MFGE8
-
Official Full Name
milk fat globule-EGF factor 8 protein -
Overview
Apoptotic cells are rapidly removed by phagocytosis to clear the living cells and tissues of intracellular materials being released from dying cells. Phagocytes recognize apoptotic cells through milk fat globule-EGF-factor 8 (MFG-E8). MFG-E8 is a secreted -
Synonyms
MFGE8;milk fat globule-EGF factor 8 protein;lactadherin;MP47;EGF/factor VIII;sperm surface protein SP47;milk fat globule glycoprotein;P47;Mfgm;SED1;MFG-E8;AA408458;AI325141
Recombinant Proteins
- Mouse
- Human
- Chicken
- Rat
- Cynomolgus
- Bovine
- Mammalian Cells
- Insect Cells
- E.coli
- HEK293
- Milk
- Wheat Germ
- In Vitro Cell Free System
- Bovine
- His
- GST
- Non
- DDK
- Myc
- Avi
- Fc
- SUMO
Background
What is MFGE8 protein?
MFGE8 gene (milk fat globule EGF and factor V/VIII domain containing) is a protein coding gene which situated on the long arm of chromosome 15 at locus 15q26. This gene encodes a preproprotein that is proteolytically processed to form multiple protein products. The major encoded protein product, lactadherin, is a membrane glycoprotein that promotes phagocytosis of apoptotic cells. This protein has also been implicated in wound healing, autoimmune disease, and cancer. Lactadherin can be further processed to form a smaller cleavage product, medin, which comprises the major protein component of aortic medial amyloid (AMA). The MFGE8 protein is consisted of 387 amino acids and MFGE8 molecular weight is approximately 43.1 kDa.
What is the function of MFGE8 protein?
MFGE8 is involved in the regulation of immune responses. It can modulate the activity of immune cells, such as macrophages, and influence the balance between pro-inflammatory and anti-inflammatory responses. This protein is known to enhance the phagocytic activity of macrophages, which is crucial for the clearance of pathogens and dead cells from the body. MFGE8 is involved in the maintenance of vascular integrity. It can help prevent the formation of blood clots and may have a role in the prevention of atherosclerosis. MFGE8 can influence cell adhesion, which is important for maintaining tissue structure and function. It may also play a role in regulating cell death (apoptosis), which is a critical process in the development and maintenance of healthy tissues. In the nervous system, MFGE8 has been shown to have neuroprotective effects, potentially helping to protect neurons from damage and degeneration.
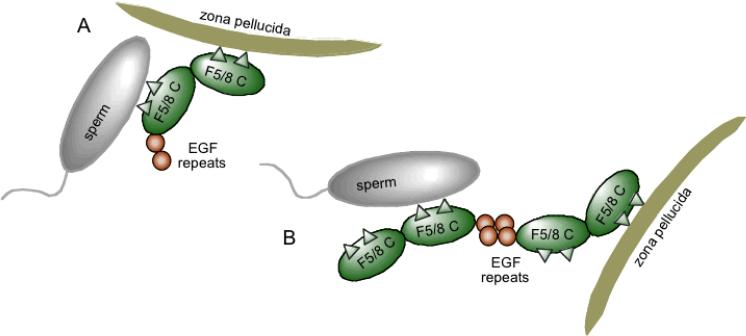
Fig1. Models for SED1/MFGE-8 function during sperm-egg binding. (Adam Raymond, 2009)
MFGE8 Related Signaling Pathway
MFGE8 can bind to integrins on the surface of cells, such as macrophages, triggering intracellular signaling events that influence cell behavior, including migration, adhesion, and phagocytosis. MFGE8 enhances the phagocytic capacity of macrophages by promoting the recognition and engulfment of apoptotic cells and pathogens. This process is essential for the clearance of cellular debris and the maintenance of tissue homeostasis. MFGE8 has been implicated in the regulation of the TGF-β signaling pathway, which plays a critical role in cell proliferation, differentiation, and immune regulation. MFGE8 may interact with the VEGF pathway, which is involved in angiogenesis and vascular permeability, contributing to processes such as wound healing and tumor growth. MFGE8 has been suggested to interact with the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway, which is important for cell fate decisions, tissue regeneration, and tumorigenesis.
MFGE8 Related Diseases
MFGE8 is a multifaceted bioactive protein that plays a key role in a variety of diseases. It regulates immune response, promotes apoptosis, affects vascular health, and participates in tissue repair. It is associated with cardiovascular disease, certain types of cancer, autoimmune diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis and systemic lupus erythematosus, neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer's and Parkinson's, inflammatory diseases, infectious diseases, metabolic diseases, and health problems such as tissue repair and regeneration.
Bioapplications of MFGE8
Its role in promoting apoptosis, regulating immune response, enhancing phagocytic function of macrophages, promoting wound healing and tissue repair has shown great application prospects in disease treatment and prevention. Applications of MFGE8 include, but are not limited to, the treatment of cardiovascular disease, the development of tumor immunotherapies, the intervention of autoimmune diseases, the protection of neurodegenerative diseases, and the management of inflammatory diseases. In addition, MFGE8's role in the remodeling and cell adhesion of the extracellular matrix also makes it a potential application in tissue engineering and regenerative medicine.
Case Study
Case Study 1: Wuming Liu, 2024
Pancreatic cancer is an extremely malignant tumor, and only a few clinical treatment options exist. MFG-E8 and kindlin-2 all play an important role in cancer progression. However, the specific mechanism occurring between MFG-E8, kindlin-2 and the migration and invasion of pancreatic cancer cells remains unelucidated. To unravel the specific mechanism, this study assessed the potential association between MFG-E8 and kindlin-2 as well as the involvement of MFG-E8 in pancreatic cancer using two pancreatic cancer cell lines (MiaPaCa-2 and PANC-1). Pancreatic cancer cells were treated with 0, 250, and 500 ng/ml MFG-E8, and the effects of MFG-E8 on the migration, invasion, and anoikis of pancreatic cancer cells were observed. Furthermore, cilengitide, a receptor blocker of MFG-E8, was used to explore the relationship between MFG-E8, kindlin-2, and pancreatic cancer progression. The findings demonstrated that MFG-E8 promotes the migration and invasion of pancreatic cancer cells and induces cell anoikis resistance in a dose-dependent manner, which was effectively counteracted by cilengitide, a receptor blocker.
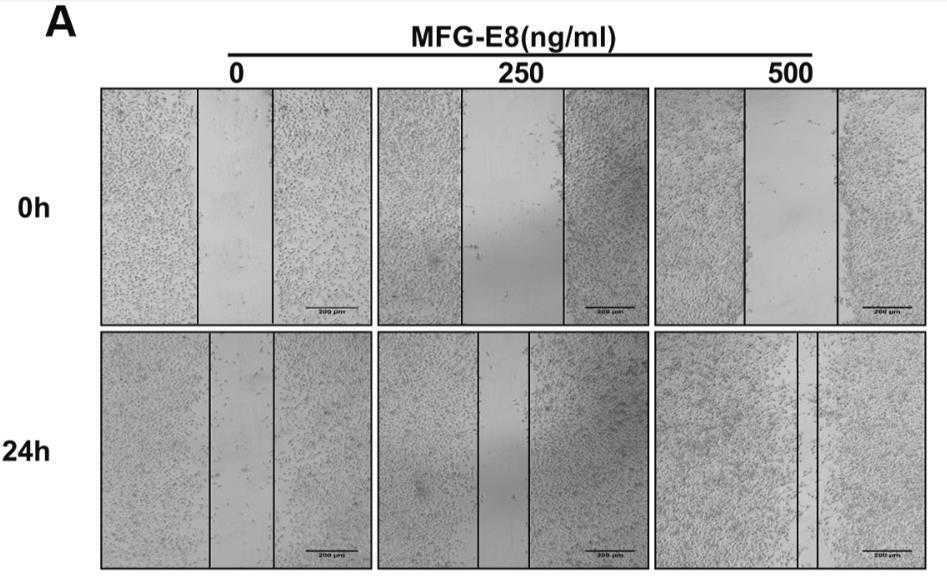
Fig1. Migration ability of MiaPaCa-2 cells was assessed through the wound-healing assay after MFG-E8 treatment.
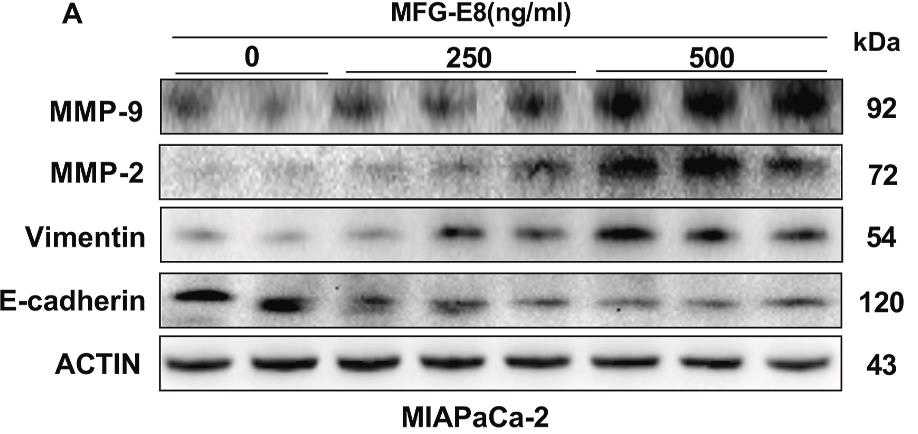
Fig2. MFG-E8 can promote the epithelial-mesenchymal transition ability of pancreatic cancer cells.
Case Study 2: Beilei Liu, 2023
Cancer-associated fibroblasts (CAFs) play vital roles in establishing a suitable tumor microenvironment. In this study, RNA sequencing data revealed that CAFs could promote cell proliferation, angiogenesis, and ECM reconstitution by binding to integrin families and activating PI3K/AKT pathways in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC). The secretions of CAFs play an important role in regulating these biological activities. Among these secretions, MFGE8 is specifically secreted by CAFs in ESCC. Additionally, the secreted MFGE8 protein is essential in CAF-regulated vascularization, tumor proliferation, drug resistance, and metastasis. By binding to Integrin αVβ3/αVβ5 receptors, MFGE8 promotes tumor progression by activating both the PI3K/AKT and ERK/AKT pathways. Interestingly, the biological function of MFGE8 secreted by CAFs fully demonstrated the major role of CAFs in ESCC and its mode of mechanism, showing that MFGE8 could be a driver factor of CAFs in remodeling the tumor environment.
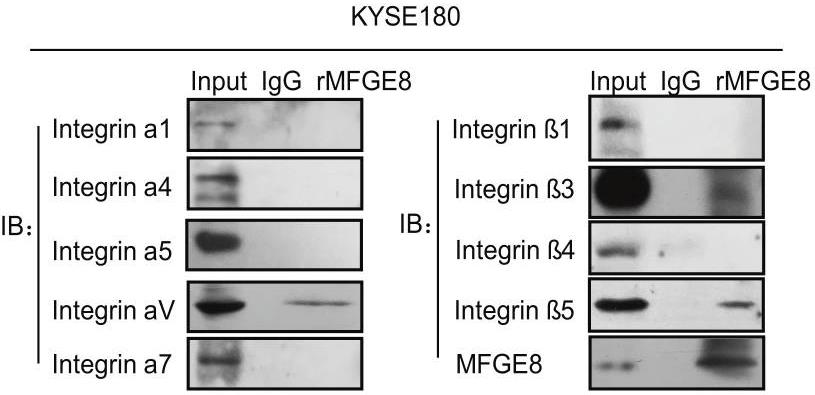
Fig3. Cell lysates prepared from K180 cell line were subjected to immunoprecipitation (IP).
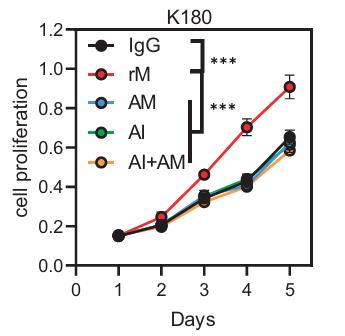
Fig4. The XTT assay showed that the proproliferative ability of recombinant protein MFGE8 (500 ng/mL) was blocked by anti-MFGE8 or Anti-Integrin αVβ3/αVβ5.
Quality Guarantee
.
.jpg)
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (MFGE8-220H)
.
.jpg)
Fig2. SDS-PAGE (MFGE8-652H)
Involved Pathway
MFGE8 involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways MFGE8 participated on our site, such as Amyloid formation,Integrins in angiogenesis,Metabolism of proteins, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with MFGE8 were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| Metabolism of proteins | SLC30A8,ARSF,ADAMTS20,BET1,ST3GAL3A,B3GNT6,DAD1,TOMM40,ARSH,GZMH |
| Amyloid formation | HIST3H2BB,ODAM,TGFBI,APCS,TTR,NAT8B,CEACAM21,SEMG1,HIST4H4,CST3 |
| Integrins in angiogenesis | ANGPTL3,CSF1R,CSF1,EDIL3 |
Protein Function
MFGE8 has several biochemical functions, for example, integrin binding,phosphatidylethanolamine binding,phosphatidylserine binding. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by MFGE8 itself. We selected most functions MFGE8 had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with MFGE8. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| integrin binding | ADAMTS13,ITGA5,WISP2,ADAM2,MMP14,ADAMTS5,THBS4,COL5A1,ICAM1,IGF1 |
| phosphatidylserine binding | ANXA13,PLCD1,CPNE1,FCHO2,OSBPL5,GAP43,MARK1,SYTL2,JPH2,THBS1 |
| phosphatidylethanolamine binding | LC3,PEBP1,ESYT2,NF1,PEMT,CD300A,ANXA11 |
Interacting Protein
MFGE8 has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with MFGE8 here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of MFGE8.
MYC
Resources
Research Area
Related Services
Related Products
References
- Aguzzi, A; Kranich, J; et al. Follicular dendritic cells: origin, phenotype, and function in health and disease. TRENDS IN IMMUNOLOGY 35:105-113(2014).
- Tibaldi, L; Leyman, S; et al. New Blocking Antibodies Impede Adhesion, Migration and Survival of Ovarian Cancer Cells, Highlighting MFGE8 as a Potential Therapeutic Target of Human Ovarian Carcinoma. PLOS ONE 8:-(2013).



