S1PR1
-
Official Full Name
S1PR1 sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor 1 -
Synonyms
S1PR1;sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor 1;EDG1, endothelial differentiation, sphingolipid G protein coupled receptor, 1;sphingosine 1-phosphate receptor 1;CD363;D1S3362;edg 1;S1P receptor 1;S1P receptor Edg-1;sphingosine 1-phosphate receptor EDG1;sphingosine 1-phosphate receptor Edg-1;endothelial differentiation G-protein coupled receptor 1;endothelial differentiation, sphingolipid G-protein-coupled receptor, 1;EDG1;S1P1;ECGF1;EDG-1;CHEDG1;FLJ58121
Recombinant Proteins
- Mouse
- Human
- Rat
- Zebrafish
- zebrafish
- Bovine
- Mammalian Cells
- Wheat Germ
- E.coli
- HEK293
- In Vitro Cell Free System
- His
- Non
- GST
- Flag
- Avi
- Fc
Background
What is S1PR1 protein?
S1PR1 (sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor 1) is a protein coding gene which situated on the short arm of chromosome 1 at locus 1p21. The protein encoded by this gene is structurally similar to G protein-coupled receptors and is highly expressed in endothelial cells. It binds the ligand sphingosine-1-phosphate with high affinity and high specificity, and suggested to be involved in the processes that regulate the differentiation of endothelial cells. Activation of this receptor induces cell-cell adhesion. The S1PR1 protein is consisted of 382 amino acids and its molecular mass is approximately 42.8 kDa.
What is the function of S1PR1 protein?
S1PR1 protein is required for normal chemotaxis toward sphingosine 1-phosphate, normal embryonic heart development, normal cardiac morphogenesis and normal egress of mature T-cells from the thymus into the blood stream and into peripheral lymphoid organs. It plays an important role in the regulation of sprouting angiogenesis, vascular maturation, the migration of osteoclast precursor cells, the regulation of bone mineralization and bone homeostasis. It could inhibit sprouting angiogenesis to prevent excessive sprouting during blood vessel development. Also it plays a role in responses to oxidized 1-palmitoyl-2-arachidonoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine by pulmonary endothelial cells and in the protection against ventilator-induced lung injury.
S1PR1 related Signaling pathways
S1PR1 is one of the five receptors for S1P. When S1P binds to S1PR1, it triggers downstream signaling events that regulate various cellular processes, including an increase in intracellular calcium levels, activation of protein kinase pathways (such as PI3K/Akt and ERK1/2), and regulation of gene expression. Meanwhile, S1P and S1PR1 signaling still plays a role in maintaining the integrity of the blood-brain barrier and T-cell migration from lymphoid organs to peripheral tissues. S1PR1 signaling is also implicated in cardiac function and protection against myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury.
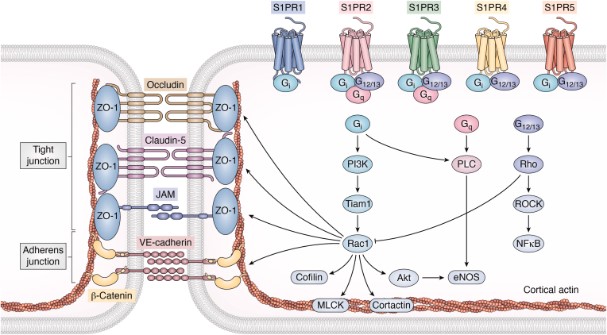
Fig6. Sphingolipid signaling regulates tight and adherens junctions through S1PRs. All S1PRs can signal via Gi, Gi activation leads to stimulation of phosphoinositide 3-kinases (PI3K) and Tiam1, which stimulate Rac1.
S1PR1 Related Diseases
Dysregulation of S1PR1 signaling has been implicated in various diseases. Some of the diseases associated with S1PR1 dysregulation include: Multiple Sclerosis (MS), Asthma, Cardiovascular diseases such as atherosclerosis, hypertension, and myocardial infarction. S1PR1 is involved in tumor growth, angiogenesis, and metastasis in various types of cancer. Altered expression or activity of S1PR1 has been linked to tumor progression and poor prognosis in several malignancies, including breast cancer, lung cancer, and colorectal cancer. Other diseases like inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) and diabetes are associated with the dysregulation of S1PR1.
Bioapplications of S1PR1
Given S1PR1 plays an important role in a variety of diseases including immunomodulation, cancer, neurological disorders and so on, drug development targeting S1PR1 has become an important therapeutic strategy. For example, Targeting S1PR1 signaling could have implications in promoting blood vessel formation in tissue engineering and regenerative medicine, as well as in treating vascular diseases such as diabetic retinopathy and atherosclerosis.
Case Study
Case Study 1: Xiaoshu Pu, 2023
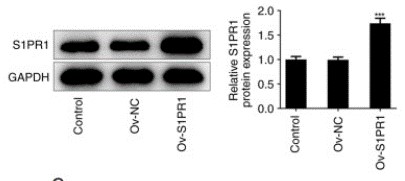
Fig1. Isorhamnetin suppresses keloid fibroblasts proliferation and metastasis by targeting S1PR1/PI3K/AKT pathway. Western blot assay was performed to detect the protein level of S1PR1.
Case Study 2: Cynthia Weigel, 2023
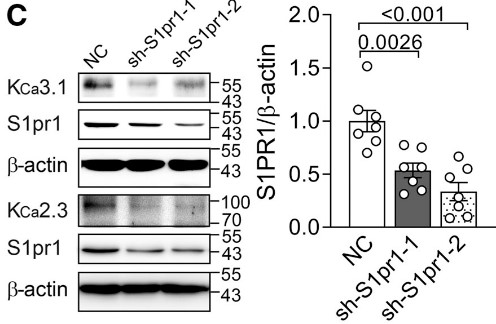
Fig2. Representative Western blotting images and quantifications of protein levels of KCa2.3, KCa3.1, and S1PR1 in HUVECs upon 0.2 μM S1P stimulation for 24 hours.
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
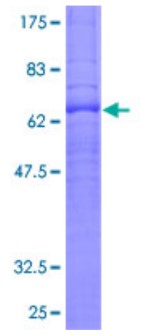
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (S1PR1-4038H) (PROTOCOL for western blot)
Involved Pathway
S1PR1 involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways S1PR1 participated on our site, such as Class A/1 (Rhodopsin-like receptors),Fc-epsilon receptor I signaling in mast cells,FoxO signaling pathway, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with S1PR1 were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| G alpha (i) signalling events | APPB,SSTR5,OXGR1A.1,PENKB,CCR6,PPY,NMUR1,CXCL13,OPN1SW1,GPR55 |
| GPCR downstream signaling | CALCA,FGD4,RGS20,RGS7,RGS6,FPR-RS4,UTS2D,ARHGEF25,DRD5,APLNR |
| GPCRs, Other | VMN1R47,GPR88,VMN1R41,GPR56,VMN1R44,GPR143,VMN1R49,GPR116,GPR132,CELSR1 |
| Class A/1 (Rhodopsin-like receptors) | EDNRB,NPSR1,CCL19A.2,MLN,AGTR1,ADORA3,GPR120,TAC3,OXTRL,CNR1 |
| Fc-epsilon receptor I signaling in mast cells | ITK,PTPN13,LAT2,DOK1 |
| FoxO signaling pathway | PLK2B,BCL6,PIK3R3A,MAPK10,PIK3R3B,AKT2,AKT3A,BNIP3,PRKAB1A,TGFB3 |
| GPCR ligand binding | XK,CNR2,PROK2,OPN1MW2,DRD5,TAAR1,PENKB,LPAR2B,RAMP3,OXGR1 |
| Lysosphingolipid and LPA receptors | LPAR5A,S1PR3,S1PR5B,LPAR2A,LPAR2B |
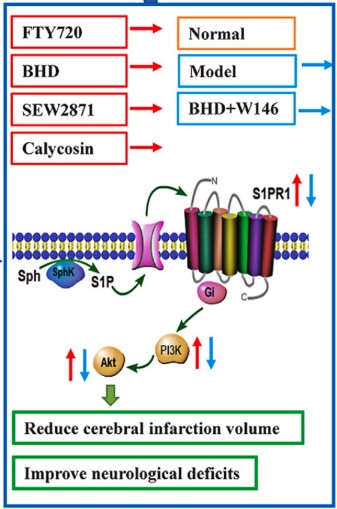
Fig2. BHD protects against cerebral ischemic injury through the S1P/S1PR1/PI3K/Akt signaling pathway.
Protein Function
S1PR1 has several biochemical functions, for example, G-protein coupled receptor activity,G-protein coupled receptor binding,sphingolipid binding. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by S1PR1 itself. We selected most functions S1PR1 had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with S1PR1. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| G-protein coupled receptor binding | GNA13B,GNAI2,ARHGEF12,ITGB4,APLN,GNAI2B,S1PR2,GNAV1,UCN2,NPB |
| G-protein coupled receptor activity | OLFR488,OR2AP1,OLFR508,RGS1,MLNR,VMN1R52,GPR97,DRD2L,TAS1R2.2,GPR132B |
| sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor activity | S1PR3A,S1PR2,S1PR5A,S1PR5B,SPHK1,S1PR4,S1PR5,GPR6,S1PR3,SPHK2 |
| sphingolipid binding | TRAF2 |
Interacting Protein
S1PR1 has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with S1PR1 here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of S1PR1.
S1PR2;SP1;CMSS1
Resources
Gene Families
Research Area
Related Services
Related Products
References
- Al-Jarallah, A; Chen, X; et al. High Density Lipoprotein Stimulated Migration of Macrophages Depends on the Scavenger Receptor Class B, Type I, PDZK1 and Akt1 and Is Blocked by Sphingosine 1 Phosphate Receptor Antagonists. PLOS ONE 9:-(2014).
- Tanaka, K; Hashizume, M; et al. Anti-interleukin-6 receptor antibody prevents systemic bone mass loss via reducing the number of osteoclast precursors in bone marrow in a collagen-induced arthritis model. CLINICAL AND EXPERIMENTAL IMMUNOLOGY 175:172-180(2014).



