MCL1
-
Official Full Name
myeloid cell leukemia sequence 1 (BCL2-related) -
Overview
MCL-1 (Myeloid cell leukemia-1) is a member of the BCL-2 family. The carboxy terminal of MCL-1 and BCL-2 share significant sequence homology. Expression of MCL-1 is increased upon exposure of ML-1 cells to various types of DNA damaging agents (e.g. ionizing radiation, ultraviolet radiation, and alkylating drugs) along with increases in GADD45 and Bax and a decrease in BCL-2. Like BCL-2, MCL-1 has the capacity to promote cell viability under conditions that otherwise cause apoptosis. This gene encodes an anti-apoptotic protein, which is a member of the Bcl-2 family. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. The longest gene product (isoform 1) enhances cell survival by inhibiting apoptosis while the alternatively spliced shorter gene products (isoform 2 and isoform 3) promote apoptosis and are death-inducing. -
Synonyms
MCL1;myeloid cell leukemia sequence 1 (BCL2-related);induced myeloid leukemia cell differentiation protein Mcl-1;BCL2L3;Mcl 1;bcl-2-like protein 3;myeloid cell leukemia ES;bcl-2-related protein EAT/mcl1;TM;EAT;MCL1L;MCL1S;Mcl-1;MCL1-ES;bcl2-L-3;mcl1/EAT;MGC1839;MGC104264;myeloid cell leukemia sequence 1, isoform 1
Recombinant Proteins
- Human
- Mouse
- Rat
- Rhesus macaque
- Chicken
- Dog
- Felis catus
- E.coli
- Mammalian Cells
- HEK293
- His
- GST
- Non
- Avi
- Fc
- SUMO
- Flag
- DDK
- Myc
Background
What is MCL1 protein?
MCL1 gene (MCL1 apoptosis regulator, BCL2 family member) is a protein coding gene which situated on the long arm of chromosome 1 at locus 1q21. MCL1 is an anti-apoptotic protein belonging to the BCL-2 family, which plays a critical role in preventing programmed cell death, or apoptosis. It is characterized by a short half-life and functions as a rapid sensor that regulates cell death, cell cycle progression, and mitochondrial homeostasis. Overexpression of MCL1 is frequently observed in various types of cancer and is associated with tumorigenesis, poor prognosis, and resistance to chemotherapy and radiotherapy. The MCL1 protein is consisted of 350 amino acids and MCL1 molecular weight is approximately 37.3 kDa.
What is the function of MCL1 protein?
MCL1 prevents programmed cell death by binding to pro-apoptotic Bcl-2 family proteins, thus maintaining the integrity of the mitochondrial membrane and inhibiting the release of cytochrome c, which is a key initiator of apoptosis. MCL1 plays a crucial role in the survival of various cell types, including hematopoietic cells, neurons, and cardiomyocytes, by sequestering BH3-only proteins that would otherwise promote apoptosis. MCL1 is involved in the differentiation of certain cell types, such as those in the hematopoietic system, where it contributes to the development and maturation of blood cells. MCL1 has also been implicated in embryonic development, where it is required for proper implantation and the survival of early-stage cells. MCL1 has been shown to modulate the inflammatory response, with its expression influencing the survival of certain immune cells, such as neutrophils and eosinophils.
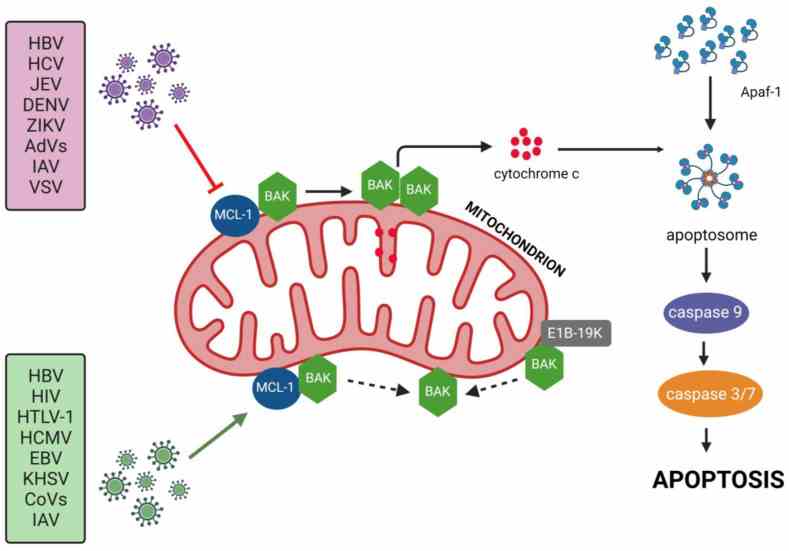
Fig1. The influence of viral infections on the Mcl-1 protein. (Zbigniew Wyżewski, 2024)
MCL1 Related Signaling Pathway
MCL1 inhibits apoptosis by preventing the permeabilization of the mitochondrial outer membrane, which is a critical step in the intrinsic apoptotic pathway. It does this by binding to pro-apoptotic BH3-only proteins and preventing their activation of the effector proteins BAX and BAK. MCL1 interacts with other members of the Bcl-2 family, including pro-apoptotic proteins like BAX, BAK, and BH3-only proteins, as well as anti-apoptotic proteins like BCL-2 and BCL-xL. MCL1 is tightly regulated at multiple levels, including transcriptional, post-transcriptional, and post-translational modifications. MCL1 also has roles beyond apoptosis, including regulation of cell cycle progression, mitochondrial homeostasis, embryonic development, autophagy, and response to cellular stresses.
MCL1 Related Diseases
Overexpression of MCL1 is frequently observed in many types of tumors and is strongly associated with tumor development, poor prognosis, and drug resistance. Advances in the study of MCL1 in hematologic tumors have shown that its overexpression is closely related to tumor progression, and is associated with resistance to targeted therapies and traditional chemotherapy drugs. The expression level, production and degradation rate of MCL1 are major molecular determinants of Bcl-2 and Mcl-1 dependence, which may be relevant for the treatment of inflammatory bowel disease. Loss of MCL1 leads to fatal heart failure and mitochondrial dysfunction in heart muscle cells. Other related diseases include neurodegenerative diseases, autoimmune diseases, psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis.
Bioapplications of MCL1
High expression of MCL1 is associated with a variety of cancers, so the development of MCL1 inhibitors is a focus in the field of cancer therapy, especially in treating tumors that are resistant to conventional chemotherapy. Small molecule inhibitors targeting MCL1 are being developed and tested to evaluate their potential in clinical trials for the treatment of hematologic malignancies and other types of cancer. The expression level of MCL1 can be used as a biomarker of cancer prognosis and treatment response, helping to guide personalized medical protocols. The role of MCL1 in the cell's response to toxic damage makes it useful in toxicological research to help understand the effects of chemicals on cells. As a key regulator of apoptosis pathway, the function of MCL1 is helpful to further understand the molecular mechanism of cell death.
Case Study
Case Study 1: Guo Chen, 2019
Here researchers discovered a cross-talk between Mcl-1 and Akt in promoting lung cancer cell growth. Depletion of endogenous Mcl-1 from human lung cancer cells using CRISPR/Cas9 or Mcl-1 shRNA significantly decreased Akt activity, leading to suppression of lung cancer cell growth in vitro and in xenografts. Mechanistically, Mcl-1 directly interacted via its PEST domain with Akt at the pleckstrin homology (PH) domain. The binding of Mcl-1/PH domain disrupted intramolecular PH/KD interactions to activate Akt. Using the Mcl-1-binding PH domain of Akt as a docking site, they identified a novel small molecule, PH-687, that directly targets the PH domain and disrupts Mcl-1/Akt binding, leading to suppression of Akt activity and growth inhibition of lung cancer in vitro and in vivo.
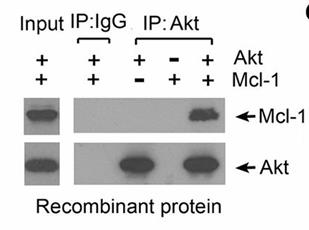
Fig1. Co-IP experiments using Akt antibody or Mcl-1 antibody were performed in cell-free systems.
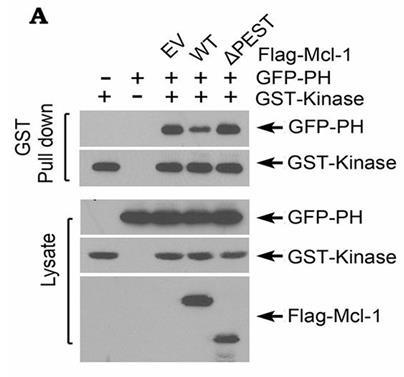
Fig2. GST-tagged kinase domain of Akt and GFP-tagged PH domain of Akt were co-transfected with Flag-tagged WT Mcl-1 or ΔPEST Mcl-1 mutant.
Case Study 2: Yvonne J Thus, 2023
The BCL-2-specific inhibitor venetoclax has been approved by the US Food and Drug Administration for chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) and acute myeloid leukemia (AML). In MCL, venetoclax has shown promising efficacy in early clinical trials; however, a significant subset of patients is resistant. By conducting a kinome-centered CRISPR-Cas9 knockout sensitizer screen, researchers identified casein kinase 2 (CK2) as a major regulator of venetoclax resistance in MCL. Targeting of CK2, either by inducible short hairpin RNA (shRNA)-mediated knockdown of CK2 or by the CK2-inhibitor silmitasertib, did not affect cell viability by itself, but strongly synergized with venetoclax in both MCL cell lines and primary samples, also if combined with ibrutinib. Furthermore, targeting of CK2 reduced MCL-1 levels, which involved impaired MCL-1 translation by inhibition of eIF4F complex assembly, without affecting BCL-2 and BCL-XL expression.
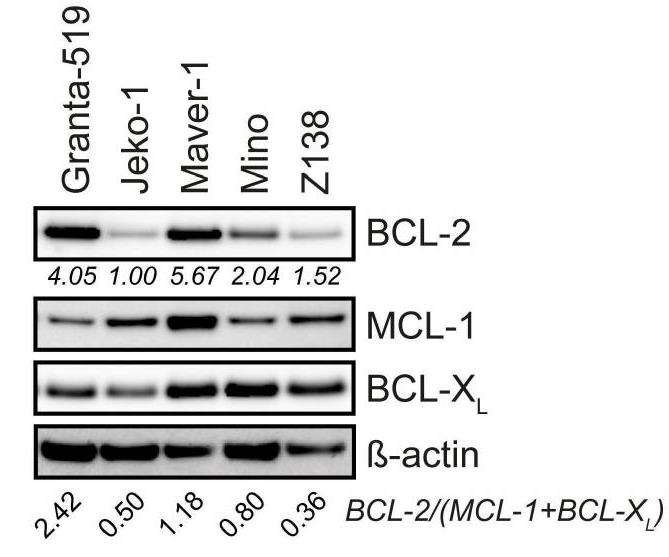
Fig3. Immunoblot analysis of BCL-2, MCL-1, and BCL-XL protein expression in MCL cell lines.
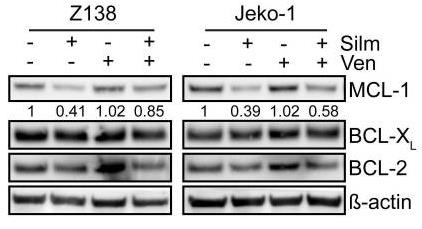
Fig4. Immunoblot analysis of MCL-1, BCL-XL and BCL-2 protein expression in Z138 and Jeko-1 cells.
Quality Guarantee
.
.jpg)
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (MCL1-780H)
.
.jpg)
Fig2. SDS-PAGE (MCL1-337HFL)
Involved Pathway
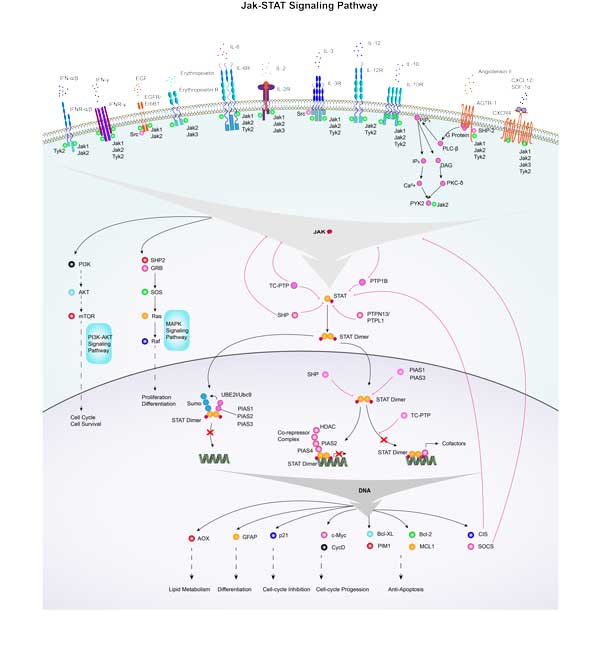
MCL1 involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways MCL1 participated on our site, such as PIK-Akt signaling pathway,Jak-STAT signaling pathway,MicroRNAs in cancer, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with MCL1 were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| Jak-STAT signaling pathway | Ifnl2,IL9,IFNA17,GFAP,IL13RA1,GM2002,IL2RA,IL5RA,IFNA14,GM13305 |
| PIK-Akt signaling pathway | VEGFB,IL2RA,LAMA2,IBSP,FGFR2,AKT1,PRKAA1,IGF1R,HRAS,TNN |
| MicroRNAs in cancer | DNMT3A,IGF2BP1,SHC1,STMN1,MMP9,PRKCA,VIM,ZEB1,ERBB3,SHC4 |
Protein Function
MCL1 has several biochemical functions, for example, BH3 domain binding,protein binding,protein channel activity. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by MCL1 itself. We selected most functions MCL1 had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with MCL1. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| protein homodimerization activity | UXS1,UGT1A7,TARS,RXRB,PON1,MTHFD1L,CPOX,NR4A3,GDNF,BAX |
| BH3 domain binding | BCL2L1,BCL2,BAX |
| protein channel activity | TOMM40L,TIMM22,TOMM40,TIMM23 |
| protein heterodimerization activity | HIST2H2AA4,SMAD1,NAE1,HIST1H2BN,HNF1A,CYBA,UNC13A,HIST3H2BB,TFAP2E,UGT1A6 |
| protein binding | TGIF2LY,TCOF1,BCL9,RAMP3,TAS2R16,FAM167A,BIK,DCTN3,ZNF317,INIP |
Interacting Protein
MCL1 has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with MCL1 here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of MCL1.
BCL2L11;BAK1
MCL1 Related Signal Pathway
Resources
Gene Families
Related Services
Related Products
References
- Wang, YN; Bhattacharya, D; et al. Adjuvant-specific regulation of long-term antibody responses by ZBTB20. JOURNAL OF EXPERIMENTAL MEDICINE 211:841-856(2014).
- Abdulghani, J; Allen, JE; et al. Sorafenib Sensitizes Solid Tumors to Apo2L/TRAIL and Apo2L/TRAIL Receptor Agonist Antibodies by the Jak2-Stat3-Mcl1 Axis. PLOS ONE 8:-(2013).