-4/5): NT-4 and NT-5 are structurally similar and often considered together. They are primarily involved in the survival and differentiation of various neuronal populations in the CNS and PNS. NT-4/5 plays a role in the development and maintenance of auditory and vestibular sensory neurons, as well as certain motor neurons.
Neurotrophins exert their effects by binding to specific receptors on the surface of target cells. The two main classes of neurotrophin receptors are Trk (Tropomyosin receptor kinase) receptors and p75NTR (p75 neurotrophin receptor). Trk receptors (TrkA, TrkB, TrkC) are receptor tyrosine kinases that mediate the downstream signaling of neurotrophins, while p75NTR is a low-affinity receptor that can modulate Trk receptor signaling and activate unique signaling pathways.
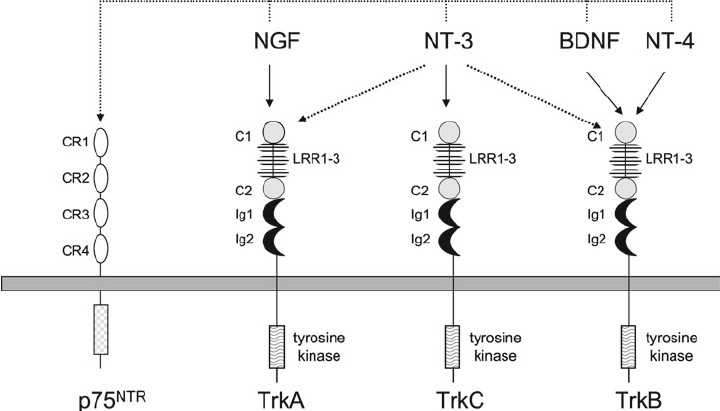 Fig.1 Neurotrophins and their receptors. (Skaper S D, 2012)
Fig.1 Neurotrophins and their receptors. (Skaper S D, 2012)
The neurotrophins display specifi c interactions with the three Trk receptors: NGF binds TrkA, BDNF and NT-4 bind TrkB, and NT-3 binds TrkC. In some cellular contexts, NT-3 can also activate TrkA and TrkB, albeit with less effi ciency. All neurotrophins bind to and activate p75 neurotrophin receptor (p75 NTR ). CR1–CR4 cysteine-rich
The expression and signaling of neurotrophins are tightly regulated during development and in adulthood. Dysregulation of neurotrophin signaling has been implicated in various neurological disorders, including neurodegenerative diseases, mood disorders, and neuropathic pain. Understanding the functions and regulatory mechanisms of neurotrophins is essential for unraveling the complexities of the nervous system and developing therapeutic strategies to target neurotrophin signaling pathways.
Physiological Functions of Neurotrophin
- Neuronal Survival and Development: Neurotrophins promote the survival and development of neurons during embryonic development and throughout life. They prevent programmed cell death (apoptosis) and support the survival of specific neuronal populations. For example, nerve growth factor (NGF) supports the survival and maintenance of sympathetic and sensory neurons, while brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) promotes the survival and differentiation of various neuronal populations in the central nervous system (CNS).
- Neuronal Differentiation and Growth: Neurotrophins influence neuronal differentiation and growth by promoting axon outgrowth and dendritic arborization. They provide guidance cues for developing axons and dendrites, helping neurons establish proper connections. Neurotrophins such as BDNF and neurotrophin-3 (NT-3) play critical roles in shaping the connectivity and circuit formation in the developing nervous system.
- Synaptic Plasticity: Neurotrophins are involved in synaptic plasticity, which is the ability of synapses to strengthen or weaken in response to activity. BDNF, in particular, plays a crucial role in synaptic plasticity by modulating synaptic transmission, promoting the formation of new synapses, and regulating long-term potentiation (LTP) and long-term depression (LTD) processes, which are fundamental for learning and memory.
- Neurotransmitter Regulation: Neurotrophins can regulate the synthesis, release, and uptake of neurotransmitters. For instance, BDNF modulates the release of neurotransmitters such as glutamate and GABA (gamma-aminobutyric acid), affecting neuronal excitability and synaptic transmission.
- Neuroprotection and Repair: Neurotrophins have neuroprotective effects, safeguarding neurons from injury, oxidative stress, and various insults. They can promote neuronal survival in the face of damaging conditions and contribute to neuronal repair and regeneration following injury. Neurotrophins are involved in processes such as axon regrowth, synaptic remodeling, and the survival of newly generated neurons in the adult brain.
- Regulation of Sensory Function: Neurotrophins play a role in the development and maintenance of sensory systems. For example, NT-3 is critical for the development of proprioceptive sensory neurons, which provide information about limb position and movement. Neurotrophins also influence the development and function of sensory organs, such as the inner ear and retina.
- Immune Modulation: Beyond their classical roles in the nervous system, neurotrophins can modulate immune responses. They can influence the survival, differentiation, and function of immune cells in the brain and periphery. For instance, NGF has been shown to regulate immune cell activation and proliferation.
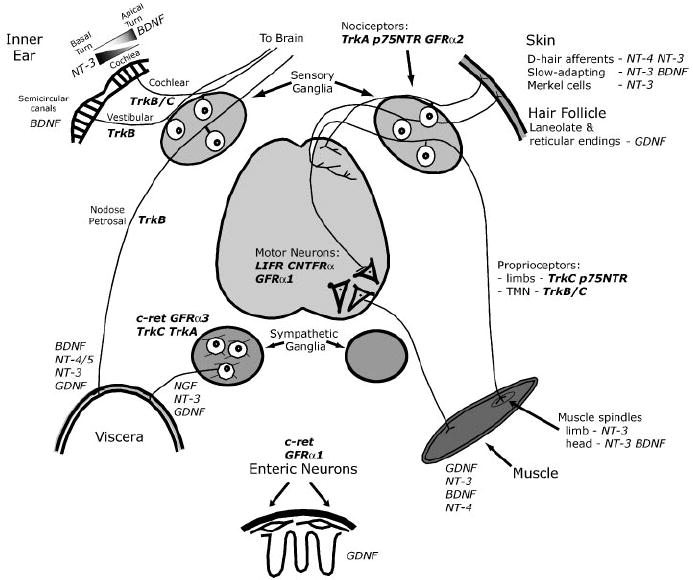 Fig.2 Summary of survival functions of neurotrophins in the peripheral nervous system. (Huang EJ, et al., 2001)
Fig.2 Summary of survival functions of neurotrophins in the peripheral nervous system. (Huang EJ, et al., 2001)
If you have any questions, requirements, or cooperation intentions, please feel free to contact us. We very much look forward to working with you and helping you achieve research and commercial success.
References:
- Huang EJ, Reichardt LF. Neurotrophins: roles in neuronal development and function. Annu Rev Neurosci. 2001;24:677-736.
- Skaper S D. The neurotrophin family of neurotrophic factors: an overview[J]. Neurotrophic factors: Methods and protocols, 2012: 1-12.

