Other Dendritic Cell CD Antigen
Related Symbol Search List
Immunology Background
Resources Available for the Study of Other Dendritic Cell CD Antigens
Creative BioMart is committed to providing superior products, tailored services, and personalized assistance to ensure that you have everything you need to explore the complexity of other dendritic cell CD antigens (in addition to key dendritic cell adhesion molecules, dendritic cell co-stimulatory molecules, dendritic cell lineage markers, and dendritic cell pathogen-recognized/uptake CD antigens).
- Our diverse product selection includes recombinant proteins, natural proteins, protein-coupled magnetic beads, cell and tissue lysates, chromatography reagents, GMP proteins, assay kits, and others.
- We also offer customized services such as custom antibody development, protein engineering, recombinant antigen production and assay development services to meet specific research requirements.
- We also provide a wealth of resources on other dendritic cell CD antigens, covering related pathways, protein functions, interacting proteins, literature reviews, and other valuable information. These resources are an invaluable asset for gaining insight into the molecular mechanisms and biological importance of other dendritic cell CD antigens.
Our Featured Products
| Cat.# | Product name | Species | Source (Host) | Tag |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CD5L-10965H | Recombinant Human CD5L, His-tagged | Human | E.coli | His |
| CD163-10910H | Recombinant Human CD163, GST-tagged | Human | E.coli | GST |
| CD274-178HF | Active Recombinant Human CD274 Protein, Fc-tagged, FITC conjugated | Human | CHO | Fc |
| IL1R1-772H | Active Recombinant Human IL1R1, His tagged | Human | HEK293 | His |
| LAMP3-632H | Recombinant Human LAMP3 protein, His-tagged | Human | HEK293 | His |
| TLR1-3257H | Recombinant Human TLR1, GST-tagged | Human | E.coli | GST |
| TLR2-3258H | Recombinant Human TLR2, GST-tagged | Human | E.coli | GST |
About Other Dendritic Cell CD Antigens
In addition to CD antigens that serve as dendritic cell adhesion molecules, dendritic cell co-stimulatory molecules, dendritic cell lineage markers, and dendritic cell pathogen recognition and uptake, a number of other CD antigens play important roles in various aspects of dendritic cell biology. These antigens include CD5L, CD163, CD274, IL1R1, LAMP3, TLR1, TLR2, and others. These CD antigens are briefly described below:
- CD5L: CD5L (CD5 antigen-like) is a soluble protein that can bind to CD14 on dendritic cells, modulating their response to lipopolysaccharide (LPS) and other microbial components. CD5L has been implicated in the regulation of inflammation and immune responses.
- CD163: CD163 is a scavenger receptor primarily expressed by macrophages and dendritic cells. It is involved in the clearance of hemoglobin and haptoglobin complexes, as well as the regulation of inflammatory responses. CD163 has been studied in the context of dendritic cell polarization and immune regulation.
- CD274 (PD-L1): CD274, also known as PD-L1 (programmed death-ligand 1), is a co-inhibitory molecule that is upregulated on dendritic cells and other immune cells in response to inflammation. Interaction of CD274 with its receptor, PD-1, can negatively regulate T cell activation, contributing to immune tolerance and immune evasion by certain pathogens or tumors.
- IL1R1: IL1R1 (Interleukin-1 receptor type 1) is a receptor for the pro-inflammatory cytokine IL-1. It is expressed on dendritic cells and other immune cells. Activation of IL1R1 on dendritic cells can lead to the production of cytokines and co-stimulation of immune responses.
- LAMP3 (CD208): LAMP3, also known as CD208 or DC-LAMP, is a lysosomal-associated membrane protein expressed on mature dendritic cells. It plays a role in antigen processing and presentation, as well as dendritic cell migration and cross-presentation of exogenous antigens.
- TLR1 and TLR2: Toll-like receptors (TLRs) are a family of pattern recognition receptors involved in sensing microbial components. TLR1 and TLR2 are expressed on dendritic cells and can recognize various bacterial and fungal molecules, initiating signaling pathways that lead to immune activation and cytokine production.
These CD antigens contribute to diverse aspects of dendritic cell biology, including immune regulation, antigen presentation, inflammation, and pathogen recognition. Their roles in dendritic cell function highlight the complex and multifaceted nature of dendritic cell-mediated immune responses.
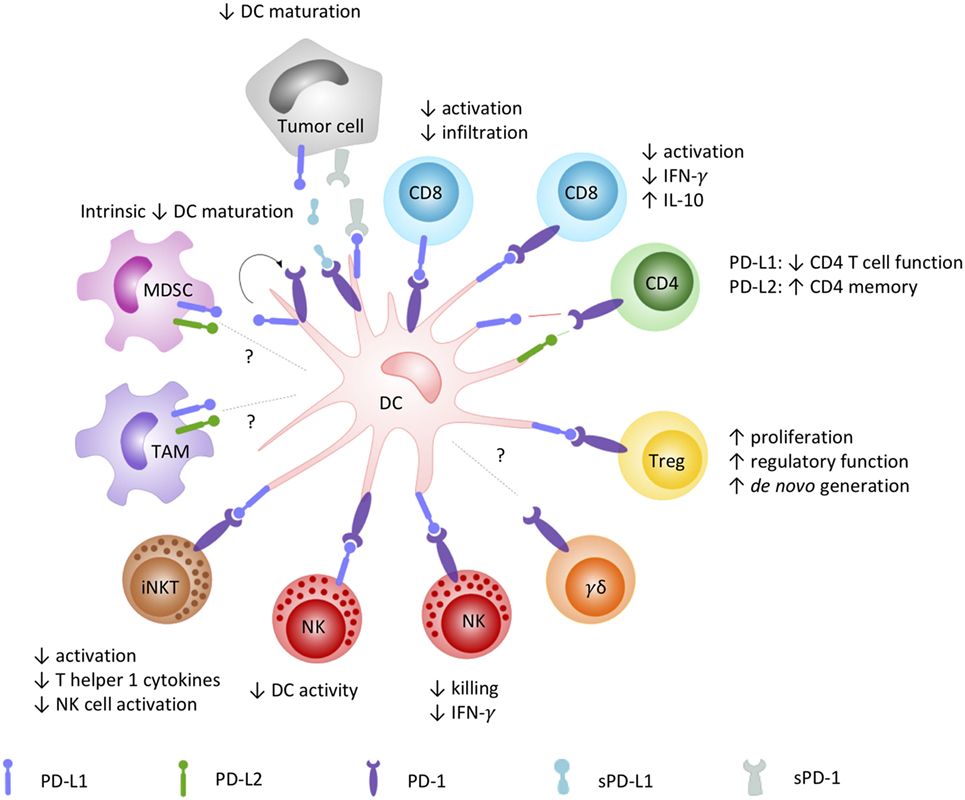 Fig.1 How the PD-1/PD-L signaling axis plays a role in DC-mediated orchestration of innate and adaptive immunity. (Versteven M, et al., 2018)
Fig.1 How the PD-1/PD-L signaling axis plays a role in DC-mediated orchestration of innate and adaptive immunity. (Versteven M, et al., 2018)
Other Dendritic Cell CD Antigens in Various Diseases
Cancer
- Expression of CD274 (PD-L1) on dendritic cells and other immune cells in the tumor microenvironment can contribute to immune evasion by engaging its receptor PD-1 on T cells. This interaction suppresses T cell activity, allowing tumors to evade immune surveillance. PD-L1 blockade has been used as an immunotherapy strategy in various cancers.
Autoimmune and Inflammatory Diseases
- CD5L, also known as apoptosis inhibitor of macrophages (AIM), has been implicated in autoimmune and inflammatory diseases. CD5L can modulate dendritic cell function and promote the differentiation of T helper 1 (Th1) cells, contributing to the pathogenesis of conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis and inflammatory bowel disease.
- In autoimmune diseases such as systemic lupus erythematosus and rheumatoid arthritis, increased CD163 expression has been observed, suggesting its potential involvement in disease pathogenesis and inflammatory processes.
- Dysregulation of CD274 expression on dendritic cells has been implicated in autoimmune diseases such as systemic lupus erythematosus, rheumatoid arthritis, and multiple sclerosis. Increased CD274 expression can contribute to immune dysregulation and immunopathology.
Infectious Diseases
- CD209 (DC-SIGN) plays a role in the recognition and uptake of various pathogens, including viruses (e.g., HIV, Ebola virus) and bacteria (e.g., Mycobacterium tuberculosis). CD209-mediated interactions can influence pathogen recognition, immune responses, and disease outcomes.
- CD206 (Mannose Receptor) is involved in the recognition and uptake of pathogens such as Mycobacterium tuberculosis and Candida albicans. Dysregulation of CD206 expression on dendritic cells can affect the immune response to infections and contribute to disease progression.
- Toll-like receptors, including TLR1 and TLR2, expressed on dendritic cells recognize microbial components and initiate immune responses against infections. Dysregulation of TLR signaling has been associated with infectious diseases such as tuberculosis, sepsis, and viral infections.
Allergic Diseases
- CD274 expression on dendritic cells has been implicated in the regulation of immune responses in allergic diseases such as asthma and allergic rhinitis. Increased PD-L1 expression may contribute to the inhibition of T cell activation and the development of allergic immune responses.
Other Diseases
- Dysregulation of IL1R1 signaling on dendritic cells has been associated with various diseases, including inflammatory bowel disease, rheumatoid arthritis, and atherosclerosis. IL1R1-mediated signaling can promote inflammation and contribute to disease pathogenesis.
- LAMP3 (CD208) is involved in antigen processing and presentation on dendritic cells. Altered expression or function of LAMP3 has been observed in diseases such as melanoma, where it can impact antigen presentation and immune responses.
It's important to note that the involvement of these CD antigens in diseases is complex, and their roles may vary depending on the specific disease context. Further research is needed to fully understand the mechanisms and therapeutic implications of these CD antigens in different diseases.
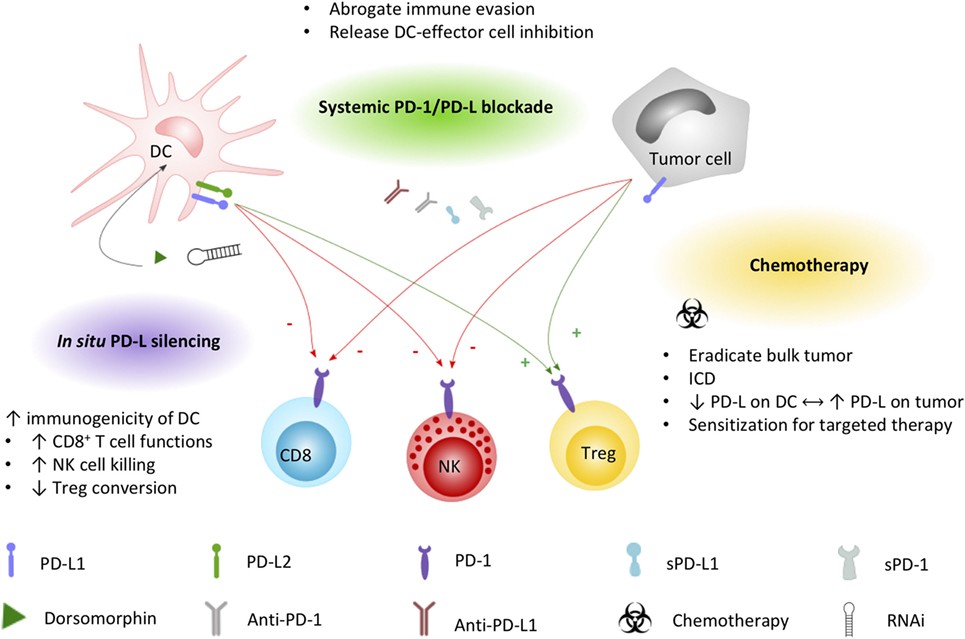 Fig.2 Applied strategies to leverage DC immunopotency by interfering PD-1/PD-L signaling. (Versteven M, et al., 2018)
Fig.2 Applied strategies to leverage DC immunopotency by interfering PD-1/PD-L signaling. (Versteven M, et al., 2018)
Choose Creative BioMart as your trusted partner, and embark on a journey of scientific exploration with confidence and precision. If you have any questions, requirements, or cooperation intentions, please feel free to contact us.
Related References
- Versteven M, Van den Bergh JMJ, Marcq E, et al. Dendritic Cells and Programmed Death-1 Blockade: A Joint Venture to Combat Cancer. Front Immunol. 2018;9:394.
- Costa F, Marchica V, Storti P, Malavasi F, Giuliani N. PD-L1/PD-1 Axis in Multiple Myeloma Microenvironment and a Possible Link with CD38-Mediated Immune-Suppression. Cancers. 2021; 13(2):164.

