TF
-
Official Full Name
transferrin -
Overview
This gene encodes a glycoprotein with an approximate molecular weight of 76.5 kDa. It is thought to have been created as a result of an ancient gene duplication event that led to generation of homologous C and N-terminal domains each of which binds one ion of ferric iron. The function of this protein is to transport iron from the intestine, reticuloendothelial system, and liver parenchymal cells to all proliferating cells in the body. This protein may also have a physiologic role as granulocyte/pollen-binding protein (GPBP) involved in the removal of certain organic matter and allergens from serum. [provided by RefSeq, Sep 2009] Transferrin is a metal-combining protein that reversibly bound to acid-soluble iron in plasma. It functions to transport iron to the bone marrow and to tissue storage organs such as the liver. Transferrin also participate in the regulation and control of iron absorption and protects against iron intoxication. Like haptoglobin, the carrier of hemoglobin, transferrin is synthesized in the liver, but unlike haptoglobin transferrin is returned to the circulation after unloading its iron in the reticuloendothelial system. This ELISA kit can be used to measure transferrin in serum, tissue extracts and other biological fluids. -
Synonyms
TF;transferrin;TFQTL1;PRO1557;PRO2086;serotransferrin;siderophilin;beta-1 metal-binding globulin;AI266983;Cd176;HP;Tfn;hpx;hypotransferrinemia with hemochromatosis;Apotransferrin;Beta 1 metal binding globulin;DKFZp781D0156;PRO1400;Serotransferrin precursor;Transferin;TRFE_HUMAN
Recombinant Proteins
- Human
- Cattle
- Pig
- Mouse
- Rat
- Chicken
- Rabbit
- Bovine
- Canine
- Sheep
- Dog
- Monkey
- HEK293
- E.coli
- Cattle
- Pig
- Oryza Sativa
- Human Cells
- Human
- Human Plasma
- Mammalian Cells
- Serum
- P.pastoris
- Bovine Serum
- Rabbit Skeletal Muscle
- Chicken Egg White
- Chicken Serum
- C-His
- Sheep Serum
- Monkey plasma
- rat plasma
- Rat
- CHO
- Yeast
- Rat Plasma
- Human Serum
- Conalbumin from Chicken egg white
- Mouse Serum
- Mouse Plasma
- Non
- GST
- Fc
- His
- mFc
- Avi
- KSI
- Flag
- DDK
- Myc
Background
What is TF protein?
TF gene (transferrin) is a protein coding gene which situated on the long arm of chromosome 3 at locus 3q22. This gene encodes a glycoprotein with an approximate molecular weight of 76.5 kDa. It is thought to have been created as a result of an ancient gene duplication event that led to generation of homologous C and N-terminal domains each of which binds one ion of ferric iron. The function of this protein is to transport iron from the intestine, reticuloendothelial system, and liver parenchymal cells to all proliferating cells in the body. This protein may also have a physiologic role as granulocyte/pollen-binding protein (GPBP) involved in the removal of certain organic matter and allergens from serum. The TF protein is consisted of 698 amino acids and TF molecular weight is approximately 77.1 kDa.
What is the function of TF protein?
This is an iron-binding protein that plays a crucial role in the transport of iron in the body. It binds and transports ferric ions (Fe(III)), increasing their solubility under physiological conditions and preventing their pro-oxidant effects. In humans, transferrin is responsible for the safe transport of iron through the bloodstream and its delivery to cells that require it. Cellular uptake of iron occurs through endocytosis mediated by the transferrin receptor (TfR). Post-translational modifications of transferrin, such as phosphorylation, glycation, and oxidation, can affect its function and may contribute to the deregulation of systemic iron transport in diseases.
TF related signaling pathway
The Tf-TfR complex is internalized into the cell via clathrin-mediated endocytosis, leading to the formation of clathrin-coated vesicles. Within the acidified environment of early endosomes, iron is released from Tf, making it available for cellular use. After delivering iron, apo-transferrin (Tf without iron) is typically routed back to the cell surface via recycling endosomes through two pathways: a fast recycling route and a slower route that involves the perinuclear recycling compartment. Various methods, including microscopy, radioactivity, and surface plasmon resonance (SPR), have been used to study the Tf trafficking pathway and the cellular machinery involved.
TF related diseases
Transferrin is an iron-binding protein, which plays an important role in transporting and storing iron in the human body, and its abnormal function or imbalance is associated with a variety of diseases. Iron deficiency anemia is a common condition characterized by insufficient iron reserves in the body, resulting in the inability of red blood cells to properly synthesize hemoglobin. Multiple myeloma, on the other hand, is a malignant tumor that causes an abnormal proliferation of plasma cells in the bone marrow. In addition, some other diseases may also cause abnormal transferrin levels, such as chronic liver disease, kidney disease, inflammatory bowel disease, etc. These diseases affect the process of synthesis, secretion, or degradation of transferrins, resulting in changes in their levels.
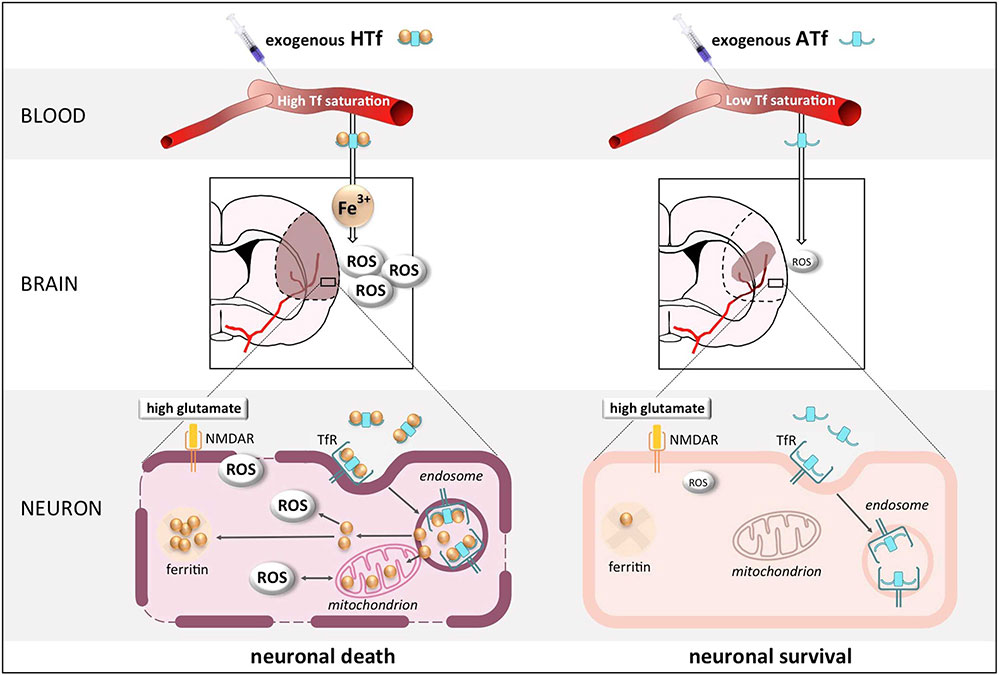
Fig1. Schematic representation showing that holotransferrin promotes and apotransferrin prevents a form of oxidative, iron- and NMDAR-dependent neuronal death in experimental stroke. (Nuria DeGregorio-Rocasolano, 2018)
Bioapplications of TF
Recombinant human transferrin rhTF, as an important supplementary factor in cell culture medium, can provide iron source and promote the growth of mammalian cells. Levels of transferrin and its receptor (TfR1) can play a role as a biomarker for certain diseases, for example in the diagnosis and therapeutic monitoring of diseases such as anemia, neurodegenerative diseases and cancer. Transferrin can act as a drug carrier to efficiently deliver drugs into cells through its receptor-mediated endocytosis, a mechanism that has been explored for cancer therapy and brain disease treatment. The ability of rhTF to bind to CD71 receptors or other ferriferic proteins can be used to specifically label and selectively enrich CD71-positive cells. rhTF can promote cell growth, reduce cell oxidative stress and anti-apoptosis, and is suitable for damage repair, organ construction and transplantation, and can enhance the survival rate of new tissues.
Case Study
Case Study 1: Deshui Zhang, 2010
Transferrin is vital in cell culture for managing cellular iron. It also enhances drug efficacy as a carrier via receptor-mediated endocytosis. To avoid contamination from blood-borne pathogens, recombinant transferrin is favored over plasma-derived forms. Researchers successfully produced recombinant human transferrin in rice, reaching 1% of seed dry weight. This rice-derived transferrin, extracted and purified to over 95% purity, matches the native protein in structure and function, including iron binding and cell growth promotion.
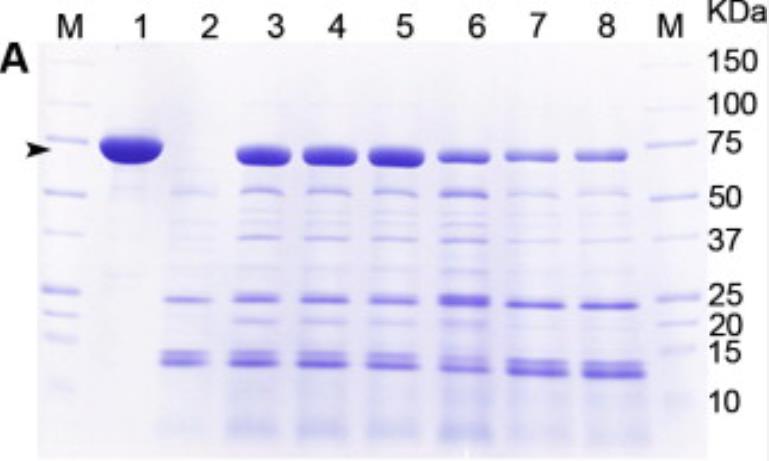
Fig1. SDS–polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS–PAGE) and immunoblot analysis of rhTF expressed in rice grain.
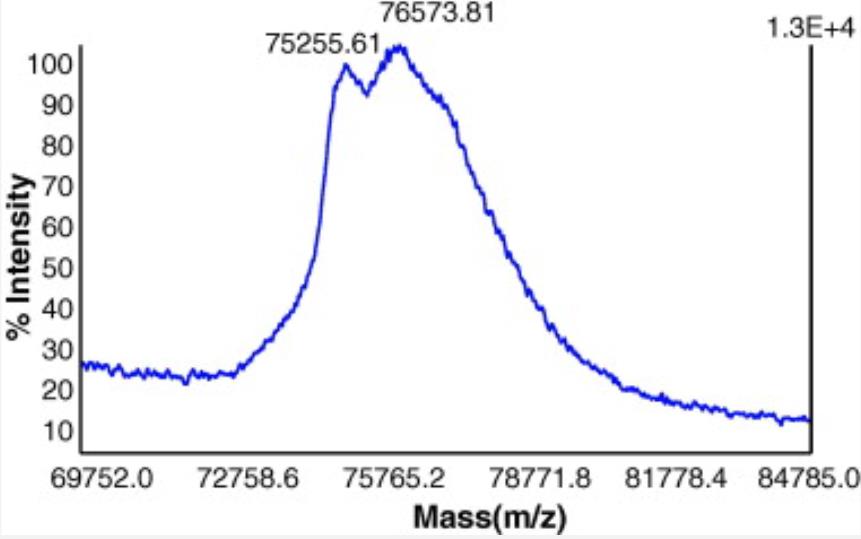
Fig2. MALDI mass spectra of purified rice-derived rhTF.
Case Study 2: María Julia Pérez, 2023
Transferrin (Tf), primarily recognized for iron transport, also has iron-independent activities. Resarchers studied the impact of apoTransferrin (aTf) on Neuro-2a (N2a) mouse neuroblastoma cells, which mimic neurons post-differentiation. Our model confirmed N2a cells' ability to internalize Tf like neurons. Tf was found to enhance N2a cell survival by reducing apoptosis and to stimulate neurite outgrowth, accelerating morphological development. Similar pro-differentiating effects were seen in primary mouse cortical neurons, where aTf treatment increased maturation rate and decreased early neuronal marker expression. Iron level experiments indicated that Tf's differentiation-promoting properties in N2a cells were maintained irrespective of iron availability, suggesting a regulatory role for iron. Additionally, N2a-microglia co-cultures showed increased IL-10 with aTf treatment, potentially promoting N2a differentiation.
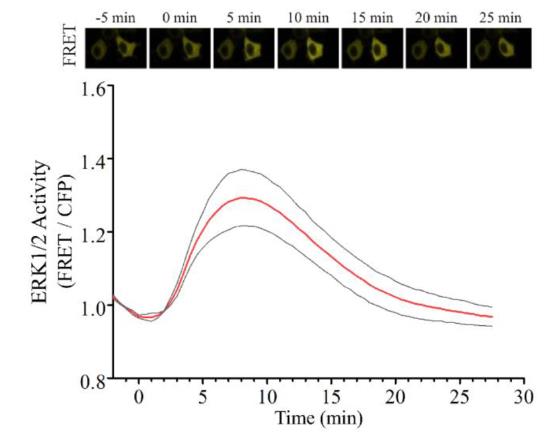
Fig3. EKAREV sensor evaluation of ERK1/2 activity in N2a cells stimulated with Tf.
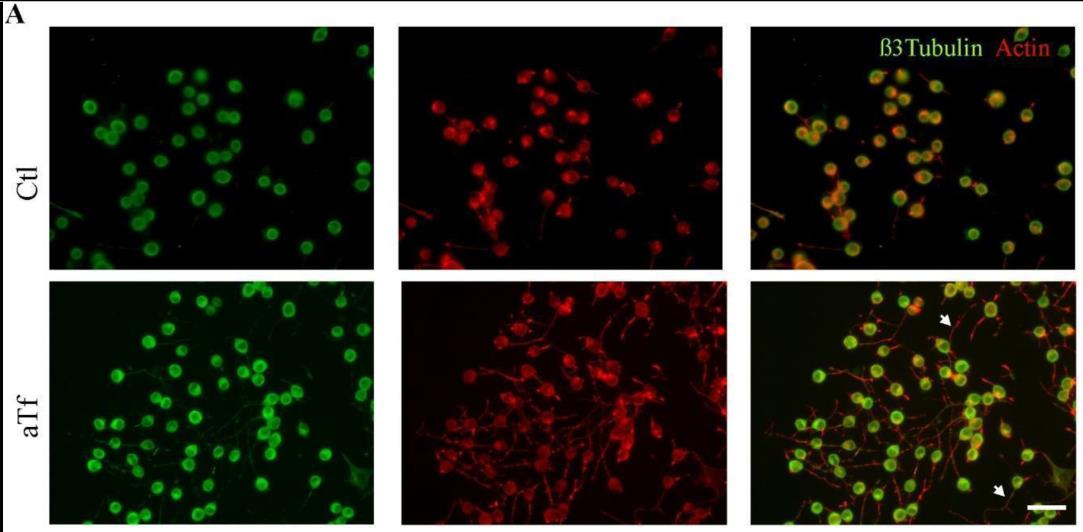
Fig4. Immunocytochemistry images of N2a cells after 2 days of Tf treatment.
Quality Guarantee
High Purity
.jpg)
Fig1. SDS-PAGE (TF-147H)
.
.jpg)
Fig2. SDS-PAGE (TF-393HFL)
Involved Pathway
TF involved in several pathways and played different roles in them. We selected most pathways TF participated on our site, such as HIF- signaling pathway,Mineral absorption, which may be useful for your reference. Also, other proteins which involved in the same pathway with TF were listed below. Creative BioMart supplied nearly all the proteins listed, you can search them on our site.
| Pathway Name | Pathway Related Protein |
|---|---|
| Mineral absorption | SLC5A1,SLC26A6,SLC30A1,TRPV6,SLC11A1,MT1B,MT1G,CYBRD1,VDR,MT1M |
| HIF- signaling pathway | INS2,NPPA,ARNT,PIK3CA,PIK3CD,INS,PDK1,Trf,MAPK3,ERBB2 |
Protein Function
TF has several biochemical functions, for example, ferric iron binding,ferric iron transmembrane transporter activity,ferrous iron binding. Some of the functions are cooperated with other proteins, some of the functions could acted by TF itself. We selected most functions TF had, and list some proteins which have the same functions with TF. You can find most of the proteins on our site.
| Function | Related Protein |
|---|---|
| ferric iron binding | ACP5,FTMT,FTH1B,TH,FTL,FTH1A,FTH1,FTHL17,MIOX,Trf |
| ferrous iron binding | BCO1,SERPINB1A,TRR1,FECH,ISCU,ALKBH3,ALKBH1,DNAJC24,PLOD1,NT5E |
| protein binding | CCDC108,BEGAIN,RNF41,CCL11,PEX13,IL7,KCNJ10,PARP16,NFATC4,GP9 |
| ferric iron transmembrane transporter activity | Trf |
| transferrin receptor binding | CD81,Trf,SNX2,SNX4,SNX1,HFE,HFE2,RGMA |
Interacting Protein
TF has direct interactions with proteins and molecules. Those interactions were detected by several methods such as yeast two hybrid, co-IP, pull-down and so on. We selected proteins and molecules interacted with TF here. Most of them are supplied by our site. Hope this information will be useful for your research of TF.
GAST;ESR1;TFRC;GTF2F2;MIS12;Akap12;TUBB4A;GRB2;SH3BP2;SMAD3;q99ib8-pro_0000045599;TIMELESS;LAMC3;PTBP3
Resources
Research Area
Related Services
Related Products
References
- Zhu, SJ; Kisiel, W; et al. Visualizing cancer and response to therapy in vivo using Cy5.5-labeled factor VIIa and anti-tissue factor antibody. JOURNAL OF DRUG TARGETING 23:257-265(2015).
- Paoletti, F; Malerba, F; et al. A comparative analysis of the structural, functional and biological differences between Mouse and Human Nerve Growth Factor. BIOCHIMICA ET BIOPHYSICA ACTA-PROTEINS AND PROTEOMICS 1854:187-197(2015).




