RHOA
-
Official Full Name
ras homolog family member A -
Overview
Ras is the name given to a family of related proteins which is ubiquitously expressed in all cells, . All Ras protein family members belong to a class of protein called small GTPase, and are involved in transmitting signals within cells (cellular signal transduction). Ras is the prototypical member of the Ras superfamily of proteins, which are all related in 3D structure and regulate diverse cell behaviours. -
Synonyms
RHOA;ras homolog family member A;ARH12, ARHA, ras homolog gene family, member A;transforming protein RhoA;Rho12;RhoA;RHOH12;h12;oncogene RHO H12;rho cDNA clone 12;Aplysia ras-related homolog 12;small GTP binding protein RhoA;ras homolog gene
Recombinant Proteins
- Human
- Rat
- Chicken
- Mouse
- E.coli
- Insect Cells
- HEK293
- Mammalian Cells
- Non
- GST
- His
- Avi
- Fc
- DDK
- Myc
- Flag
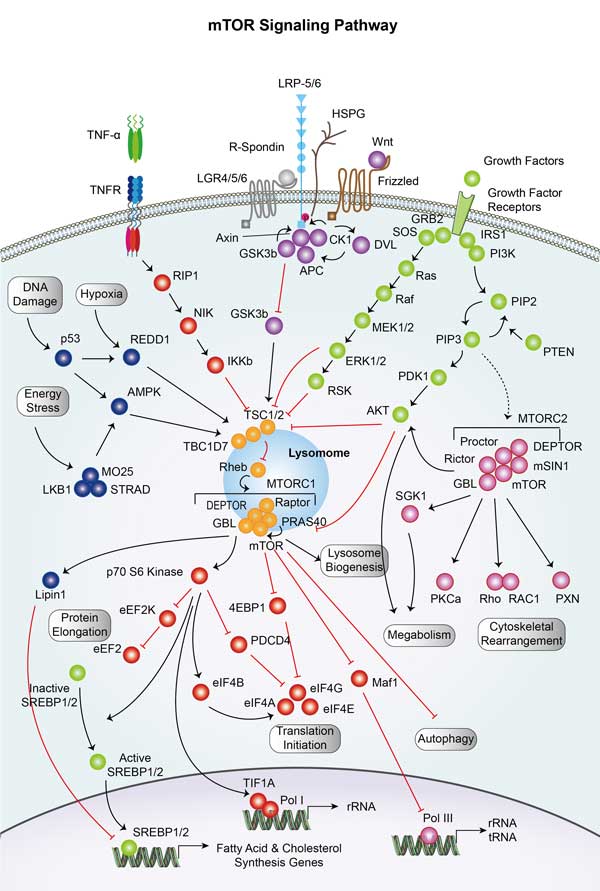
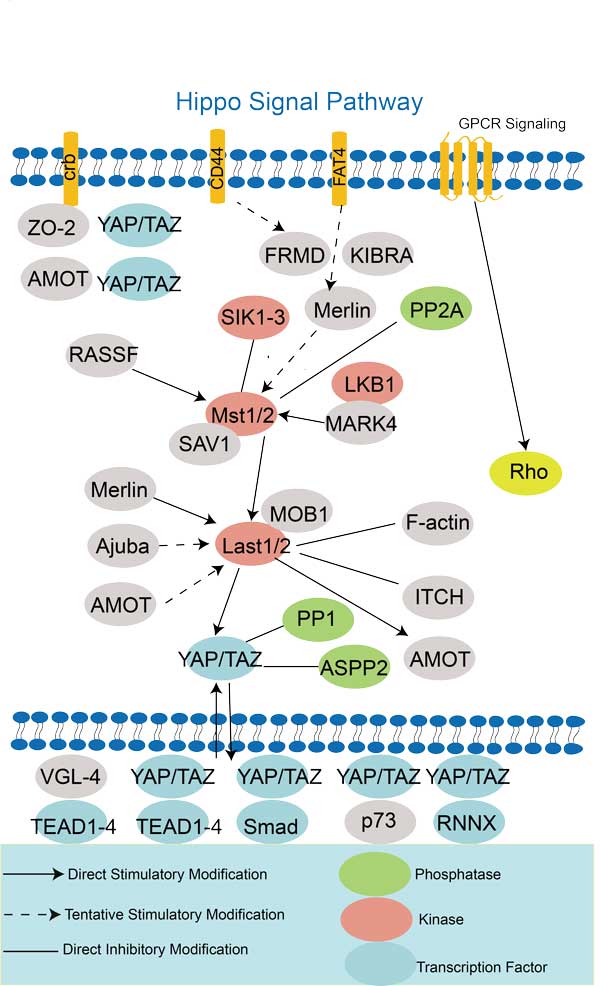
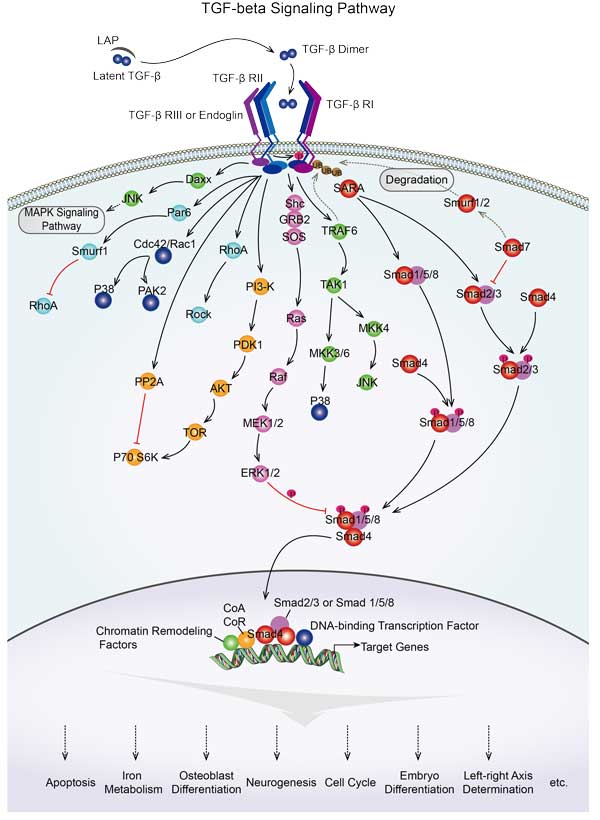
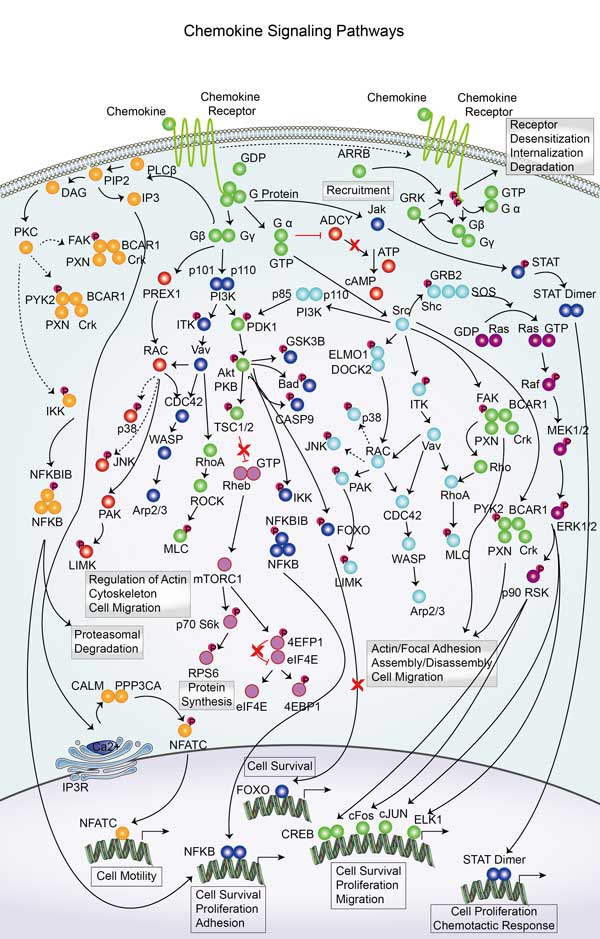
Involved Pathway
RHOA involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways RHOA participated on our site, such as Ras signaling pathway,Rap signaling pathway,cGMP-PKG signaling pathway, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with RHOA were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| MicroRNAs in cancer | RPS6KA5,ABL1,STAT3,SHC1,HOXD10,PDCD4,APC,EZR,PRKCA,CDC25A |
| Ras signaling pathway | GNG10,REL,GNG11,GNG4,PAK6,VEGFC,CDC42,IGF1R,RASGRP3,GRB2 |
| cGMP-PKG signaling pathway | SLC25A5,PPP3CA,PIK3R1,PPP3CB,VDAC1,BDKRB2,BAD,MAP2K2,ATP2A2,GNAI3 |
| Regulation of Actin Cytoskeleton | ITGA11A,FGF20B,RAC2,ITGA10,Itgam&Itgb2,RRAS2,PDGFRA,PDGFC,APC,MYL7 |
| Focal adhesion | MYL2B,DIAPH1,TLN2A,RAPGEF1,PXN,SRMS,MYLK2,ITGB5,BCL2,FIGF |
| Neurotrophin signaling pathway | PSEN1,FASLG,NFKBIB,NTF3,NFKBIA,FOXO3,CALM1,MAPK8,RAC1,PSEN2 |
| Axon guidance | EPHA7,ITGB3A,CSK,PHB,EFNA1,ARPC4,GNAI3,RANBP9,DUSP5,SEMA3A |
| Bacterial invasion of epithelial cells | PIK3CG,CLTC,CBLC,RAC1,BCAR1,SEPT3,SHC1,PIK3R5,PXN,SEPT1 |
| Proteoglycans in cancer | ARHGEF12,SDC1,WNT9B,HGF,PIK3CB,GAB1,FGF2,MSN,CAV1,KRAS |
Protein Function
RHOA has several biochemical functions, for example, GDP binding,GTP binding,GTPase activity. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by RHOA itself. We selected most functions RHOA had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with RHOA. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| GTPase activity | RALB,RRAS,RAB3C,NKIRAS2,RAB14L,RAB2A,GBP1,MXC,SRPR,RAB34A |
| GTP binding | TUBE1,REM2,GNAI2A,THG1L,ANXA6,GNAI2B,IFT27,PCK1,GNAT3,TUBB |
| protein binding | LDOC1,CD177,VAMP3,HNRNPC,CTAGE5,RPL11,VIM,SAMD4A,ASPA,VPS29 |
| GDP binding | RAB40C,RAB31,RAB5B,RAB7L1,RAB3B,MIEF1,IIGP1,RAB10,RAB35,RAB8B |
| myosin binding | CALM,GIPC1,SMYD1B,CALD1,FXYD1,ACTC1,STX4A,CALD1B,ARFGEF2,TRIM32 |
| Rho GDP-dissociation inhibitor binding | RAC1 |
| protein domain specific binding | LIN7B,RXRA,ARR3,TJP1,SCN5A,STX1A,YWHABA,IGBP1,HIST2H4A,KPNB1 |
Interacting Protein
RHOA has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with RHOA here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of RHOA.
RTKN;ARHGDIA;DAAM1;ARHGEF11
RHOA Related Signal Pathway
Resources
Gene Families
Research Area
Related Services
Related Products
References
- Chinestra, P; Olichon, A; et al. Generation of a Single Chain Antibody Variable Fragment (scFv) to Sense Selectively RhoB Activation. PLOS ONE 9:-(2014).
- Fichter, CD; Gudernatsch, V; et al. ErbB targeting inhibitors repress cell migration of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma and adenocarcinoma cells by distinct signaling pathways. JOURNAL OF MOLECULAR MEDICINE-JMM 92:1209-1223(2014).