VEGF Receptor
Related Symbol Search List
Immunology Background
Available Resources for VEGF Receptor Research
At Creative BioMart you can find a wide range of products related to VEGF receptors, including recombinant proteins and other key products. In addition, we offer customized services to meet your specific requirements, ensuring you get the product you need.
In addition to our products and services, we offer a wealth of resources for your reference. Our resources cover all aspects of the VEGF receptor, including the involved pathways, protein function, interacting proteins, related articles, research areas, and other relevant topics. These resources will be invaluable to researchers wishing to deepen their understanding of VEGF receptor and their role in physiological processes.
Our Featured Products
About VEGF Receptor
VEGF (Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor) receptors are a group of cell surface receptors that play a critical role in angiogenesis, the formation of new blood vessels from existing ones. VEGF receptors are primarily involved in mediating the effects of VEGF ligands, which are key regulators of blood vessel development and maintenance. Here's an introduction to VEGF receptors:
VEGF Receptor Types
- VEGF Receptor 1 (VEGFR-1, also known as Flt-1): VEGFR-1 is a transmembrane receptor tyrosine kinase that binds to VEGF-A, VEGF-B, and Placental Growth Factor (PlGF). It is expressed on endothelial cells, macrophages, and some tumor cells. VEGFR-1 plays a role in vessel development, immune cell recruitment, and tumor angiogenesis.
- VEGF Receptor 2 (VEGFR-2, also known as Flk-1/KDR): VEGFR-2 is the primary receptor responsible for mediating the effects of VEGF-A. It is predominantly expressed on endothelial cells and is crucial for endothelial cell proliferation, migration, and survival during angiogenesis. VEGFR-2 signaling is essential for blood vessel formation and maintenance.
- VEGF Receptor 3 (VEGFR-3, also known as Flt-4): VEGFR-3 primarily functions in the lymphatic system, regulating lymphatic vessel development and lymphangiogenesis. It binds to VEGF-C and VEGF-D, which are specifically involved in lymphatic vessel growth. VEGFR-3 is also expressed on some blood vessels and plays a role in angiogenesis.
Structure and Activation
- VEGF receptors are receptor tyrosine kinases (RTKs) with an extracellular ligand-binding domain, a transmembrane domain, and an intracellular kinase domain.
- Ligand binding to the extracellular domain of VEGF receptors induces receptor dimerization and activation.
- Upon activation, VEGF receptors undergo autophosphorylation, leading to the recruitment of intracellular signaling molecules and the activation of downstream signaling pathways.
Signaling Pathways and Functions
- Activation of VEGF receptors triggers several intracellular signaling pathways, including the PI3K-Akt, Ras-MAPK, and PLCγ pathways.
- These signaling pathways regulate endothelial cell proliferation, migration, survival, and vascular permeability, all of which are essential for angiogenesis and vascular development.
- VEGF receptor signaling also influences cell-cell adhesion, extracellular matrix remodeling, and the recruitment of inflammatory cells.
Therapeutic Implications
- Given the critical role of VEGF receptors in angiogenesis, they have become significant targets for therapeutic intervention.
- Anti-VEGF therapies, such as monoclonal antibodies and small molecule inhibitors, have been developed to block VEGF receptor signaling and inhibit pathological angiogenesis in diseases like cancer and macular degeneration.
- Modulating VEGF receptors and their downstream signaling pathways holds promise for the development of novel treatments for various vascular and inflammatory disorders.
Understanding the structure, activation, and signaling pathways of VEGF receptors is crucial for unraveling the mechanisms of angiogenesis and developing therapeutic strategies to target pathological angiogenesis in diseases.
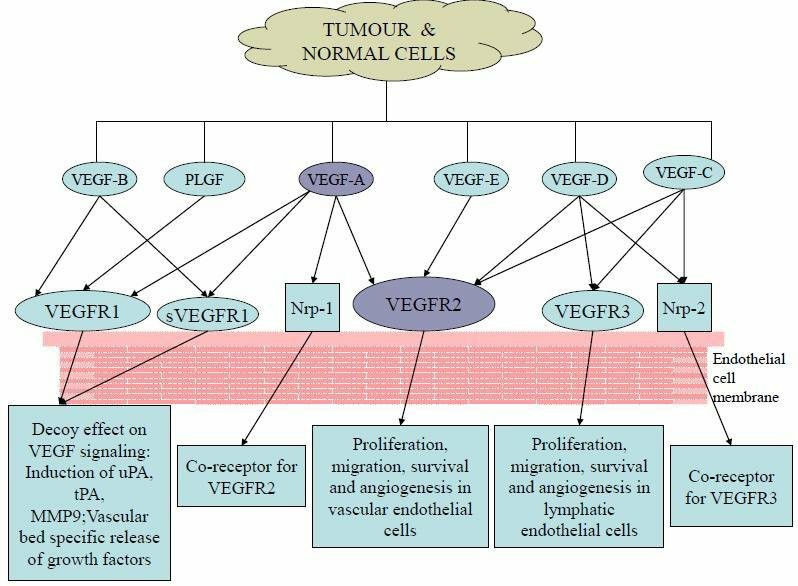 Fig.1 Types of VEGF, Receptors & their binding interactions. (Thanigaimani, et al., 2009)
Fig.1 Types of VEGF, Receptors & their binding interactions. (Thanigaimani, et al., 2009)
Regulatory Mechanism and Signaling Pathways of VEGF Receptors
The regulatory mechanisms and signaling pathways of VEGF receptors (VEGFRs) involve complex interactions and downstream signaling events. Here's an overview of the regulatory mechanisms and signaling pathways associated with VEGF receptors:
Ligand Binding and Receptor Activation
- VEGF ligands, including VEGF-A, VEGF-B, VEGF-C, and VEGF-D, bind to the extracellular domains of VEGFRs.
- Ligand binding induces receptor dimerization or oligomerization, leading to conformational changes in the receptor structure.
- This conformational change activates the intrinsic tyrosine kinase activity of VEGFRs, resulting in the phosphorylation of specific tyrosine residues within the receptor.
Downstream Signaling Pathways
Phosphorylated tyrosine residues on VEGFRs act as docking sites for various intracellular signaling molecules and adaptor proteins. The major downstream signaling pathways activated by VEGFRs include:
Phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K)-Akt pathway: Activation of PI3K leads to the production of phosphatidylinositol-3,4,5-trisphosphate (PIP3), which recruits and activates Akt. This pathway promotes endothelial cell survival, migration, and proliferation.
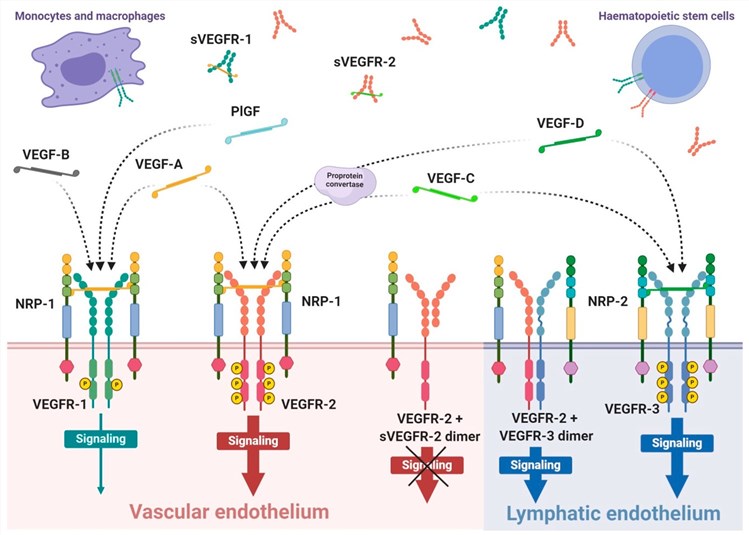 Fig.2 Scheme of expression of VEGF receptors and specificity of VEGF ligands. (Masłowska K, et al., 2021)
Fig.2 Scheme of expression of VEGF receptors and specificity of VEGF ligands. (Masłowska K, et al., 2021)
- Ras-mitogen-activated protein kinase (Ras-MAPK) pathway: Activation of Ras initiates a kinase cascade, including Raf, MEK, and ERK, resulting in the activation of transcription factors that regulate gene expression related to cell proliferation and migration.
- Protein kinase C (PKC) pathway: Activation of PKC influences endothelial cell migration and permeability.
- Src kinase pathway: Src family kinases play a role in VEGFR-mediated signaling, regulating endothelial cell survival and migration.
- Signal transducer and activator of transcription (STAT) pathway: Activation of STAT proteins by VEGFRs contributes to endothelial cell proliferation and survival.
Negative Regulation
- VEGF receptor signaling is tightly regulated to maintain vascular homeostasis.
- Various negative regulators, including phosphatases and endocytic proteins, help control the duration and intensity of VEGFR signaling.
- Protein tyrosine phosphatases (PTPs), such as VE-PTP, dephosphorylate and inactivate VEGFRs.
- Internalization and degradation of VEGFRs through endocytosis play a role in attenuating signaling.
Crosstalk with Other Signaling Pathways
- VEGFR signaling can interact with other signaling pathways, such as Notch, Wnt, and transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-β), influencing angiogenesis and vascular development.
- Crosstalk between VEGFR and other receptor tyrosine kinases, such as epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) and platelet-derived growth factor receptor (PDGFR), can modulate angiogenic processes.
Understanding the regulatory mechanisms and signaling pathways of VEGF receptors is crucial for developing therapeutic interventions targeting angiogenesis-related diseases. Modulating these pathways holds therapeutic potential for diseases such as cancer, retinopathy, and cardiovascular disorders. However, further research is needed to fully elucidate the complexity of VEGF receptor signaling and its interactions with other signaling networks.
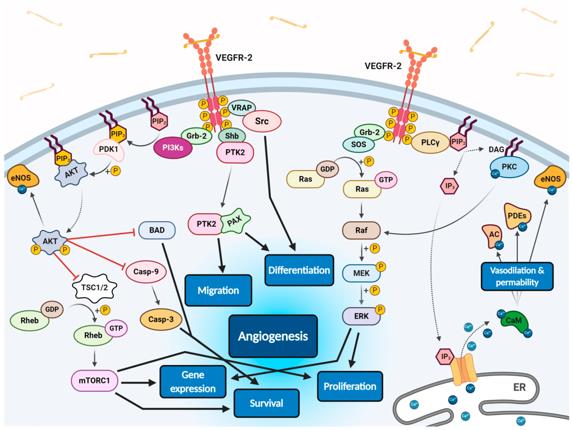 Fig.3 Scheme of endothelial signal transduction of VEGF-VEGFR-2 ligand-receptor molecular complex. (Masłowska K, et al., 2021)
Fig.3 Scheme of endothelial signal transduction of VEGF-VEGFR-2 ligand-receptor molecular complex. (Masłowska K, et al., 2021)
The autophosphorylation of receptor tyrosine kinase domains caused by VEGF binding stimulates multiple specific VEGFR-associated proteins (VRAPs) and adaptor molecules inducing concurrent intracellular signalling pathways that promotes proliferation, differentiation, migration, gene expression and apoptosis survival of endothelium leading to angiogenesis.
If you have any questions, requirements, or cooperation intentions, please feel free to contact us. We very much look forward to working with you and helping you achieve research and commercial success.
References:
- Thanigaimani, Shivshankar & Kichenadasse, G & Mangoni, Arduino. (2009). Acute Effects of Anti-vegf Therapy on Endothelial Function and Arginine Metabolism.
- Masłowska K, Halik PK, Tymecka D, Misicka A, Gniazdowska E. The Role of VEGF Receptors as Molecular Target in Nuclear Medicine for Cancer Diagnosis and Combination Therapy. Cancers. 2021; 13(5):1072. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13051072

